Introduction
The financial services sector is navigating an increasingly complex landscape, where managing supplier relationships has become more critical than ever. In this context, the SIG framework emerges as an essential tool, providing organizations with a systematic approach to assess and mitigate risks associated with third-party providers. As regulatory pressures intensify and cyber threats evolve, institutions must consider how to effectively leverage SIG to enhance their supplier oversight and ensure compliance. A closer examination of the multifaceted role of SIG reveals not only its historical significance but also its transformative impact on vendor management in 2025 and beyond.
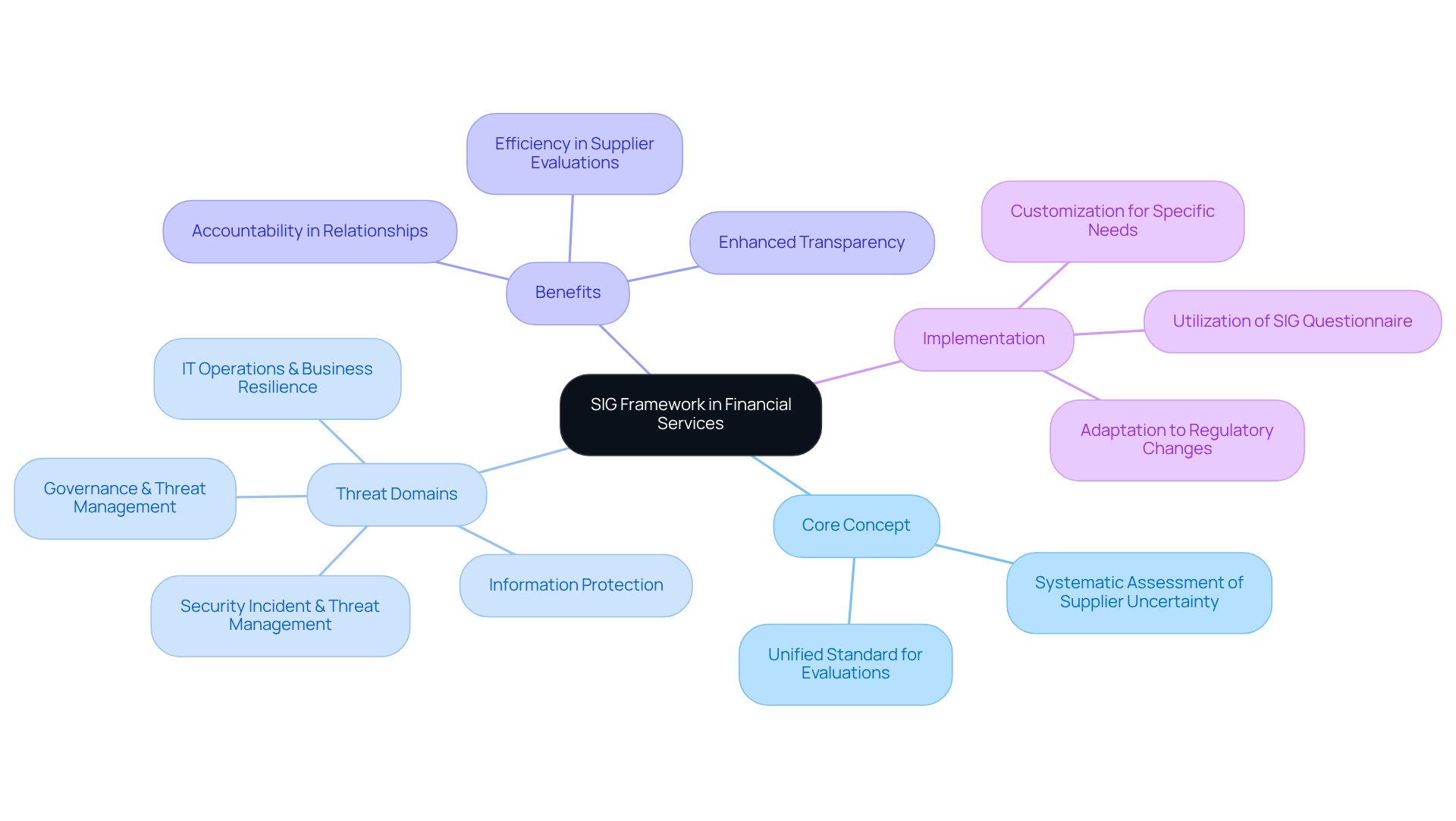
Define SIG: The Core Concept in Financial Services
The SIG framework serves as a vital tool in the financial services sector, designed to systematically assess and manage supplier uncertainty. It features a comprehensive set of questions aimed at evaluating the security, privacy, and compliance practices of external providers. By utilizing the SIG questionnaire, organizations can establish a unified standard that streamlines supplier evaluations, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements while effectively mitigating risks associated with outsourcing critical functions.
