4 Best Practices for High Availability Software in Financial Services

Introduction
High availability in the financial services sector serves as a critical lifeline, ensuring that institutions remain operational amidst potential disruptions. The stakes are significant, with thousands of dollars potentially lost per minute during outages. Consequently, implementing effective high availability software is paramount for maintaining customer trust and adhering to regulatory compliance.
As organizations strive for the elusive goal of 99.99% uptime, they encounter the challenge of navigating complex infrastructures and adapting to evolving best practices. This raises an important question: what essential strategies can safeguard against downtime and enhance system resilience in this competitive landscape?
Define High Availability in Financial Services
High availability software in the services sector refers to the capability of systems to remain operational and accessible with minimal downtime, typically aiming for 99.99% uptime or higher. This capability is crucial in banking and investment sectors, where even a brief outage can result in significant monetary losses and regulatory penalties. For instance, e-commerce outages can lead to an average loss of $9,000 per minute, underscoring the economic stakes involved.
High availability software is achieved through strategies such as:
- Redundancy
- Failover mechanisms
- Load balancing
These strategies collectively ensure continuous operation during failures or maintenance. In monetary services, HA goes beyond being a mere technical necessity; it is a regulatory requirement. Institutions must comply with stringent operational standards to protect sensitive financial data and maintain customer trust.
The market for high reliability solutions was valued at USD 13.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2025 to 2032, reflecting the increasing importance of HA in the sector. Furthermore, as defined by TechTarget, HA is the ability of a system to operate continuously without failing for a specified period. Implementing high availability software not only mitigates risks associated with interruptions but also enhances overall reliability, thereby fostering customer trust and satisfaction in a competitive market.
Eliminating single points of failure is critical to ensure that if one component fails, others can seamlessly take over, preserving operational integrity.
Establish Requirements and Best Practices for High Availability
To achieve high availability in financial services, organizations must prioritize several essential requirements and best practices:
-
Redundancy: Organizations should create duplicate structures and components to eliminate single points of failure. This includes deploying multiple servers, databases, and network paths to ensure continuous operation. Cloud redundancy is particularly crucial for meeting regulatory requirements regarding data protection and sovereignty.
-
Failover Mechanisms: It is essential to implement automated failover solutions that can seamlessly switch to backup resources in the event of a primary resource failure. This ensures continuous operation without the need for manual intervention. Automated failover mechanisms facilitate swift transitions to backup solutions, which is vital for maintaining client trust.
-
Load Balancing: Distributing workloads across multiple servers prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck. This strategy not only enhances performance but also boosts overall availability by utilizing high availability software, ensuring that critical services remain operational even during peak times.
-
Regular Testing: Conducting routine failover and recovery tests is necessary to verify that infrastructures can effectively manage failures. Simulating outages and confirming that backup solutions activate as intended is crucial for operational resilience. Regular testing helps financial institutions refine recovery processes and improve recovery time objectives (RTOs).
-
Monitoring and Alerts: Ongoing observation of system performance and accessibility, along with notifications for any irregularities, is essential. This proactive approach enables swift responses to potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. Continuous monitoring is critical for identifying weaknesses in recovery protocols.
-
Compliance and Documentation: Ensuring that all strategies involving high availability software adhere to industry regulations and are thoroughly documented is vital. This is important for audits and maintaining trust with clients and regulators, especially in a landscape where compliance is paramount. As emphasized by industry specialists, the average expense of a data breach in the finance sector is $6.08 million, underscoring the significance of these practices.
Measure High Availability: Key Metrics and Evaluation
Measuring high availability software requires tracking several key metrics that provide insights into system performance and reliability.
-
Uptime Percentage serves as the most straightforward metric, calculated by dividing the total operational time by the total time within a specified period. In the financial industry, utilizing high availability software to achieve 99.99% uptime is considered standard.
-
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) assesses the average duration between failures of the system, offering valuable insight into its reliability.
-
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) measures the average time taken to restore functionality after a failure occurs. A lower MTTR signifies a more resilient infrastructure supported by high availability software.
-
Application Uptime specifically monitors the accessibility of essential functions within applications, ensuring that users can access necessary features without interruption.
