5 Best Practices for Choosing a Continuous Delivery Tool

Introduction
Selecting an appropriate continuous delivery tool is essential for organizations operating within regulated industries, where compliance and security are of utmost importance. As businesses aim to automate their software release processes, they encounter the challenge of ensuring that each deployment meets rigorous regulatory standards. This article explores best practices for choosing a continuous delivery tool that not only improves efficiency but also mitigates compliance risks.
How can organizations effectively navigate the complexities of regulatory requirements while reaping the benefits of continuous delivery?
Define Continuous Delivery in Regulated Industries
Continuous Delivery (CD) in regulated industries involves using a continuous delivery tool to automate the software release process while ensuring compliance with industry regulations. In sectors such as finance and healthcare, where data security and regulatory adherence are critical, CD must integrate stringent controls and validation processes.
Neutech offers extensive engineering services, leveraging expertise in React, Python, GoLang, Node.js, and AWS DevOps. This allows companies to utilize a continuous delivery tool for automating deployment while ensuring that each release complies with regulatory standards, including those set by the SEC for financial services and HIPAA for healthcare.
By defining CD within this framework, organizations can better understand the importance of incorporating regulatory checks into their distribution pipelines. This approach minimizes the risks associated with software releases. Neutech’s specialized software development capabilities position them as an ideal partner for navigating the complexities of using a continuous delivery tool in regulated environments.