In 2026, the importance of SIG in supplier risk management is underscored by the increasing complexity of third-party relationships and the evolving regulatory landscape. Financial institutions face mounting pressure to enhance their oversight of suppliers, particularly in response to emerging threats such as AI-driven attacks and intensified regulatory scrutiny. The SIG framework not only boosts efficiency but also promotes transparency and accountability in supplier relationships, which are essential in the highly regulated financial sector.
Organizations that implement SIG for their supplier evaluations have reported significant benefits. The framework encompasses 21 critical threat domains that guide Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) programs, addressing areas such as:
- Governance & Threat Management
- Information Protection
- IT Operations & Business Resilience
- Security Incident & Threat Management
This thorough approach allows companies to tailor their evaluations to specific threat profiles, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of their supplier landscape.
Importantly, the SIG Core 2025 includes 627 questions, while the SIG Lite 2025 comprises 128 questions, reflecting the extensive nature of SIG’s framework. Industry leaders recognize the value of SIG in enhancing vendor management. As Katie Dorkings, Director of Sales, remarked, “The SIG Questionnaire is the number one tool that everybody in Risk Management uses. No questions asked!” This endorsement emphasizes the crucial role of SIG in establishing a robust third-party information security and business resilience assessment program. By adopting SIG, financial services organizations can safeguard their operations while simultaneously building trust with stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to effective management of uncertainties.
