4 Best Practices for Health Care Software Development Success

Introduction
In an industry where precision and compliance are paramount, the development of health care software presents unique challenges and opportunities. As technology evolves, understanding best practices is essential for developers who aim to create effective, user-friendly solutions that meet regulatory standards. Developers must ensure their software not only complies with stringent regulations like HIPAA and FDA guidelines but also enhances the user experience for diverse patient populations. This article explores four critical best practices that can pave the way for success in health care software development, focusing on:
- Compliance
- User experience
- Quality assurance
- The importance of continuous improvement
Understand Regulatory Compliance in Healthcare Software Development
In health care software development, understanding regulatory compliance is crucial. Developers must familiarize themselves with laws such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), which governs the privacy and security of patient information. Furthermore, adherence to FDA regulations is essential for health care software development programs that qualify as medical devices.
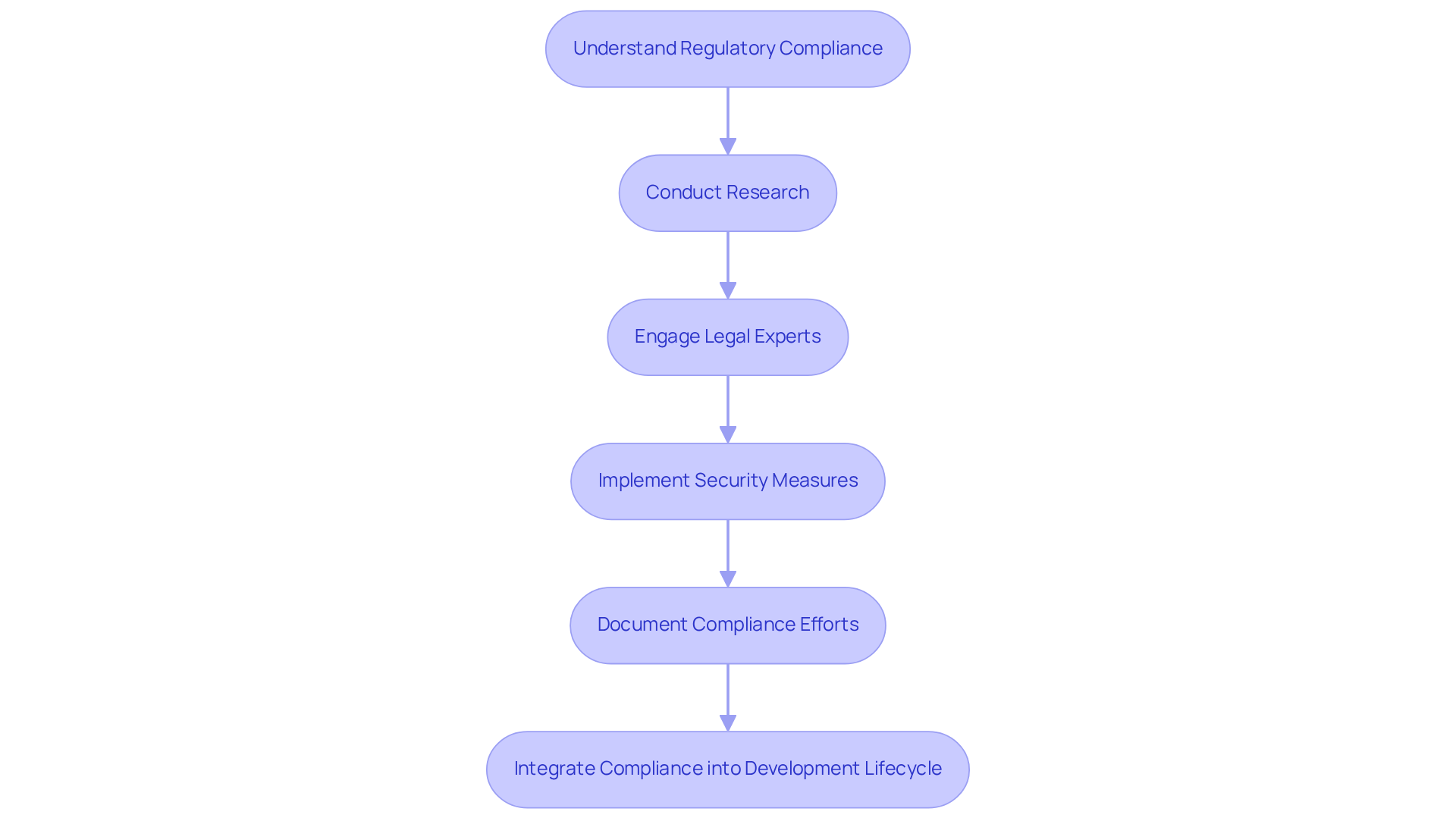
To ensure compliance, developers should:
- Conduct thorough research on applicable regulations and standards.
