4 Best Practices for Revenue Cycle Management Software Success
Introduction
Understanding the complexities of revenue cycle management (RCM) software is essential for organizations that seek to optimize their financial health. By implementing effective practices, these entities can streamline their processes, enhance patient satisfaction, and improve cash flow. However, the journey toward successful implementation presents various challenges.
What key strategies can facilitate a seamless transition and effective utilization of RCM software? This article explores best practices, essential components, and common pitfalls to avoid, offering a comprehensive roadmap for organizations aiming to elevate their revenue cycle management efforts.
Understand Core Components of RCM Software
To effectively manage revenue cycles, organizations must grasp the core components of revenue cycle management software. These components typically include:
- Client Registration: This initial step involves collecting client information, ensuring that all necessary data is accurate and complete.
- Insurance Verification: Confirming patient insurance information is crucial to avoid reimbursement denials and to guarantee that the services provided are covered.
- Charge Capture: Accurately capturing charges for services rendered is essential for billing and revenue collection.
- Coding: Proper coding of services is vital for compliance and reimbursement, as it directly influences the submissions made to insurers.
- Request Submission: This process entails sending requests to payers for reimbursement, which must be executed accurately and promptly to prevent delays.
- Payment Posting: Recording payments received from insurers and patients is necessary for maintaining accurate financial records.
- Denial Management: Efficiently managing denied claims is critical for recovering lost income and enhancing overall cash flow.
- Reporting and Analytics: Utilizing data analytics to monitor performance and identify trends can lead to informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
Understanding these elements enables organizations to effectively implement revenue cycle management software, ensuring that all aspects of the income cycle are optimized for success.
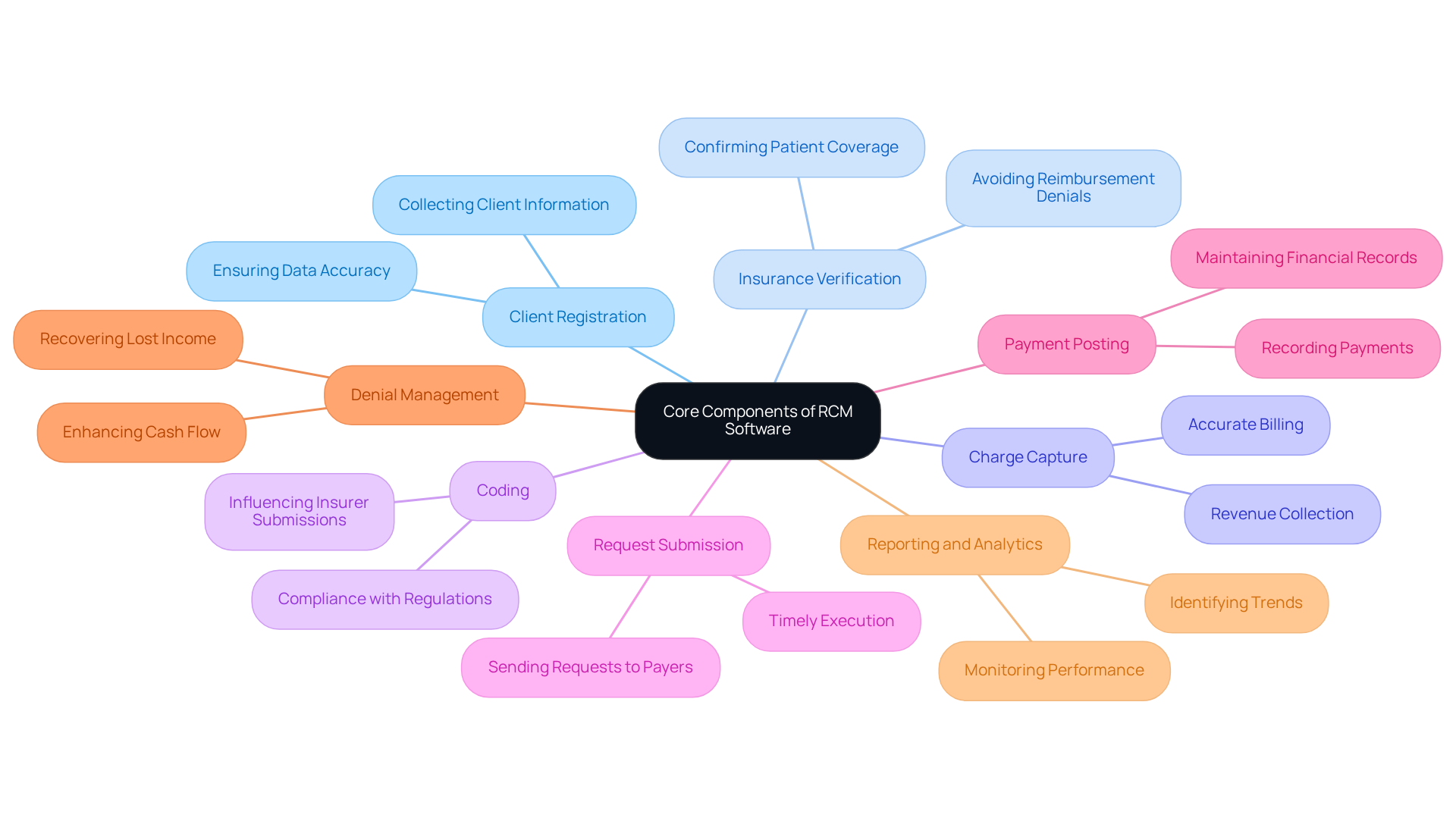
Implement Key Steps in the Revenue Cycle Process
To ensure a successful revenue cycle, organizations should implement the following key steps:
-
Pre-Registration: Gathering visitor information before their appointment is crucial for optimizing the registration process and minimizing wait times. Effective pre-registration significantly enhances client satisfaction and operational efficiency.