Contextualize SIG: Its Importance in Financial Services
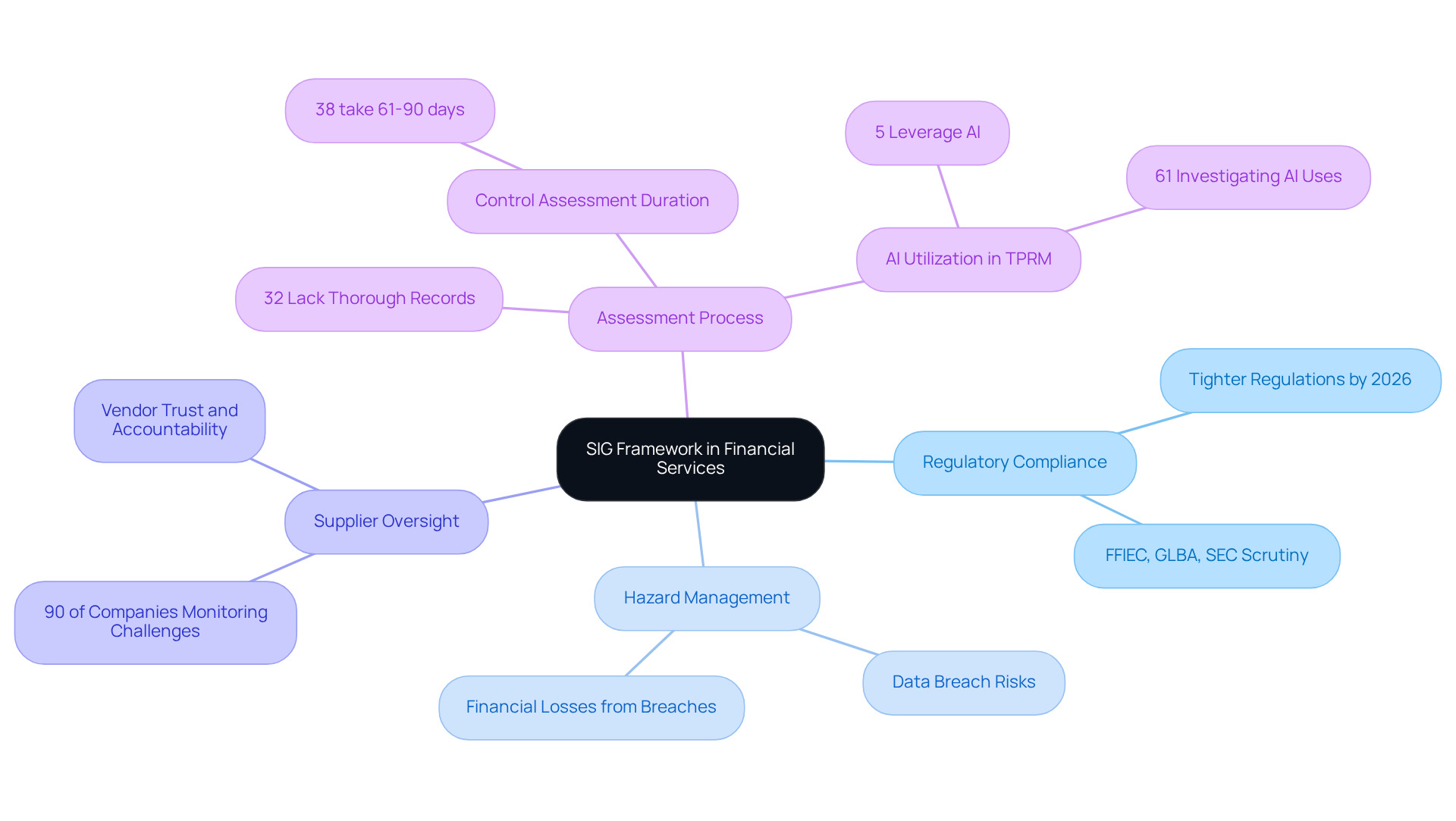
In the financial services sector, regulatory compliance and hazard management are paramount. The SIG framework serves as a crucial tool in this context. As financial institutions increasingly depend on external providers for services such as IT solutions and data management, a systematic assessment of service provider challenges becomes essential. The SIG framework enables these organizations to rigorously evaluate the security and compliance standards of their suppliers.
By conducting SIG assessments, institutions can uncover potential vulnerabilities within their supply chains. This process is vital for protecting sensitive financial data and preserving trust with clients and regulators. A proactive approach to supplier threat management is essential, especially in an environment where data breaches and compliance failures can result in significant financial losses and reputational damage.
With 90% of companies monitoring challenges from sourcing and selection phases, the need for strong supplier oversight is evident. This necessity is amplified as regulatory expectations are set to tighten in 2026, transforming supplier oversight into a regulatory requirement rather than merely a best practice. Furthermore, only 32% of organizations maintain a thorough record of third parties sharing sensitive information, highlighting a considerable gap in supplier management practices.
Financial institutions that effectively implement SIG assessments not only enhance their compliance stance but also equip themselves to manage the complexities of supplier relationships more adeptly.