- Engage legal experts to interpret complex compliance requirements accurately.
- Implement security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive data.
- Document compliance efforts meticulously, providing evidence during audits.
Real-world examples illustrate the consequences of non-compliance, as companies have faced significant fines. This underscores the importance of integrating adherence into the health care software development lifecycle from the outset.
Prioritize User Experience and Accessibility in Design
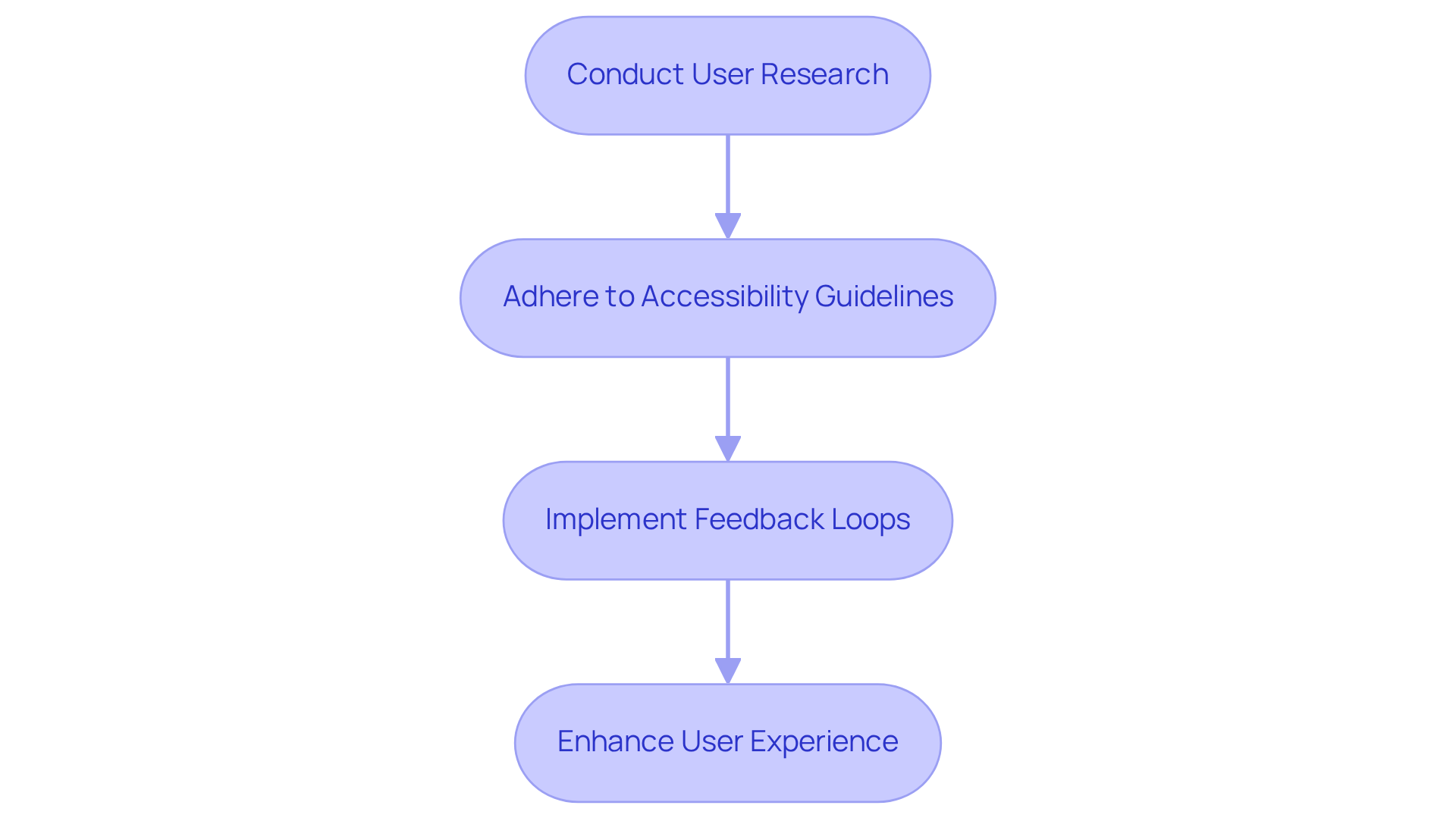
In health care software development, patient experience (UX) and accessibility are critical components, especially for individuals who may lack technical skills. To enhance UX and ensure accessibility, developers should take the following steps:
-
First, conducting user research is essential to identify the needs and preferences of diverse patient populations. This ensures that the health care software development accommodates a wide range of requirements, ultimately improving user satisfaction.