-
Insurance Verification: Confirming insurance eligibility and benefits prior to service delivery is essential for minimizing the risk of denial of reimbursement. Statistics indicate that 45% of claim denials stem from missing or inaccurate information collected during intake, while 56% of providers cite patient information errors as a primary cause of claims denials. This underscores the need for thorough verification processes. For instance, Providence Health uncovered $30M in missed coverage through automated eligibility verification, demonstrating the tangible benefits of implementing revenue cycle management software.
-
Charge Capture: Implementing automated systems for charge capture can drastically reduce errors and ensure that all services rendered are billed accurately. Practices utilizing revenue cycle management software report up to 40% fewer billing errors, which directly impacts income. Automated eligibility verification tools can achieve 99.5% accuracy compared to 80-85% for manual processes, further emphasizing the effectiveness of automation in reducing errors.
-
Accurate Coding: Training staff on the latest coding practices and utilizing advanced coding software enhances accuracy and compliance. Regular education programs on coding techniques can significantly reduce medical errors and employee turnover, leading to a more dependable revenue cycle management software.
-
Timely Submission of Requests: Establishing a routine for submitting requests promptly after services are rendered is vital for improving cash flow. Delays in submission can result in prolonged cash flow periods and heightened administrative challenges.
-
Follow-Up on Claims: Regularly monitoring the status of submitted claims and following up on outstanding payments can help recover revenue more efficiently. This proactive approach ensures that potential issues are addressed before they escalate.
-
Billing: Implementing clear and concise billing statements enhances understanding and prompts timely payments. Almost 80% of individuals indicate that price estimates enhance their care experience, emphasizing the significance of clarity in billing.
-
Feedback Loop: Establishing a feedback system to learn from rejected requests and patient inquiries promotes ongoing process enhancement. Examining trends in claim denials can assist entities in refining their practices and minimizing future errors.
By adhering to these steps, entities can establish a more effective revenue cycle management software that optimizes earnings and reduces delays.