Identify Regulatory Compliance Needs for Tool Selection
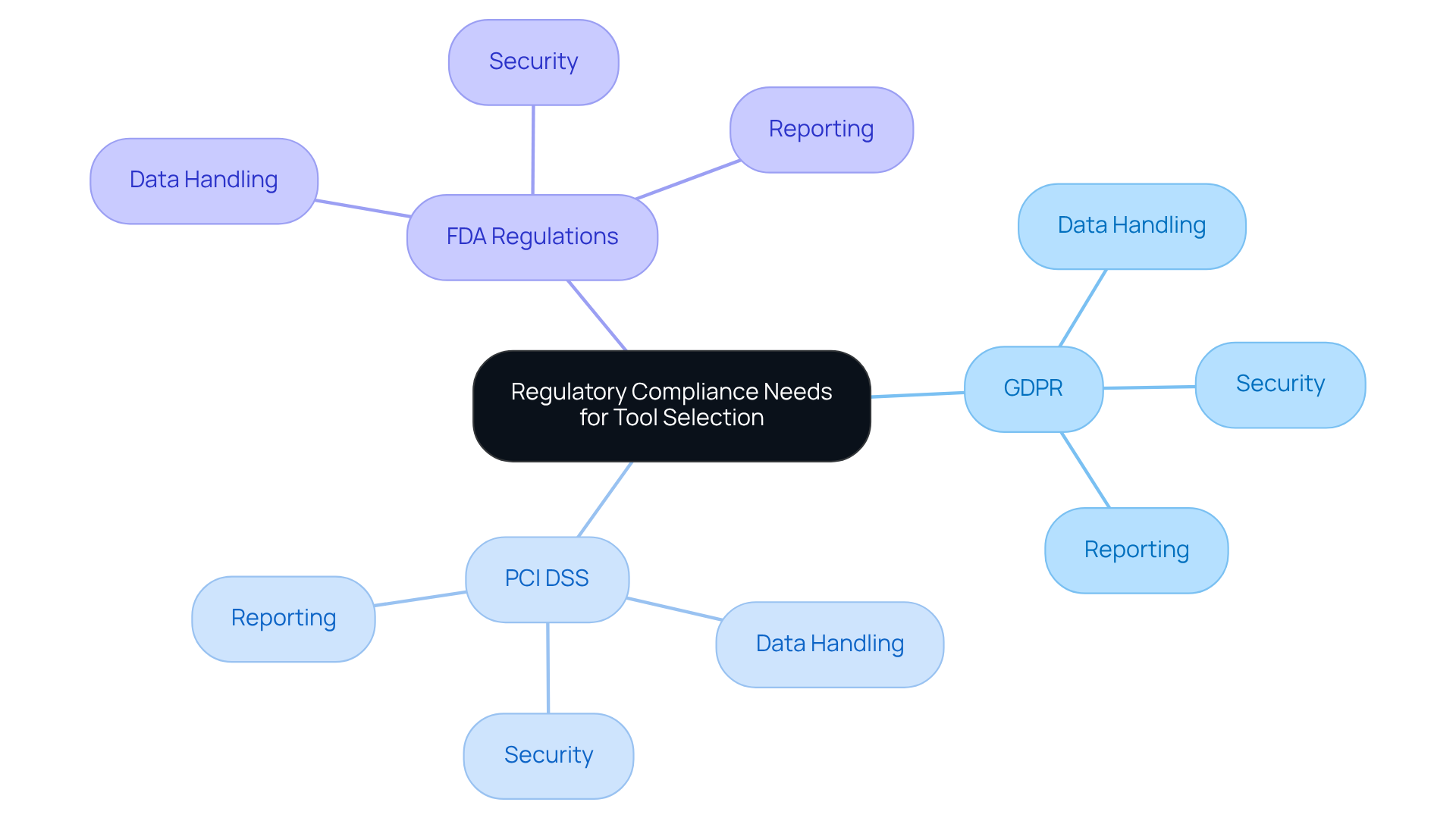
Choosing a continuous deployment resource necessitates a thorough evaluation of regulatory requirements. Organizations must pinpoint the specific regulations relevant to their industry, such as:
- GDPR for data protection
- PCI DSS for payment processing
- FDA regulations for healthcare software
Each regulation imposes unique requirements concerning data handling, security, and reporting. By carefully mapping these compliance needs, organizations can ensure that their selected tools not only facilitate efficient delivery but also incorporate essential compliance features, including:
- Audit trails
- Automated reporting
- Robust security controls
This proactive approach significantly mitigates the risk of non-compliance and enhances the integrity of the software distribution process.
Evaluate Key Features and Capabilities of Continuous Delivery Tools
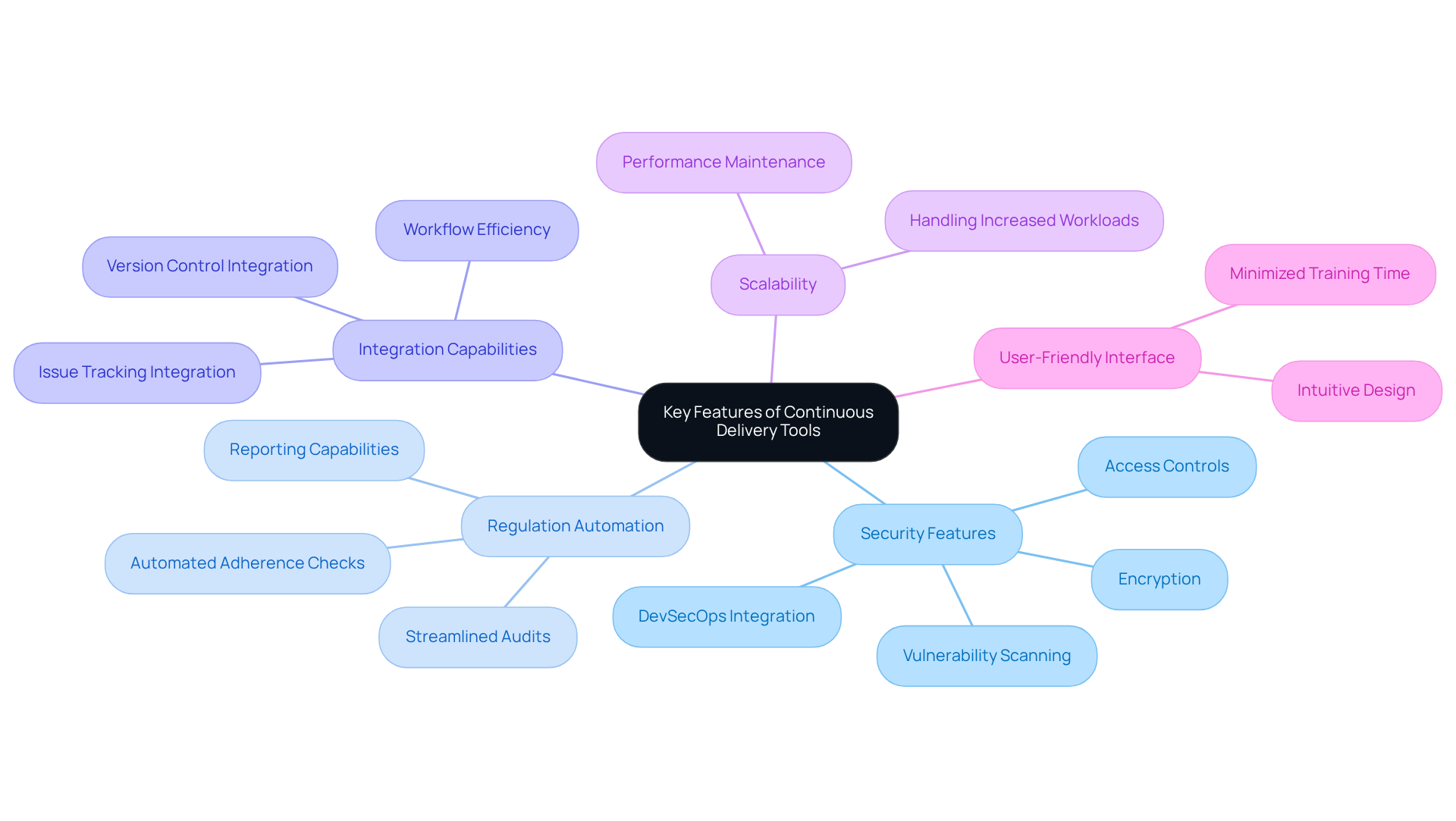
When evaluating a continuous delivery tool, organizations in regulated industries must prioritize several essential features and capabilities.
-
Security Features: Robust security measures are non-negotiable. Tools should include encryption, access controls, and comprehensive vulnerability scanning to safeguard sensitive data. Companies investing in DevSecOps have reported experiencing fewer breaches and reduced downtime, underscoring the importance of integrating security into the development lifecycle. As Jason Healey notes, “Innovative practices such as DevSecOps… allow technology teams to continuously commit and deploy code with security built into the entire software life cycle.”
-
Regulation Automation: Automated adherence checks and reporting capabilities are vital for streamlining audits and ensuring conformity to industry regulations. This feature not only simplifies the compliance process but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
-
Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing systems, such as version control and issue tracking applications, is crucial for maintaining workflow efficiency. A well-integrated resource can significantly reduce friction in development processes, allowing teams to focus on delivering value.
-
Scalability: As organizations expand, their tools must scale accordingly to handle increased workloads without sacrificing performance. This adaptability is essential for maintaining service quality in dynamic environments.
-
User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive user interface can minimize training time and improve adoption rates among team members. Tools that prioritize usability empower teams to leverage their full potential quickly.
By concentrating on these essential characteristics, companies can select a continuous delivery tool that not only enhances their deployment processes but also ensures adherence to strict industry regulations. By 2026, CI/CD pipelines are expected to be highly automated and intelligent, with every code commit triggering a standard workflow, making these features even more essential.