-
Second, adherence to accessibility guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), is paramount in health care software development. These guidelines provide essential standards for accommodating individuals with disabilities in the context of health care software development. Following these standards not only fulfills legal obligations but also enhances usability for all users in health care software development, potentially increasing revenue by providing a competitive advantage.
-
Third, implementing feedback loops allows users to share their experiences, facilitating continuous improvement and adaptation in health care software development. This iterative process is vital for maintaining relevance in a rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, especially in health care software development.
For instance, in health care software development, a telemedicine application designed with user-friendly features, such as straightforward appointment scheduling and clear instructions, can significantly enhance user satisfaction and engagement. Given that the telemedicine market is projected to reach $150.8 billion by 2026, prioritizing accessibility in health care software development is not merely a regulatory requirement; it represents a strategic advantage in a fast-changing medical environment. Furthermore, with 1.3 billion individuals, or 16% of the global population, experiencing significant disabilities, the necessity for accessibility in health care software development becomes increasingly critical.
Implement Comprehensive Testing and Quality Assurance Practices
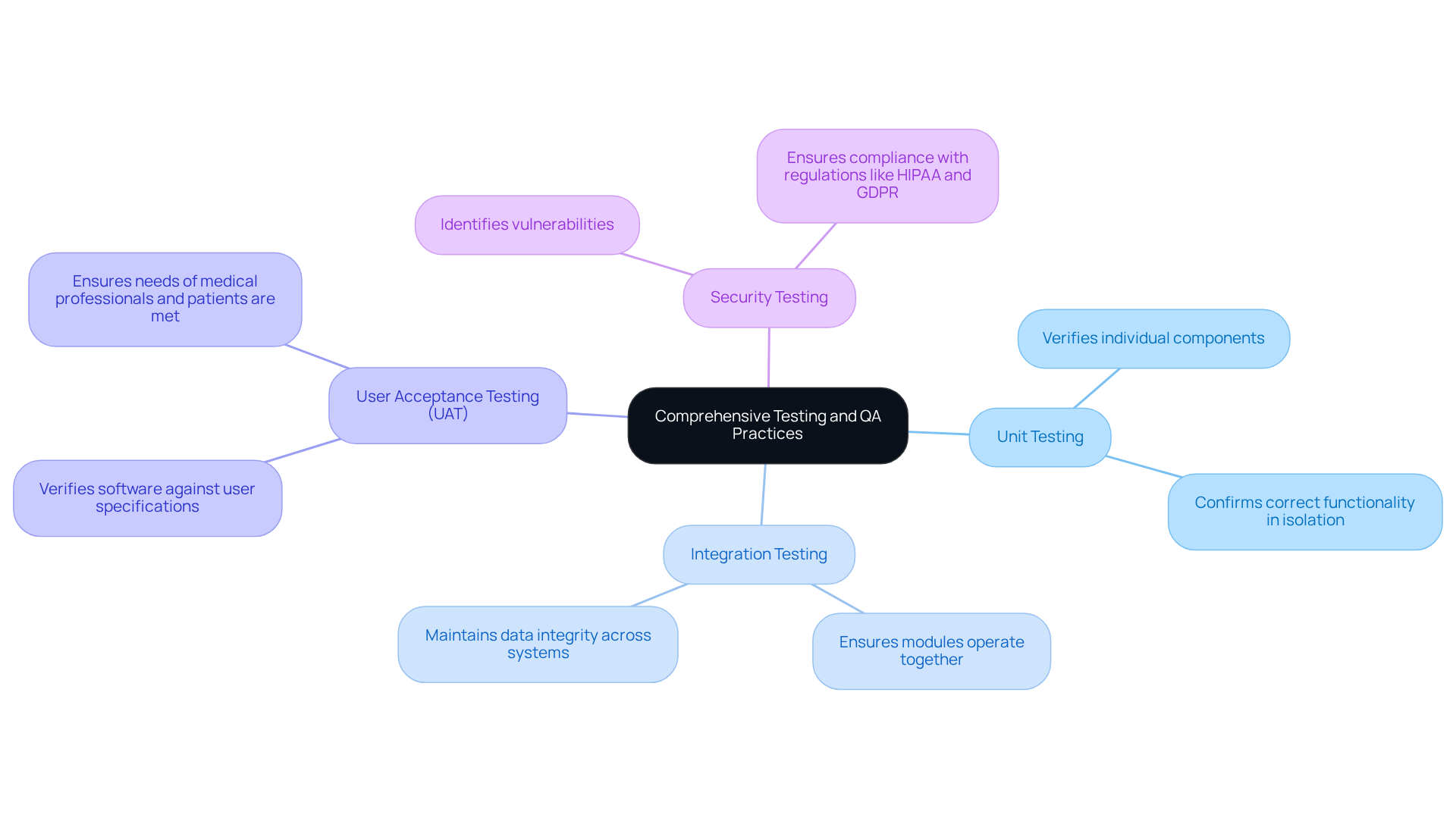
Thorough testing and quality assurance (QA) practices are essential in health care software development for medical applications. They ensure that programs comply with stringent regulatory standards and safeguard user data. Developers should implement a comprehensive testing strategy that encompasses several key components:
- Unit Testing: This involves verifying individual components to confirm their correct functionality in isolation.