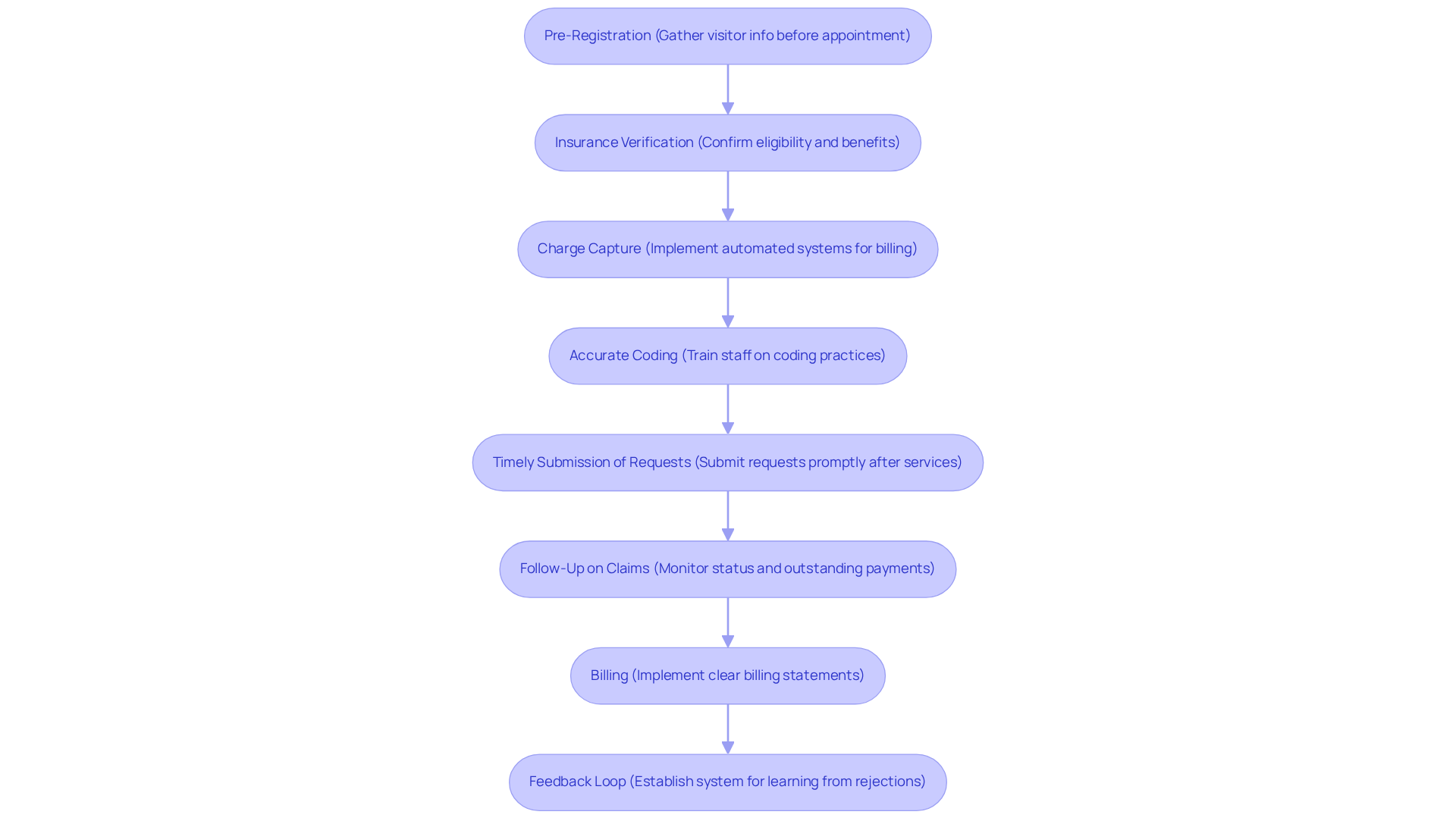
Monitor Performance Metrics for Continuous Improvement
To drive continuous improvement in revenue cycle management, organizations must closely monitor several key performance metrics:
- Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R): This metric reflects the average time taken to collect payments after services are rendered. Aiming for fewer than 30 days is ideal, as high-performing teams resolve over 60% of new accounts receivable within this timeframe.
- Clean Submission Rate: This percentage indicates the proportion of requests submitted without errors. Organizations should aim for a clean submission rate above 90%, as enhancements in this area can result in quantifiable ROI within the first month of implementing AI solutions.
- Denial Rate: Tracking the percentage of claims denied by payers is crucial for identifying billing process issues. Leading organizations maintain denial rates below 5%, which can significantly enhance cash flow.
- Net Collection Rate: This metric measures the percentage of collectible income that is actually collected. High-performing practices usually attain net collection rates of 95% or greater, indicating effective financial cycle strategies.
- Cost to Collect: Understanding the expenses associated with collecting payments helps organizations pinpoint inefficiencies. The goal should be to keep this cost as low as possible, ideally below 2% of total revenue.
- Client Satisfaction Scores: Monitoring feedback from individuals regarding billing processes can reveal areas needing enhancement. High satisfaction scores correlate with improved payment performance, particularly as individuals encounter rising out-of-pocket responsibilities. Strengthening patient financial engagement by clearly communicating balances and offering flexible payment options is essential.
