Master Healthcare Data Warehouse Models for Effective Implementation

Introduction
In an era where data-driven decision-making is crucial, healthcare organizations must effectively harness the power of data warehouses. These systems streamline operations and enhance patient care through informed analytics. However, implementing a successful healthcare data warehouse presents several complexities, including:
- Navigating regulatory compliance
- Overcoming information silos
To ensure that their data warehouse meets current demands and adapts to future challenges, organizations can adopt various strategies.
Define Healthcare Data Warehouse Models
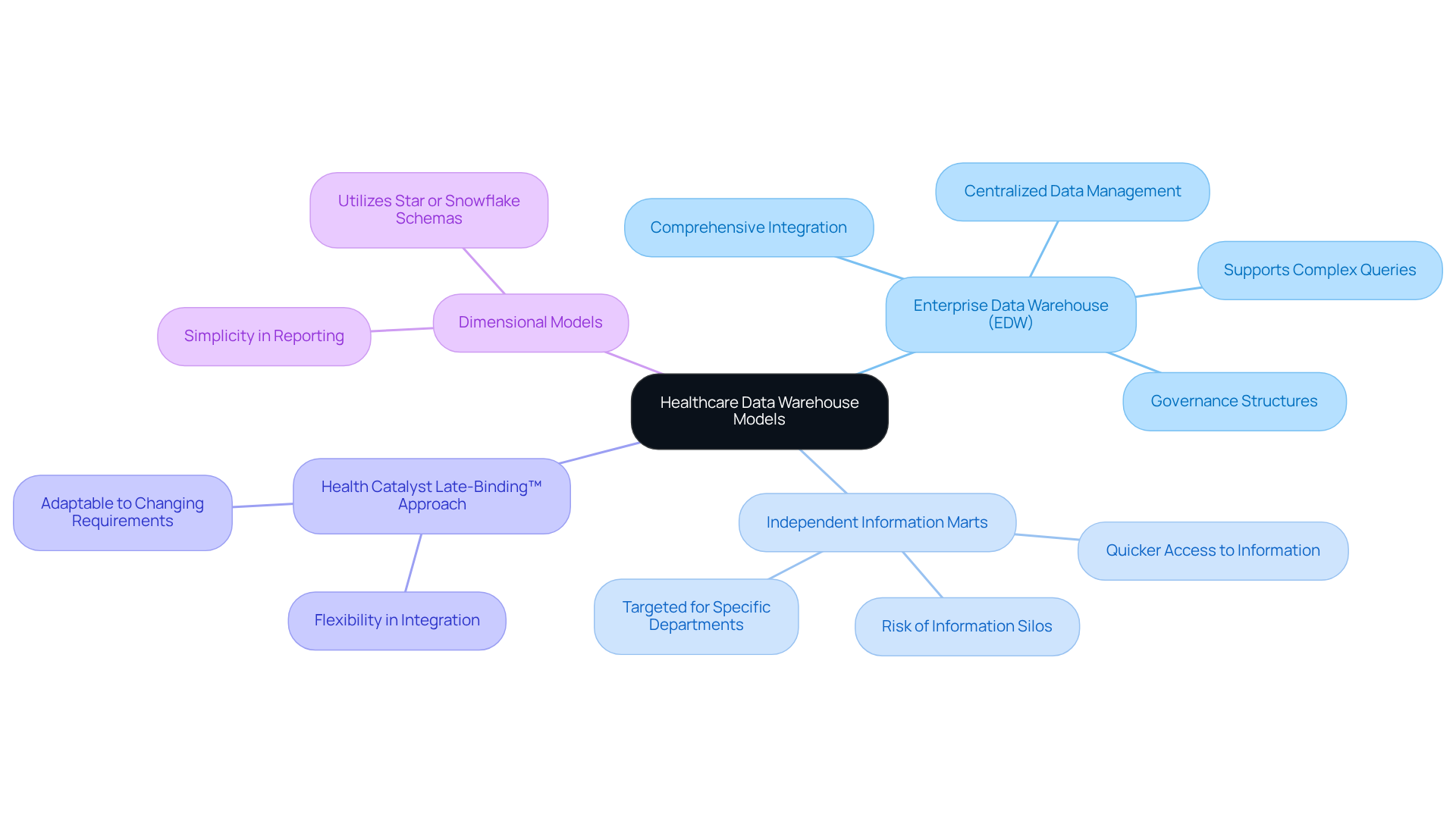
Healthcare data warehouse models can be categorized into several types, each serving distinct purposes:
-
Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW): This model integrates information from various sources across the enterprise, providing a comprehensive view of all operations. It supports complex queries and analytics, making it ideal for large medical systems.