- Integration Testing: This step ensures that various modules operate together seamlessly, which is vital for maintaining data integrity across systems.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): This process verifies the software against user specifications, ensuring it meets the needs of both medical professionals and patients.
- Security Testing: This critical phase identifies vulnerabilities that could jeopardize sensitive personal information, thereby maintaining trust and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Statistics reveal that many mobile health applications receive low ratings for security and privacy, highlighting the urgent need for rigorous QA processes. For example, a case study titled ‘Ensuring Patient Safety’ illustrates how medical applications that undergo thorough QA can avert costly recalls and enhance patient safety, ultimately leading to better outcomes and reduced operational risks. Furthermore, the use of automated testing tools significantly boosts efficiency and accuracy in the testing process, making it an indispensable element of health care software development in the medical sector.
Embrace Continuous Improvement and Iteration in Development
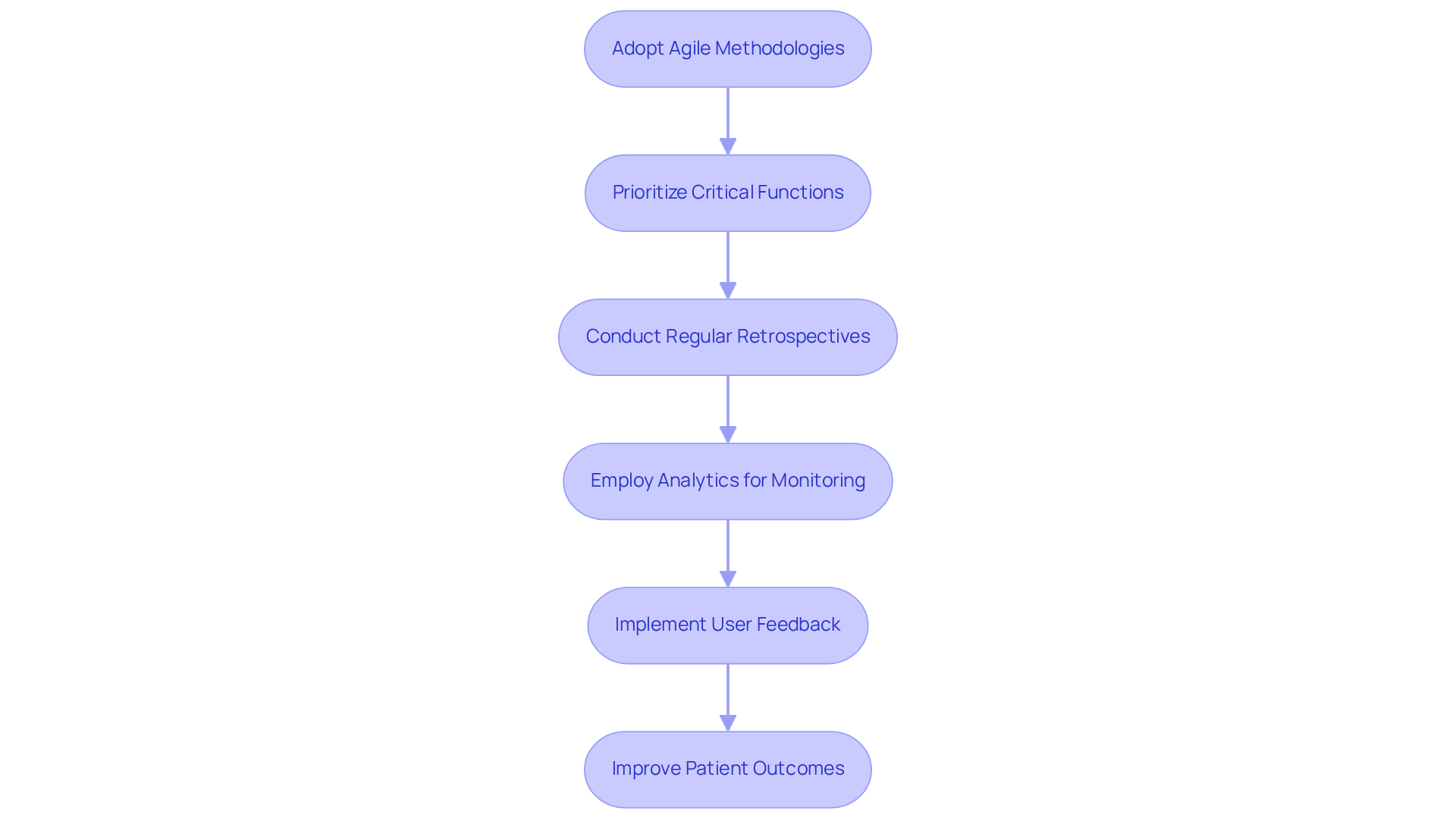
In the fast-paced medical environment, embracing continuous improvement and iteration is essential for success. Developers should adopt agile methodologies that promote flexibility and responsiveness to change. This approach allows teams to quickly adapt to evolving requirements, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes. Initial versions of medical application development utilizing agile are likely to prioritize critical functions early in the process, ensuring that essential features are addressed from the outset.
Regular retrospectives are crucial for evaluating what works and what doesn’t. This practice fosters a culture of learning that drives innovation and efficiency. Additionally, employing analytics to monitor engagement helps pinpoint areas for improvement, ensuring that technological solutions remain focused on individuals and are effective.
For instance, during the COVID-19 lockdown, health care software development for healthcare applications that implemented regular updates based on user feedback demonstrated significant improvements in patient satisfaction and retention. By refining the program, developers can ensure it remains relevant and efficient in addressing the diverse needs of users. This ultimately results in improved health outcomes and enriched user experiences. As Kokol noted, the application of agile software development in health care software development ensures significant functionality, enhancing continuity of care and overall satisfaction.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing best practices in healthcare software development is essential for achieving success in this complex and highly regulated industry. By concentrating on regulatory compliance, user experience, comprehensive testing, and continuous improvement, developers can create solutions that not only fulfill legal requirements but also enhance patient care and satisfaction.