Trace the Origins of SIG: Historical Development and Evolution
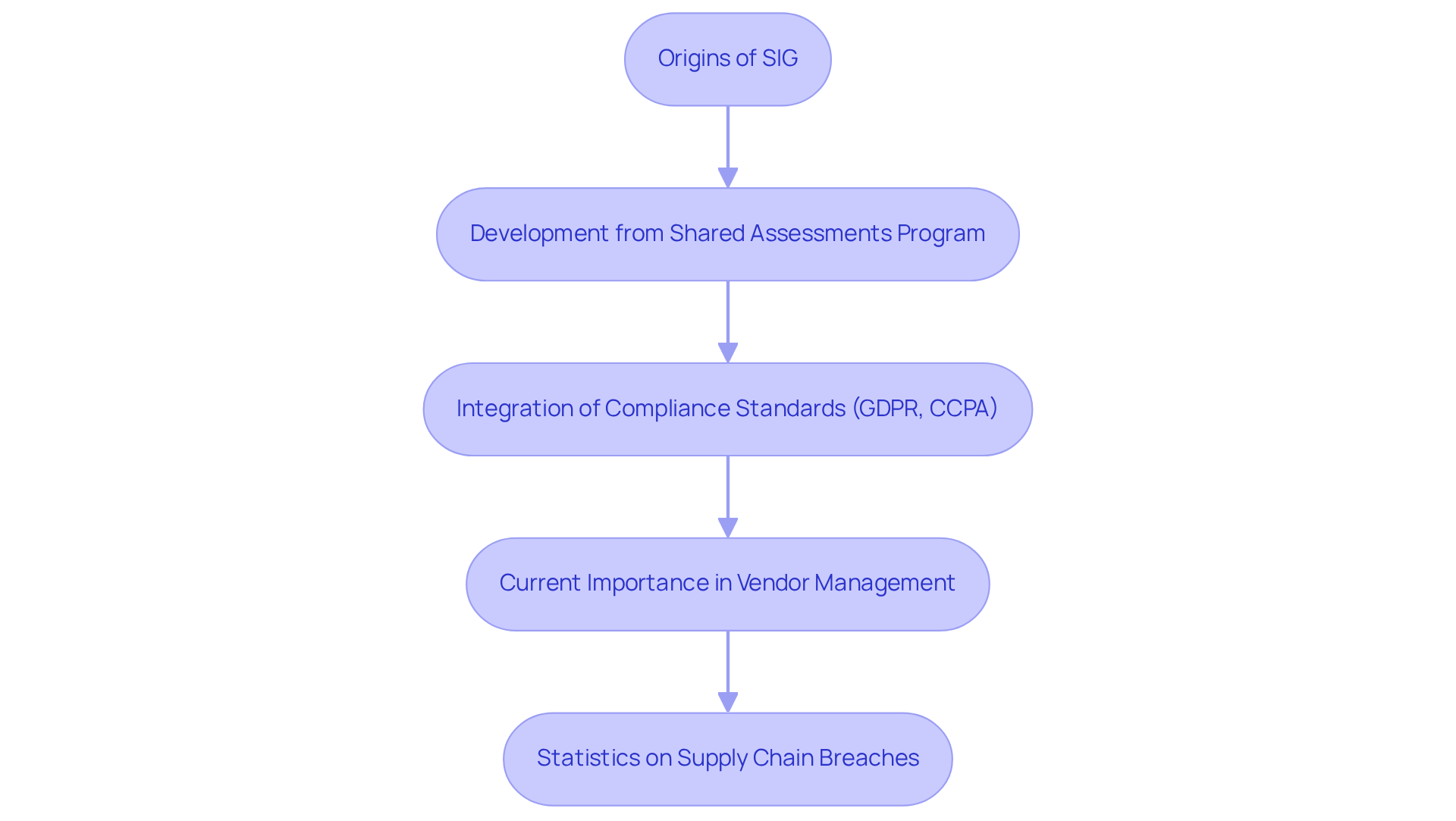
The SIG framework was developed to establish a consistent method for assessing suppliers in the financial services sector. Originating from the Shared Assessments Program, SIG was specifically designed to tackle the challenges associated with evaluating third-party providers amidst evolving regulatory requirements.
Over the years, SIG has undergone multiple iterations, integrating insights from industry stakeholders and aligning with emerging compliance standards such as GDPR and CCPA. This evolution underscores the increasing complexity of cyber threats and the critical need for financial institutions to uphold stringent management protocols.
Today, SIG stands as an essential tool for organizations seeking to navigate the intricate landscape of vendor management effectively. Notably, 97% of entities have encountered supply chain breaches, highlighting the urgent necessity for robust frameworks like SIG. As Emily Bonnie, Senior Content Marketing Manager at Secureframe, notes, “87% of entities say the primary objective of their TPRM program is to decrease exposure,” which further emphasizes the significance of effective management practices.