-
Independent Information Marts: These smaller, targeted information warehouses cater to specific departments or functions within a healthcare organization. They enable quicker access to relevant information but may lead to information silos if not managed effectively.
-
Health Catalyst Late-Binding™ Approach: This innovative model allows for flexibility in information integration, enabling organizations to adapt to changing information requirements without extensive re-engineering.
-
Dimensional Models: Designed for simplicity in reporting and analytics, these models often utilize star or snowflake schemas to organize information into facts and dimensions.
Understanding the healthcare data warehouse model is essential for healthcare organizations to choose the appropriate architecture that satisfies their analytical needs and regulatory compliance requirements.
Identify Key Features for Successful Implementation
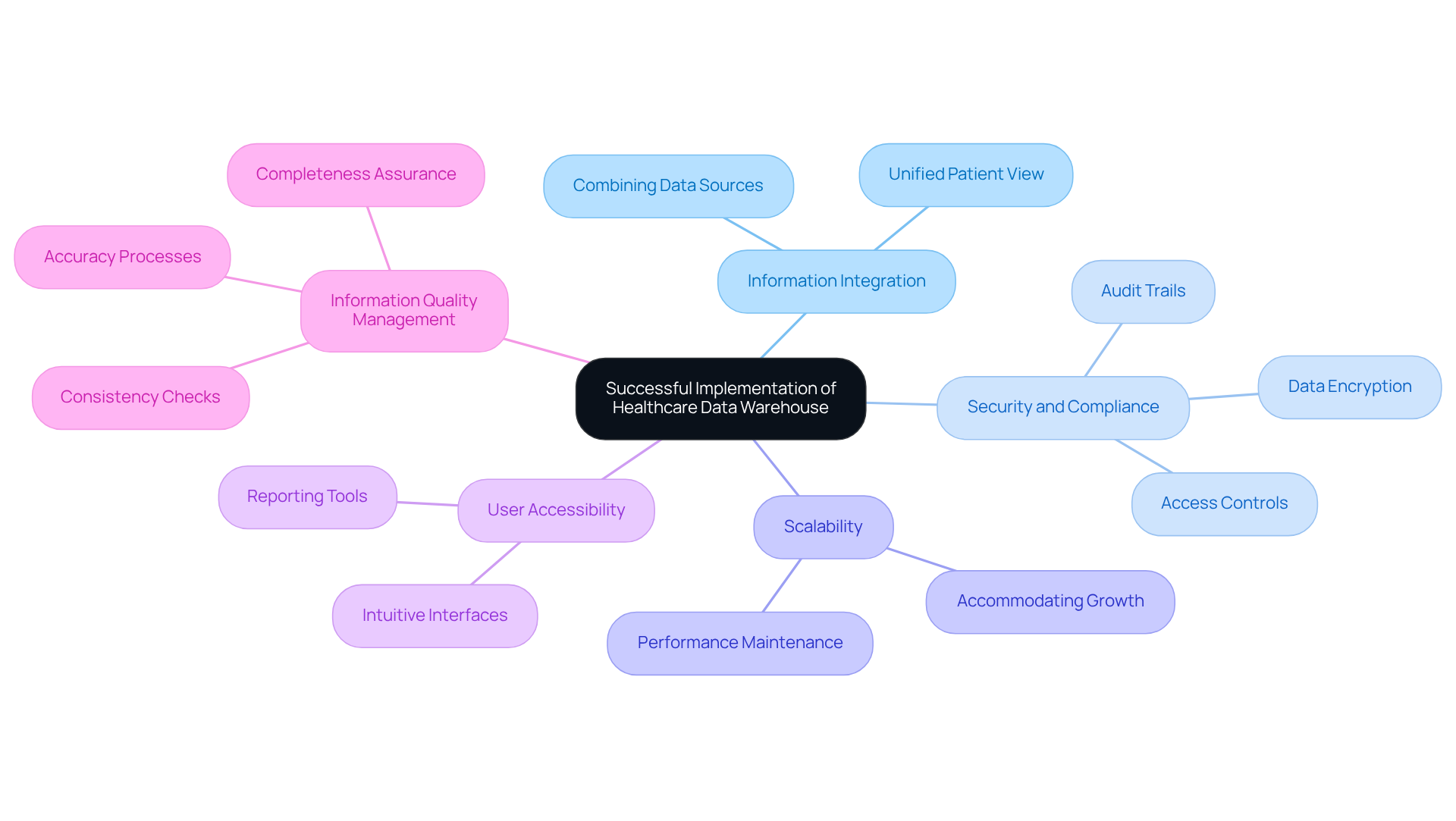
The successful implementation of a healthcare data warehouse relies on several critical features:
-
Information Integration: The ability to seamlessly combine data from diverse sources, such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs), laboratory systems, and billing software, is essential. This integration ensures a unified view of patient information.
-