Key insights from the article underscore the necessity of adhering to regulations such as HIPAA and FDA standards, which are designed to protect patient data and ensure software safety. Furthermore, prioritizing user experience and accessibility can significantly enhance engagement, particularly for individuals with diverse needs. Rigorous testing and quality assurance practices are crucial for safeguarding user data and maintaining trust, while an agile development approach encourages ongoing enhancements that adapt to the evolving healthcare landscape.
As the healthcare sector continues to evolve, embracing these best practices will be vital for developers aiming to create impactful software solutions. By committing to regulatory compliance, prioritizing user-centric design, implementing thorough testing, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, developers can not only meet current demands but also anticipate future trends in healthcare software development. This proactive approach will ultimately lead to improved health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is regulatory compliance important in healthcare software development?
Regulatory compliance is crucial in healthcare software development to ensure the privacy and security of patient information, as well as to meet legal requirements such as HIPAA and FDA regulations.
What laws should developers be familiar with in healthcare software development?
Developers should familiarize themselves with laws such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and FDA regulations, especially for software that qualifies as medical devices.
What steps should developers take to ensure compliance?
Developers should conduct thorough research on applicable regulations, engage legal experts for accurate interpretation of compliance requirements, implement security measures like encryption and access controls, and document compliance efforts meticulously.
What are the potential consequences of non-compliance in healthcare software development?
Non-compliance can lead to significant fines and legal repercussions for companies, highlighting the importance of integrating compliance into the software development lifecycle from the outset.
How can documentation help in the compliance process?
Meticulous documentation of compliance efforts provides evidence during audits, demonstrating that the necessary steps have been taken to adhere to regulatory requirements.