Ensure Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
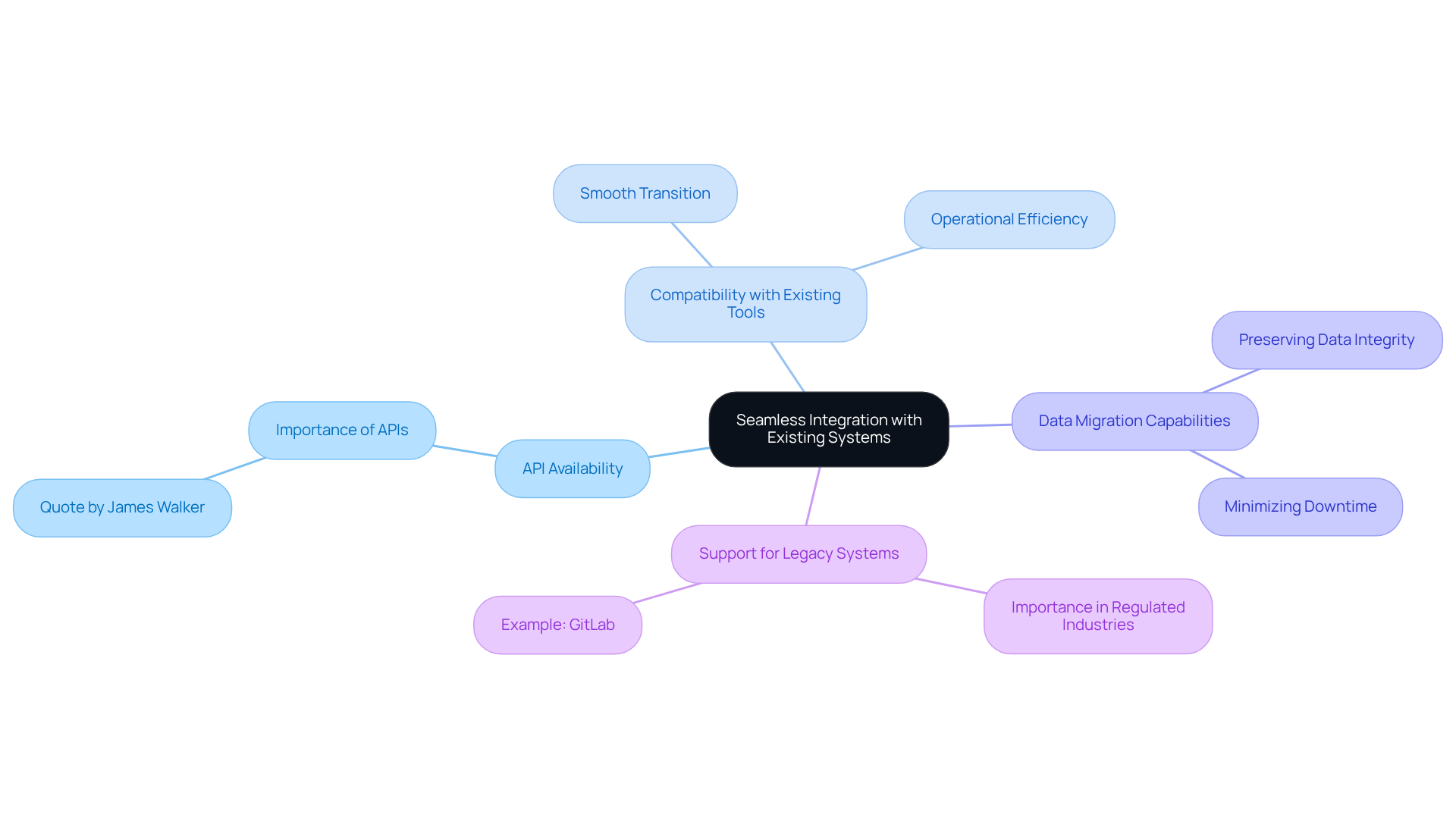
To ensure the successful execution of a continuous delivery tool, organizations must prioritize seamless integration with their existing systems. This involves assessing the effectiveness of potential resources in integrating with current infrastructure, including version control systems, testing frameworks, and deployment environments.
-
API Availability: Tools should provide robust APIs that facilitate integration with other software and services. As James Walker notes, “CD solutions need to be capable of automating your entire deployment workflow,” underscoring the critical role of APIs in achieving this objective.
-
Compatibility with Existing Tools: It is essential to evaluate whether the CD tool can operate alongside existing tools without necessitating significant changes to workflows. This compatibility is vital for ensuring a smoother transition and enhancing operational efficiency.
-
Data Migration Capabilities: Organizations must ensure that the software can manage data migration seamlessly, preserving data integrity and minimizing downtime. Effective data migration is crucial for maintaining service continuity during transitions.
-
Support for Legacy Systems: In regulated industries, legacy systems often play a crucial role; therefore, the selected tool should support these systems to prevent disruptions. The incorporation of platforms such as GitLab has proven effective in managing legacy systems while improving deployment processes.