Security and Compliance: Due to the sensitive nature of medical data, strong security measures – including encryption, access controls, and audit trails – are vital for safeguarding patient information and adhering to regulations like HIPAA.
-
Scalability: The data warehouse must be capable of expanding in tandem with the organization’s growth, accommodating increasing volumes and user demands without compromising performance.
-
User Accessibility: Intuitive interfaces and reporting tools are necessary to allow healthcare professionals to easily access and analyze data, thereby supporting informed decision-making.
-
Information Quality Management: Establishing processes to ensure accuracy, consistency, and completeness is crucial for reliable analytics and reporting.
By focusing on these features, healthcare organizations can enhance the efficiency of their data management initiatives.
Implement Proven Strategies for Effective Deployment
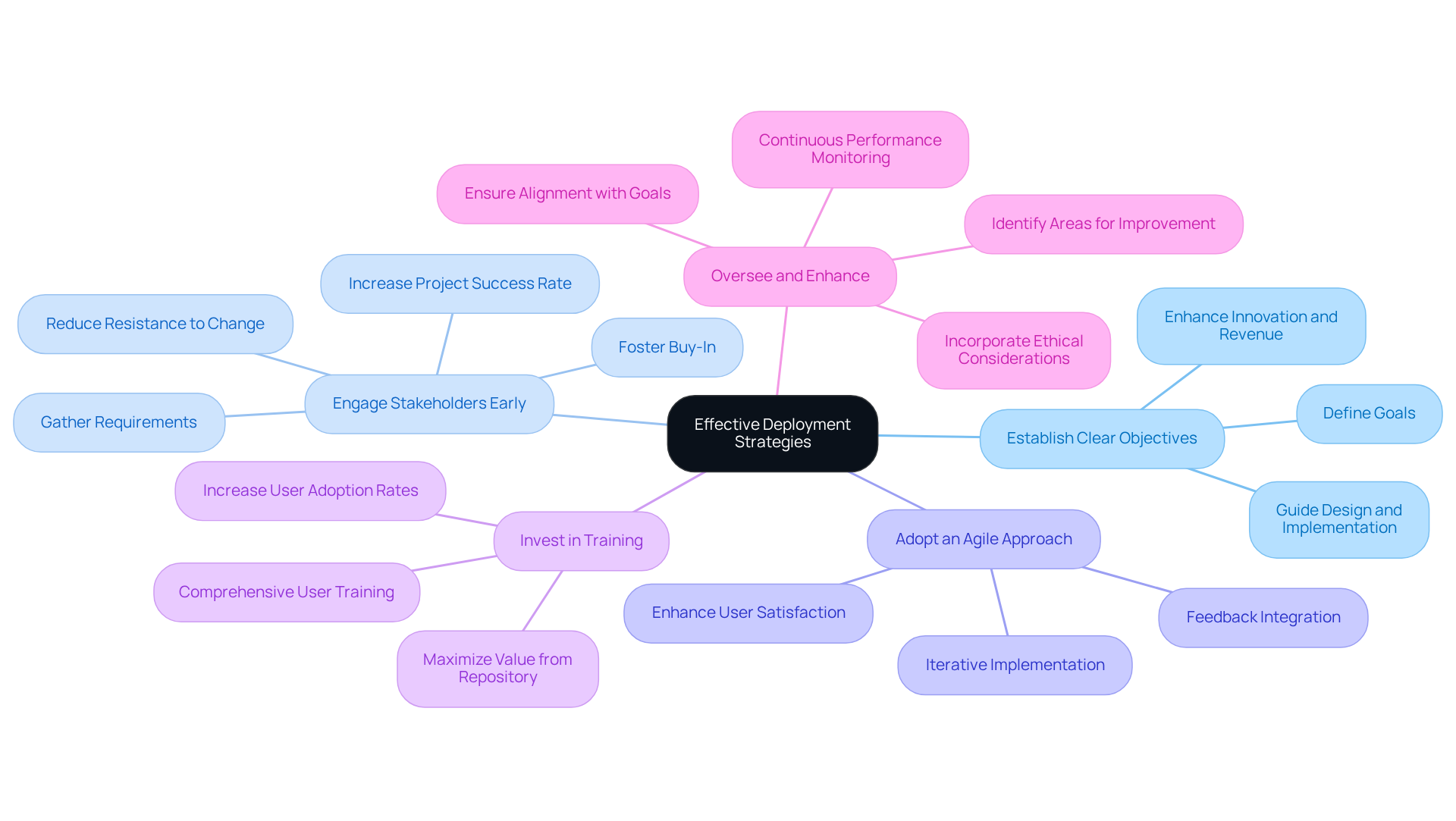
To ensure the effective deployment of a healthcare data warehouse, organizations should consider several key strategies:
-
Establish Clear Objectives: It is essential to clearly define the goals of the information storage project, including specific analytics and reporting requirements. This clarity will guide the design and implementation process, ensuring alignment with organizational priorities. Notably, the implementation of a healthcare data warehouse model can enhance innovation, insight, and revenue for entities, making the establishment of clear objectives crucial.
-
Engage Stakeholders Early: Involving key stakeholders from various departments during the planning phase is vital to gather requirements and ensure that the information repository meets their needs. Early engagement fosters buy-in and reduces resistance to change, which is critical for successful implementation. Research indicates that projects with strong stakeholder engagement are six times more likely to succeed. As Rostyslav Fedynyshyn notes, healthcare organizations increasingly utilize their information resources within the healthcare data warehouse model to accelerate research and innovation.
-
Adopt an Agile Approach: Implementing the information repository in iterative phases allows for adjustments based on feedback and evolving requirements. This flexibility can lead to a more responsive and effective solution, thereby enhancing user satisfaction and operational efficiency.
-
Invest in Training: Comprehensive training for users is essential to ensure they can effectively utilize the information repository and its tools. Investing in human capital is crucial for maximizing the value derived from the information repository, as firms that prioritize training experience a 20% increase in user adoption rates.
