Introduction
Understanding the concept of a tenant in software is essential in the context of today’s multi-tenant architecture. In this framework, multiple users share a single application instance while maintaining distinct data and settings. This approach not only enhances resource efficiency but also upholds security and compliance standards, particularly in sensitive sectors such as finance and healthcare.
As organizations increasingly adopt these shared systems, they encounter the challenge of balancing performance with privacy. The question arises: how can businesses leverage the advantages of multi-tenancy while safeguarding their unique data requirements?
Define Tenant in Software: Core Concept and Meaning
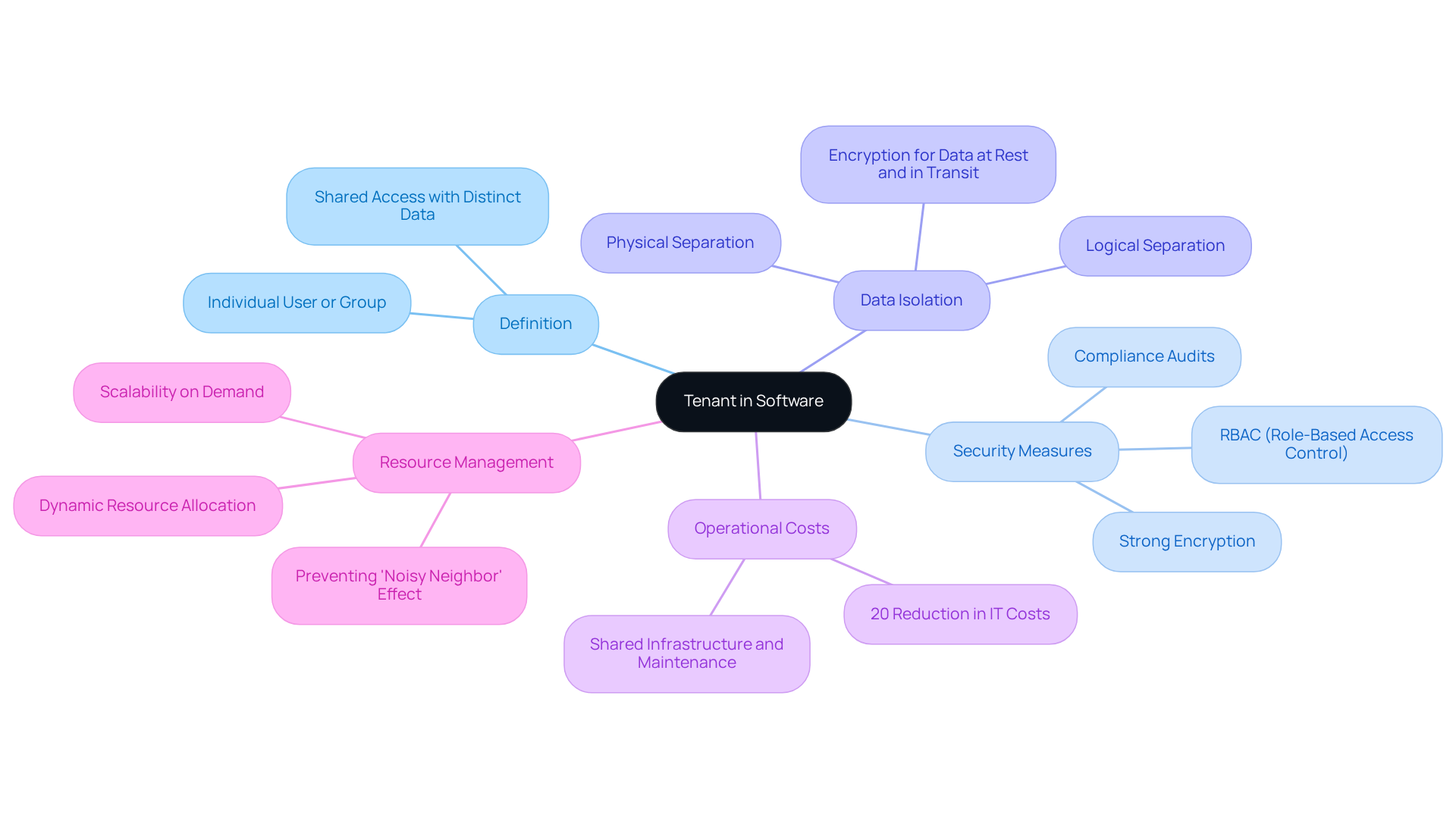
In application architecture, what is a tenant in software refers to an individual user or a group of users who share access to an application while maintaining distinct data and configurations. This concept illustrates what is a tenant in software, as it is particularly prevalent in shared environments where multiple users operate on a single instance of the software. This setup facilitates efficient resource sharing while ensuring robust data isolation.
To understand what is a tenant in software, it is crucial that each tenant upholds its own policies, access guidelines, and audit configurations, which are essential for ensuring security and compliance, especially in regulated sectors such as finance and healthcare. For instance, banks utilize shared systems to securely manage account information and transactions, while healthcare providers evaluate patient outcomes across departments without breaching HIPAA regulations.