- Claim Turnaround Time: This metric tracks the duration from claim submission to payment receipt. Shorter turnaround times, ideally under 30 days, indicate a more efficient income cycle process.
Furthermore, entities should actively confirm individual eligibility and insurance coverage for the new plan year, particularly as coverage renews each January. Consistently assessing these metrics enables companies to make data-informed choices, refine strategies, and enhance their revenue cycle management software practices, ultimately resulting in improved financial performance and patient engagement. Conducting a year-end audit of coding accuracy and charge capture is also crucial for improving cash flow and preventing denials.
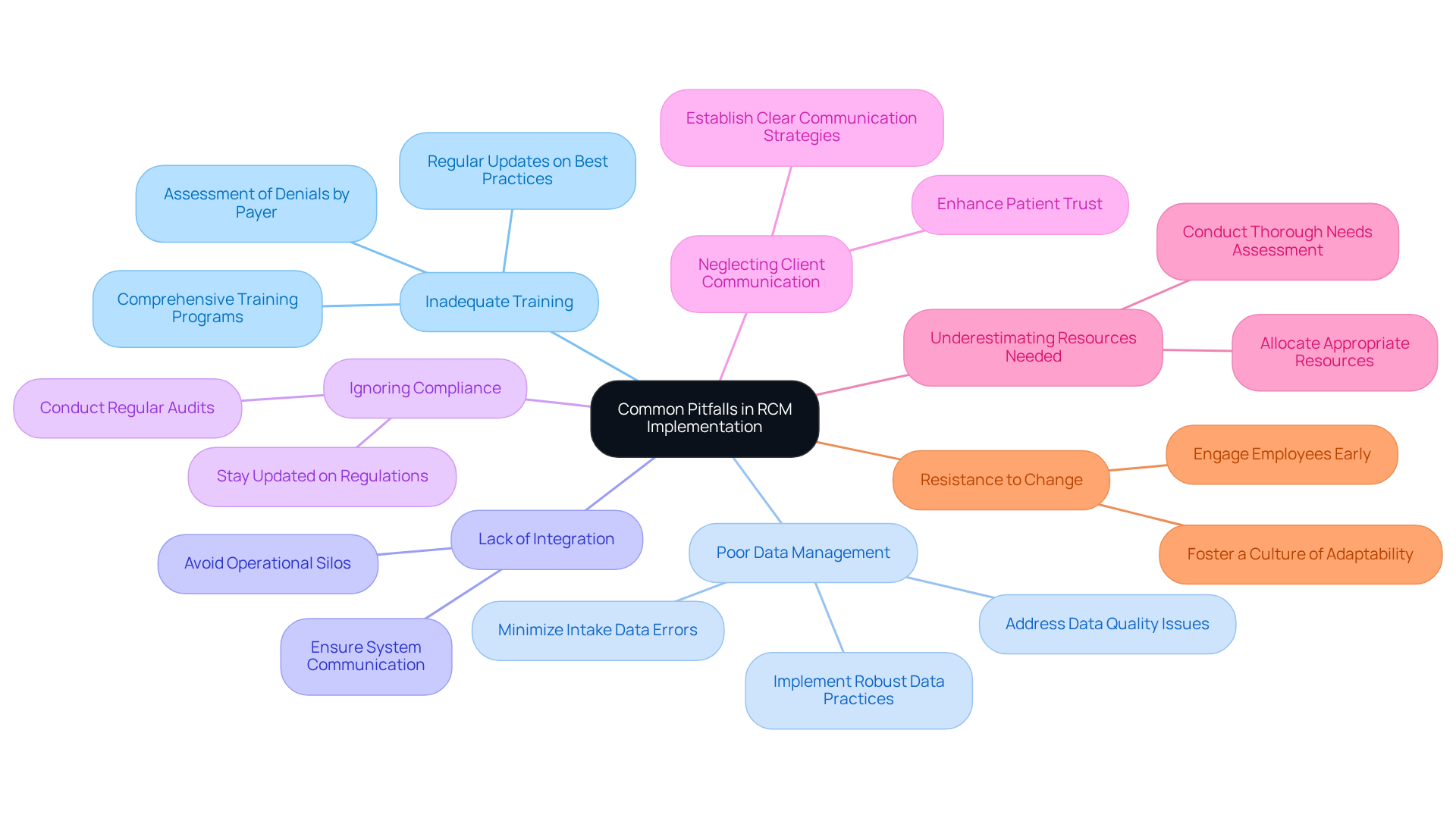
Avoid Common Pitfalls in RCM Implementation
To ensure a successful implementation of revenue cycle management software, organizations must be vigilant about avoiding common pitfalls that can undermine their efforts.