-
Oversee and Enhance: Continuous supervision of the information repository’s performance is necessary to make modifications that improve functionality and user experience. Regular assessments can help identify areas for improvement, ensuring that the system remains aligned with organizational goals and adapts to changing needs. For instance, organizations that implement ongoing optimization strategies report a 15% reduction in operational costs annually. Furthermore, ethical considerations in information monetization, such as maintaining patient trust and compliance, are essential for responsible management. Incorporating these considerations will further enhance the effectiveness of the information storage.
Overcome Implementation Challenges and Risks
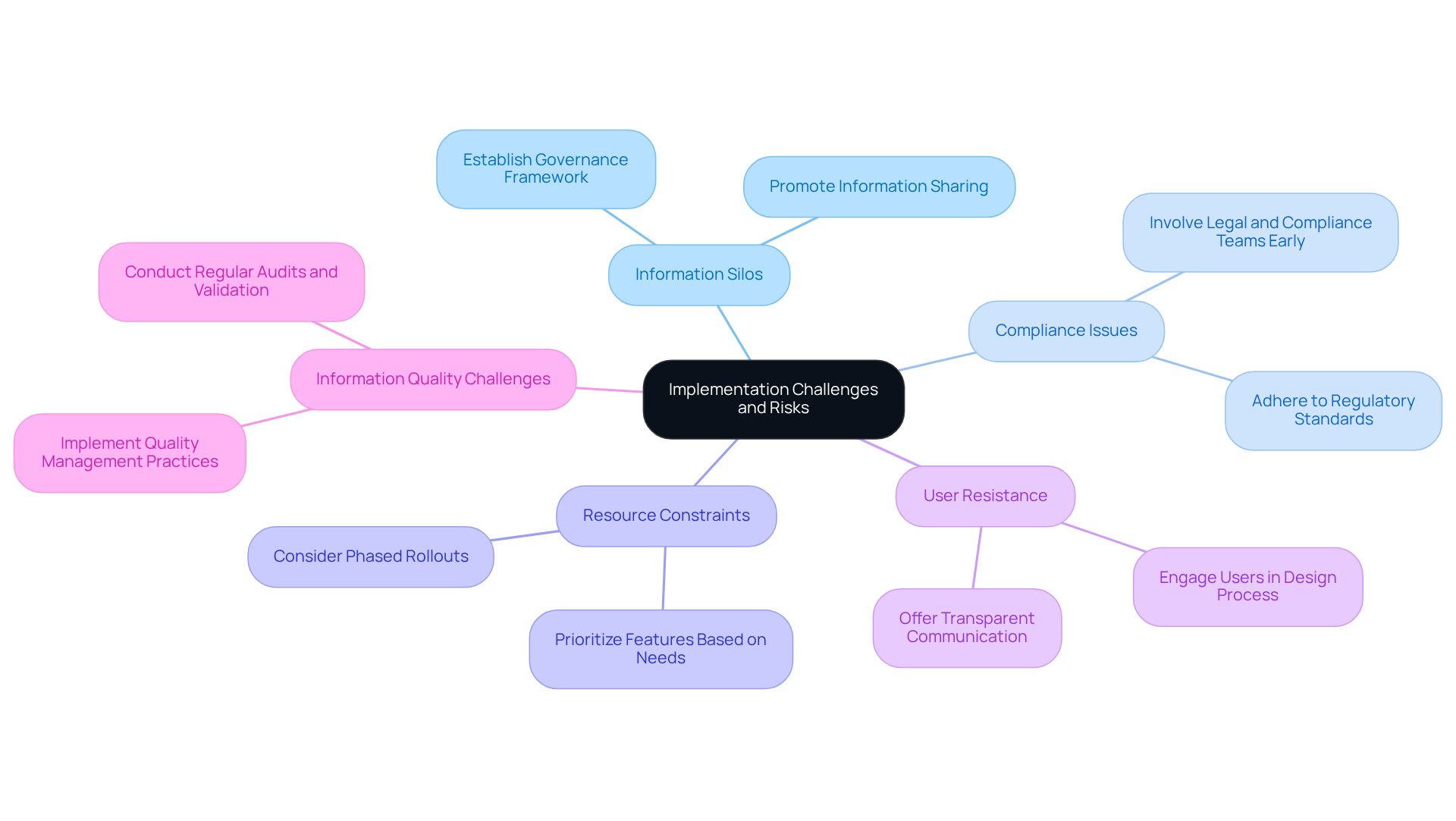
Implementing a healthcare data warehouse model presents several challenges and risks that organizations must navigate effectively.