-
Time to Recover (TTR) evaluates how swiftly a system can revert to normal operations following a failure, which is crucial for maintaining operational levels in economic environments.
-
Lastly, User Experience Metrics involve observing user experience aspects, such as response times and transaction success rates. These metrics provide further context to the quantitative data, ensuring that high availability software results in a positive user experience.
Implement High Availability Solutions: Case Studies and Guidance
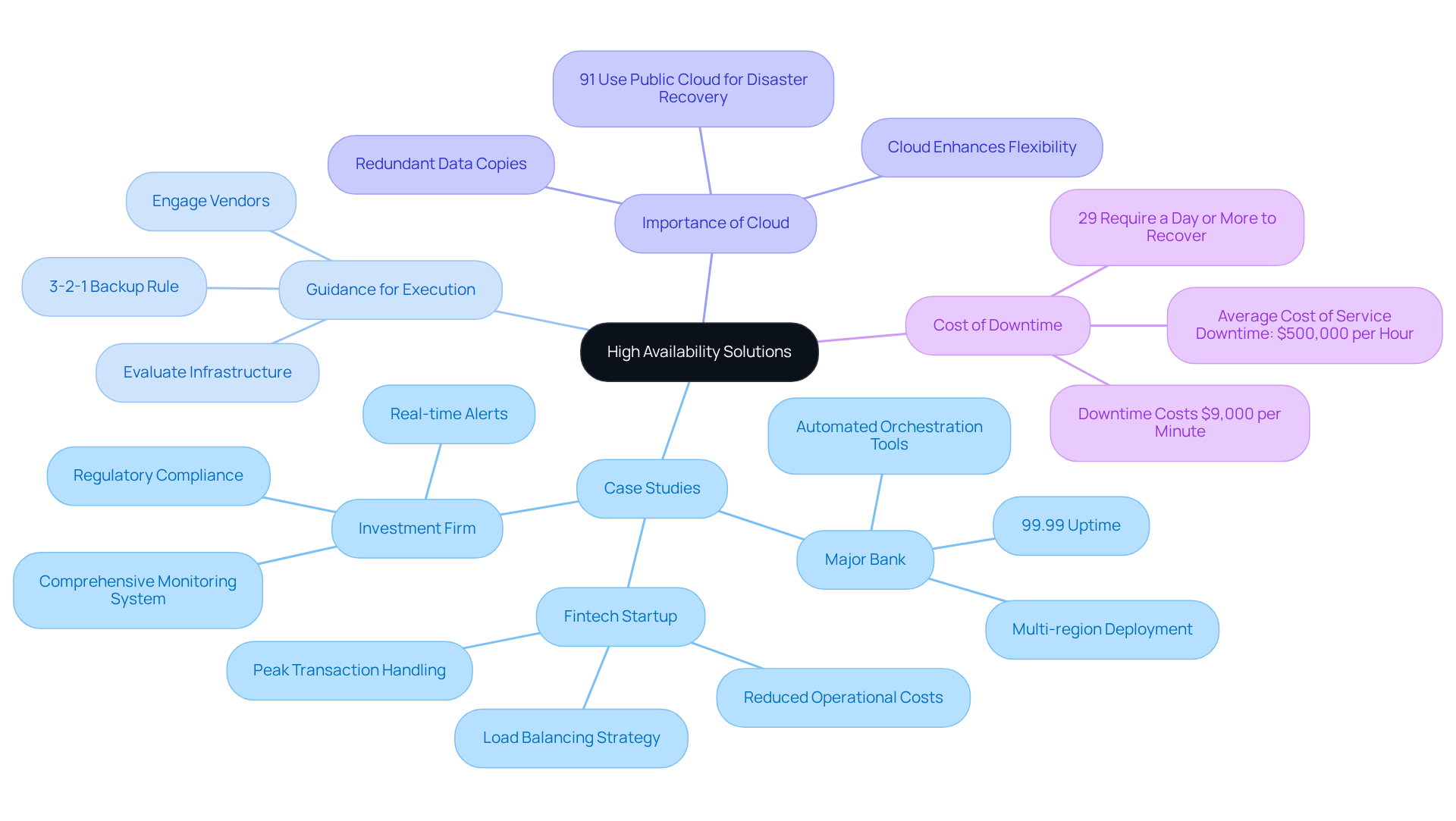
Several organizations in the financial services sector have successfully implemented high availability solutions, showcasing effective practices:
-
Case Study: Major Bank’s Disaster Recovery Plan: A leading bank executed a multi-region deployment strategy, ensuring that its offerings remained functional even during regional outages. By utilizing automated orchestration tools, the bank achieved a 99.99% uptime, significantly enhancing customer trust and satisfaction.