Moreover, the substantial growth of TPRM programs overseeing at least 250 suppliers-doubling from 2020 to 2023-illustrates the increasing intricacy of supplier management that SIG addresses. Despite these advancements, challenges persist; only 34% of organizations express confidence that a primary third party would inform them of a data breach, reinforcing the ongoing relevance of SIG in today’s data security environment.
Examine Key Characteristics of SIG: Functions and Components
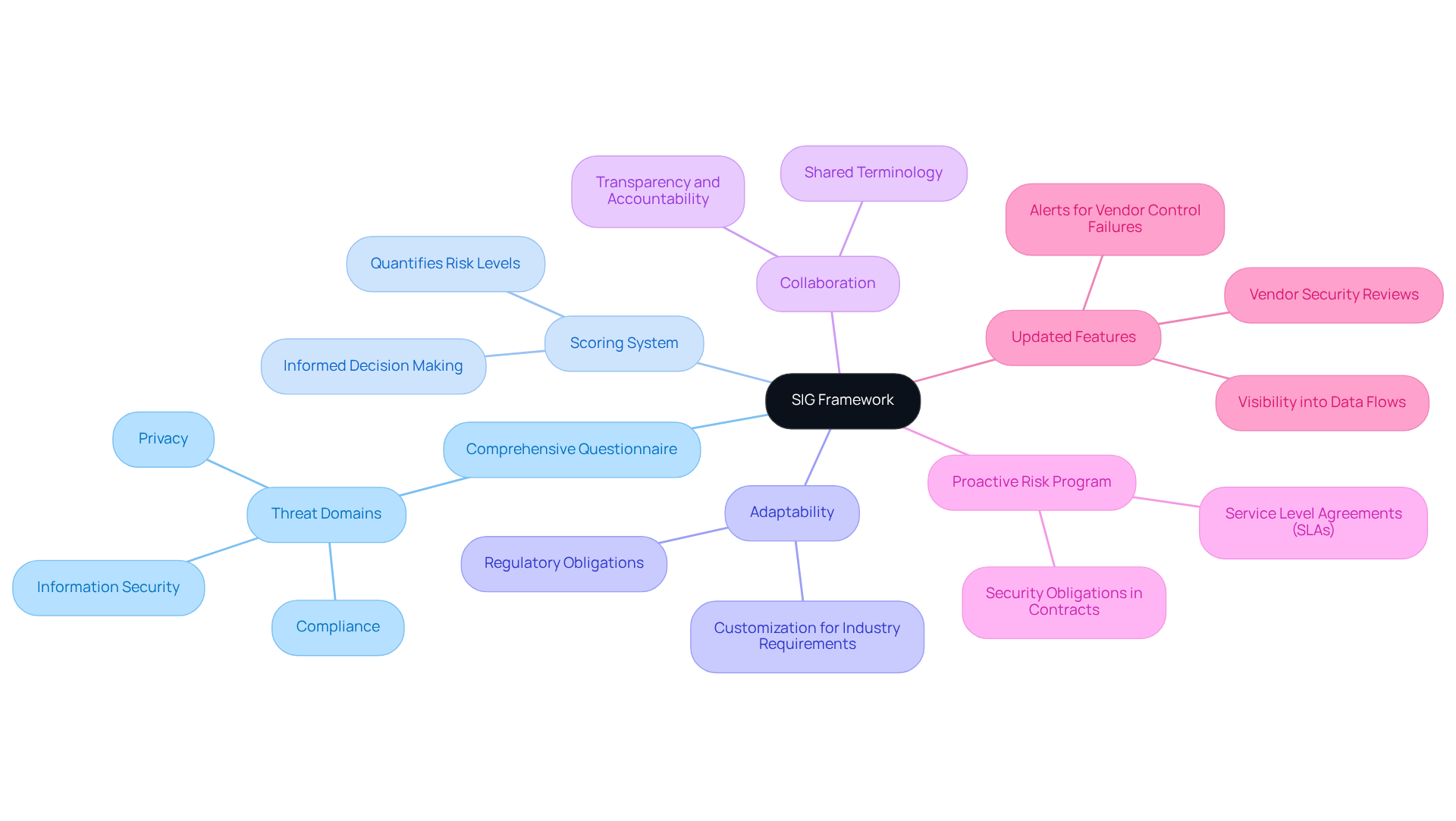
The efficiency in supplier evaluations is significantly enhanced by several critical elements defined in the SIG framework. At its core, it features a comprehensive questionnaire that addresses various threat domains, such as information security, privacy, and compliance. This systematic approach enables companies to assess vendors consistently and thoroughly.