By focusing on integration, organizations can enhance their continuous delivery processes through the use of a continuous delivery tool while maintaining operational continuity. Furthermore, with 89% of executives anticipating that agentic AI will become the industry standard for software development within three years, the significance of API integration in CD tools cannot be overstated.
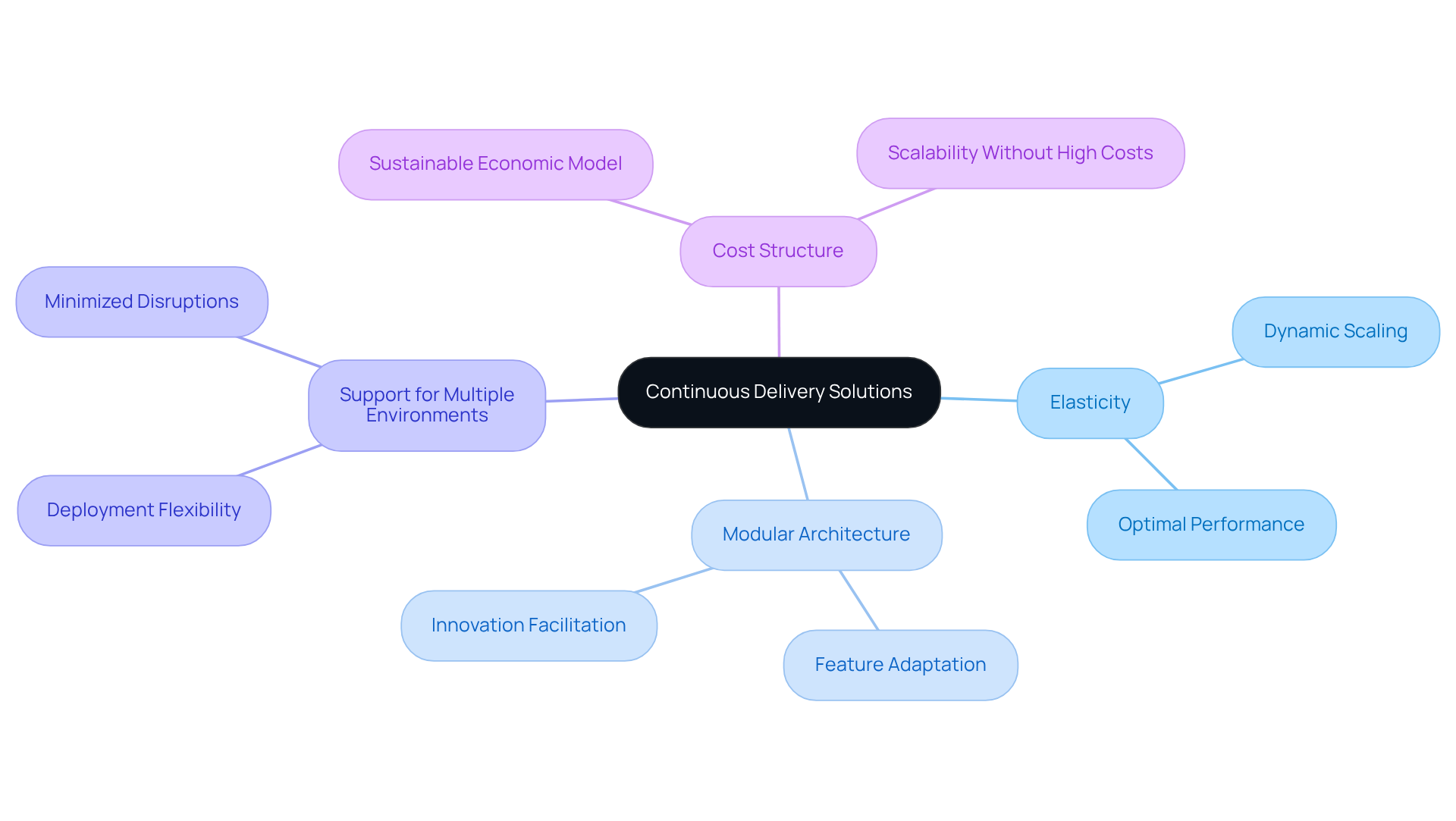
Choose Scalable and Flexible Continuous Delivery Solutions
When selecting a continuous delivery tool, companies must prioritize scalability and flexibility to effectively accommodate future growth and evolving requirements. Key factors to consider include:
-
Elasticity: The tool should dynamically scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak periods. This adaptability is essential for maintaining service quality in fluctuating environments. As James Walker notes, “Tools designed for cloud-native operation are generally more scalable than those that must be operated locally.”