-
Case Study: Fintech Startup’s Load Balancing Strategy: A fintech startup adopted a load balancing approach across its application servers, enabling it to handle peak transaction loads without downtime. This strategy not only improved performance but also reduced operational costs by optimizing resource usage.
-
Case Study: Investment Firm’s Monitoring System: An investment firm integrated a comprehensive monitoring system that provided real-time alerts for any performance issues. This proactive approach allowed the firm to address potential failures before they affected service access, maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
-
Guidance for Execution: Organizations aiming to adopt high reliability solutions should begin by evaluating their existing infrastructure and identifying essential components that require redundancy. Engaging with experienced vendors and leveraging cloud-based solutions can enhance flexibility and scalability in achieving high availability. Notably, 91% of organizations utilize the public cloud for disaster recovery, underscoring its significance. Additionally, adhering to the 3-2-1 Backup Rule can provide a solid framework for disaster recovery planning. Organizations should also recognize that downtime costs approximately $9,000 per minute, emphasizing the urgency of implementing these solutions. Furthermore, insights from experts indicate that 52% of organizations can restore critical systems within 12 hours after a severe data loss event, serving as a benchmark for recovery capabilities.
Conclusion
High availability in financial services transcends a mere technical requirement; it stands as a critical component that protects institutions from substantial operational risks and financial losses. Achieving and maintaining high availability necessitates the implementation of robust strategies that ensure systems remain functional with minimal downtime, thereby reinforcing customer trust and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Essential practices for achieving high availability include:
- Redundancy to eliminate single points of failure
- Automated failover mechanisms for seamless transitions during outages
- Load balancing to optimize resource utilization
Furthermore, regular testing and continuous monitoring are vital for ensuring that systems can effectively manage disruptions. The significance of compliance and thorough documentation is paramount, as these elements are crucial for maintaining trust with clients and regulators alike.
In an increasingly competitive landscape, the importance of high availability cannot be overlooked. Organizations must prioritize these practices not only to mitigate risks but also to enhance overall reliability and customer satisfaction. As the financial services sector continues to evolve, adopting innovative solutions and learning from successful case studies will be instrumental in achieving the high availability necessary to thrive in this dynamic environment. The call to action is unequivocal: invest in high availability systems now to secure a resilient future in financial services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does high availability mean in financial services?
High availability in financial services refers to the capability of systems to remain operational and accessible with minimal downtime, typically aiming for 99.99% uptime or higher.
Why is high availability crucial in banking and investment sectors?
High availability is crucial because even a brief outage can lead to significant monetary losses and regulatory penalties. For example, e-commerce outages can result in an average loss of $9,000 per minute.
What strategies are used to achieve high availability software?
Strategies to achieve high availability software include redundancy, failover mechanisms, and load balancing, which collectively ensure continuous operation during failures or maintenance.
Is high availability just a technical necessity in financial services?
No, high availability is not only a technical necessity but also a regulatory requirement. Financial institutions must comply with stringent operational standards to protect sensitive financial data and maintain customer trust.
What is the market outlook for high availability solutions?
The market for high availability solutions was valued at USD 13.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2025 to 2032, indicating the increasing importance of high availability in the sector.
How does high availability enhance customer trust and satisfaction?
Implementing high availability software mitigates risks associated with interruptions and enhances overall reliability, which fosters customer trust and satisfaction in a competitive market.
What is a critical aspect of ensuring high availability?
Eliminating single points of failure is critical to ensure that if one component fails, others can seamlessly take over, preserving operational integrity.