A key component of SIG is its scoring system, which quantifies risk levels, allowing entities to make informed decisions based on clear metrics. Additionally, SIG is inherently adaptable, permitting organizations to customize assessments to meet specific industry requirements or regulatory obligations. This flexibility is vital for financial institutions striving to maintain compliance while effectively managing supplier relationships.
Moreover, the SIG fosters collaboration among stakeholders by establishing a shared terminology for addressing supplier challenges, thereby promoting a culture of transparency and accountability within organizations. As entities navigate the complexities of supplier management in 2026, the establishment of a proactive risk program becomes imperative. Furthermore, incorporating clear security obligations and service level agreements (SLAs) in supplier contracts is essential to ensure compliance and protect sensitive data.
The updated SIG, released on September 19, 2025, reflects these evolving needs, highlighting the significance of vendor security reviews and the establishment of processes for visibility into data flows and alerts for vendor control failures.
Conclusion
The SIG framework stands as a cornerstone in the financial services sector, offering a structured approach to managing supplier risk and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. By implementing SIG, organizations can adeptly navigate the complexities of third-party relationships, thereby safeguarding their operations and reinforcing trust with clients and regulators alike.
This article underscores the significance of SIG through its comprehensive assessment capabilities, which cover critical threat domains and feature a robust scoring system. The framework not only enables thorough evaluations of suppliers but also promotes transparency and collaboration among stakeholders. As financial institutions encounter mounting pressures from evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging cyber threats, the ability to tailor SIG assessments to specific needs becomes essential.
The necessity of adopting the SIG framework cannot be overstated. As the financial services industry continues to confront the challenges of supplier management, organizations must prioritize proactive risk management strategies. Embracing SIG not only bolsters compliance efforts but also positions institutions to cultivate resilient supplier relationships that endure over time. The future of effective vendor management relies on a commitment to frameworks like SIG, ensuring that financial institutions can confidently navigate an ever-changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the SIG framework in financial services?
The SIG framework is a tool designed to assess and manage supplier uncertainty in the financial services sector, focusing on evaluating the security, privacy, and compliance practices of external providers.
How does the SIG framework benefit organizations?
By utilizing the SIG questionnaire, organizations can establish a unified standard for supplier evaluations, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and effectively mitigating risks associated with outsourcing critical functions.
Why is the SIG framework increasingly important in 2026?
The importance of SIG is heightened due to the growing complexity of third-party relationships and evolving regulatory landscapes, as financial institutions face pressure to enhance oversight of suppliers amid emerging threats like AI-driven attacks.
What areas does the SIG framework cover in Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM)?
The SIG framework addresses 21 critical threat domains, including Governance & Threat Management, Information Protection, IT Operations & Business Resilience, and Security Incident & Threat Management.
How many questions are included in the SIG Core 2025 and SIG Lite 2025?
The SIG Core 2025 includes 627 questions, while the SIG Lite 2025 comprises 128 questions.
What do industry leaders think about the SIG framework?
Industry leaders recognize SIG as a valuable tool for enhancing vendor management, with endorsements highlighting it as the primary tool used in Risk Management.
How does adopting SIG help financial services organizations?
By adopting SIG, organizations can safeguard their operations and build trust with stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to effective management of uncertainties in supplier relationships.