-
Inadequate Training: Comprehensive training is crucial; without it, staff may make errors in billing and coding. Regular training sessions should be scheduled to keep everyone updated on best practices and software functionalities. As Stacey LaCotti observes, “Providers that assess denials by payer, reason, and value of the request, then prioritize solutions at intake, prior authorization, and coding, usually experience the most significant enhancements.”
-
Poor Data Management: Inaccurate or incomplete individual data is a leading cause of denial issues, with studies indicating that 26% of rejections stem from data problems at individual intake. Implementing robust data management practices is essential to minimize these risks. The case study on “Common Reasons for Healthcare Claim Denials” highlights that addressing data quality issues could significantly reduce claim denials.
-
Lack of Integration: Failing to integrate revenue cycle management software with existing systems can create operational silos, hindering efficiency. Ensuring that all systems communicate effectively is vital for streamlined processes.
-
Ignoring Compliance: Staying updated on regulatory changes is critical; neglecting this can lead to compliance issues. Regular audits and updates to processes are necessary to maintain adherence to evolving standards. Neglecting compliance can result in significant financial repercussions, as highlighted in the case study on “The Role of Compliance in Revenue Cycle Management.”
-
Neglecting Client Communication: Inadequate communication concerning billing can result in client dissatisfaction and postponed payments. Establishing clear and proactive communication strategies is essential for enhancing patient trust and ensuring timely collections.
-
Underestimating Resources Needed: Organizations often misjudge the resources required for successful implementation. A thorough assessment of needs and capabilities should be conducted beforehand to allocate appropriate resources.
-
Resistance to Change: Staff may resist new processes or technologies. Engaging employees early in the implementation process can help mitigate resistance and foster a culture of adaptability.
By recognizing these pitfalls and taking proactive measures to address them, organizations can significantly enhance their chances of successful implementation of revenue cycle management software, ultimately improving their financial health and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of revenue cycle management (RCM) software is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their financial processes. By grasping the core components of RCM software and adhering to established practices, organizations can enhance their revenue cycles, reduce errors, and ultimately improve cash flow. The integration of efficient systems and proactive strategies enables entities to excel in a competitive landscape.
Key insights include:
- The significance of thorough client registration
- Insurance verification
- Accurate charge capture
- Timely submission of requests
Furthermore, monitoring performance metrics such as days in accounts receivable and clean submission rates fosters continuous improvement. It is equally crucial to recognize and avoid common pitfalls in RCM implementation, including inadequate training and poor data management, to ensure a smooth transition and successful outcomes.
As organizations pursue excellence in revenue cycle management, a commitment to ongoing education, effective communication, and strategic resource allocation becomes vital. Embracing these best practices not only enhances operational efficiency but also cultivates stronger relationships with clients, paving the way for sustained financial success. Prioritizing these strategies empowers organizations to optimize their revenue cycle management software, yielding better results in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core components of revenue cycle management (RCM) software?
The core components of RCM software include Client Registration, Insurance Verification, Charge Capture, Coding, Request Submission, Payment Posting, Denial Management, and Reporting and Analytics.
What is involved in the Client Registration process?
Client Registration involves collecting client information and ensuring that all necessary data is accurate and complete.
Why is Insurance Verification important in RCM?
Insurance Verification is crucial to confirm patient insurance information, which helps avoid reimbursement denials and ensures that the services provided are covered.
What does Charge Capture refer to in the context of RCM?
Charge Capture refers to the accurate recording of charges for services rendered, which is essential for billing and revenue collection.
How does Coding impact revenue cycle management?
Proper Coding of services is vital for compliance and reimbursement, as it directly influences the submissions made to insurers.
What is the purpose of Request Submission in RCM?
Request Submission entails sending requests to payers for reimbursement, which must be executed accurately and promptly to prevent delays.
What is involved in Payment Posting?
Payment Posting involves recording payments received from insurers and patients, which is necessary for maintaining accurate financial records.
Why is Denial Management critical in RCM?
Denial Management is critical for efficiently managing denied claims, which helps in recovering lost income and enhancing overall cash flow.
How do Reporting and Analytics contribute to RCM?
Reporting and Analytics utilize data analytics to monitor performance and identify trends, leading to informed decision-making and continuous improvement.