-
Information Silos pose a significant hurdle, as organizations often struggle to integrate data from disparate sources. This can lead to incomplete or inconsistent datasets. To mitigate this issue, it is essential to establish a robust governance framework that promotes information sharing and collaboration across departments.
-
Compliance Issues are another critical concern. Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory requirements necessitates early involvement of legal and compliance teams. This ensures that the information repository adheres to all relevant laws and standards, thereby reducing the risk of non-compliance.
-
Resource Constraints can also hinder implementation efforts. Organizations may face limited budgets and personnel, which can impede progress. To address this, it is advisable to prioritize features and functionalities based on organizational needs and consider phased rollouts. This approach allows for more effective management of resource allocation.
-
User Resistance is a common challenge during change management. To foster acceptance of the new information system, it is crucial to offer transparent communication about its advantages. Engaging users in the design process can further enhance their buy-in and willingness to adapt.
-
Finally, Information Quality Challenges must be addressed to maintain the efficiency of the information storage system. Erroneous or outdated information can compromise data integrity. Implementing information quality management practices, including regular audits and validation processes, is vital to uphold high standards of data integrity.
By proactively addressing these challenges, healthcare organizations can significantly enhance the likelihood of a successful implementation of the healthcare data warehouse model.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of healthcare data warehouse models is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their data management strategies. By selecting the appropriate model – be it an Enterprise Data Warehouse, Independent Information Marts, or the Health Catalyst Late-Binding™ Approach – healthcare entities can effectively leverage their data for enhanced analytics and informed decision-making.
This article emphasizes critical features necessary for successful implementation, including:
- Information integration
- Security
- Scalability
- User accessibility
- Information quality management
It also highlights the significance of established strategies such as:
- Setting clear objectives
- Engaging stakeholders
- Adopting an agile methodology
- Investing in training
- Maintaining ongoing oversight
to ensure that the data warehouse adapts to evolving organizational needs.
Navigating the challenges associated with healthcare data warehouse implementation is crucial for achieving success. Proactively addressing issues such as:
- Information silos
- Compliance challenges
- Resource limitations
- User resistance
- Information quality concerns
can significantly improve the chances of developing a robust and effective data management system. By embracing these best practices, healthcare organizations not only foster innovation and insight but also position themselves to meet the demands of an increasingly data-driven environment. Organizations are encouraged to prioritize these elements to fully realize the potential of their healthcare data warehouse initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are healthcare data warehouse models?
Healthcare data warehouse models are frameworks that categorize and organize data for healthcare organizations, serving distinct purposes based on their analytical needs.
What is an Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)?
An Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) integrates information from various sources across the enterprise, providing a comprehensive view of all operations and supporting complex queries and analytics, making it suitable for large medical systems.
What are Independent Information Marts?
Independent Information Marts are smaller, targeted information warehouses that cater to specific departments or functions within a healthcare organization, allowing quicker access to relevant information but potentially creating information silos if not managed properly.
What is the Health Catalyst Late-Binding™ Approach?
The Health Catalyst Late-Binding™ Approach is an innovative model that allows for flexibility in information integration, enabling organizations to adapt to changing information requirements without extensive re-engineering.
What are Dimensional Models in healthcare data warehousing?
Dimensional Models are designed for simplicity in reporting and analytics, often utilizing star or snowflake schemas to organize information into facts and dimensions for easier understanding and access.
Why is understanding healthcare data warehouse models important for organizations?
Understanding healthcare data warehouse models is essential for healthcare organizations to choose the appropriate architecture that meets their analytical needs and complies with regulatory requirements.