-
Modular Architecture: A modular design enables organizations to add or remove features as necessary, facilitating smooth adaptation to new processes or technologies. This flexibility is increasingly important as businesses strive to innovate and respond to market changes. The continuous delivery tool market is projected to reach USD 12.25 billion by 2030, underscoring the growing demand for such adaptable solutions.
-
Support for Multiple Environments: The ability to deploy across various environments – development, testing, and production – is crucial for organizations operating within complex ecosystems. This capability ensures that software can be tested and released efficiently, minimizing disruptions. For instance, large enterprises accounted for 57.9% of the market share in 2023, driven by compliance and regulatory demands that necessitate robust deployment strategies.
-
Cost Structure: Evaluating whether the pricing model allows for scaling without incurring prohibitive costs is vital. A sustainable economic model ensures that the tool remains viable as usage increases, supporting long-term growth.
By focusing on these elements, organizations can ensure that their continuous delivery tool not only meets current demands but also supports their long-term strategic goals in a rapidly changing market landscape.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate continuous delivery tool is essential for organizations, especially in regulated industries where compliance and security are critical. By recognizing the specific challenges and requirements of these sectors, businesses can adopt continuous delivery practices that not only boost efficiency but also guarantee adherence to necessary regulations. This strategic approach to tool selection establishes a solid foundation for successful software deployment while mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
The article outlines key best practices, emphasizing the importance of:
- Defining regulatory compliance needs
- Assessing essential features of delivery tools
- Ensuring seamless integration with existing systems
- Choosing scalable and flexible solutions
Each of these practices is crucial in developing a robust continuous delivery framework that aligns with both operational objectives and regulatory mandates. By prioritizing security features, automating compliance checks, and enhancing integration capabilities, organizations can significantly refine their deployment processes.
In conclusion, the importance of selecting the right continuous delivery tool cannot be overstated. As the software development landscape continues to evolve, organizations must remain diligent in their selection processes to ensure they are equipped with tools that not only address current demands but also adapt to future challenges. By embracing these best practices, businesses will be empowered to navigate the complexities of continuous delivery in regulated environments, fostering innovation while upholding the highest standards of compliance and security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Continuous Delivery (CD) in regulated industries?
Continuous Delivery (CD) in regulated industries refers to the use of a continuous delivery tool to automate the software release process while ensuring compliance with industry regulations, particularly in sectors like finance and healthcare where data security and regulatory adherence are critical.
How does Neutech support Continuous Delivery in regulated industries?
Neutech provides extensive engineering services and expertise in technologies such as React, Python, GoLang, Node.js, and AWS DevOps, enabling companies to automate deployment through a continuous delivery tool while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards like SEC for financial services and HIPAA for healthcare.
Why is it important to integrate regulatory checks into the Continuous Delivery process?
Integrating regulatory checks into the Continuous Delivery process helps organizations minimize risks associated with software releases and ensures that each release complies with necessary regulatory standards.
What are the key regulatory compliance needs to consider when selecting a Continuous Delivery tool?
Key regulatory compliance needs include identifying specific regulations relevant to the industry, such as GDPR for data protection, PCI DSS for payment processing, and FDA regulations for healthcare software.
What features should organizations look for in Continuous Delivery tools to ensure compliance?
Organizations should look for features such as audit trails, automated reporting, and robust security controls in Continuous Delivery tools to facilitate efficient delivery while meeting compliance requirements.
How does a proactive approach to compliance impact software distribution?
A proactive approach to compliance significantly mitigates the risk of non-compliance and enhances the integrity of the software distribution process.