Data isolation is vital in systems with multiple users, as it protects sensitive information and ensures that one user’s activities do not adversely affect another’s. Statistics reveal that businesses can significantly lower IT operational costs by sharing infrastructure and maintenance expenses, with multi-tenancy resulting in a 20% reduction in these costs. Abdullah Farag emphasizes that ‘strong encryption, RBAC, and compliance audits assist in ensuring privacy across all user environments,’ highlighting the necessity for stringent security measures in shared settings.
Moreover, it is essential to recognize that resource-intensive activities by one user can impact the performance of others, necessitating intelligent systems that dynamically allocate resources based on demand. Understanding users and their functions is crucial, as it supports the operational dynamics of shared systems, which relate to what is a tenant in software, and are increasingly prevalent in cloud computing and SaaS applications.
Contextualize Tenancy: Role in Multi-Tenant Architecture
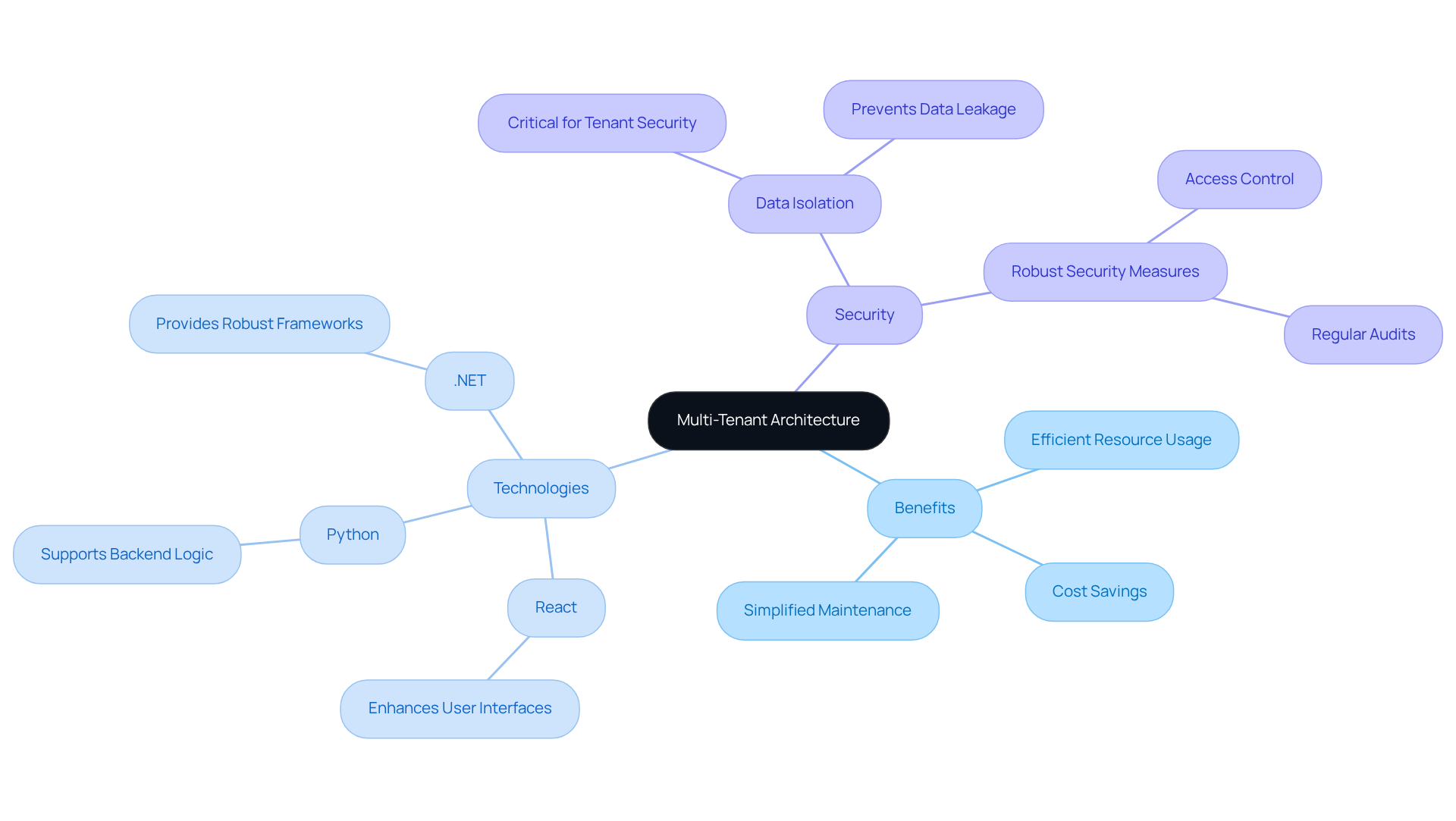
In multi-user architecture, a single instance of a software application serves multiple users, each with its own data and configurations. This design promotes efficient resource usage, as the underlying infrastructure is shared among users, which lowers costs and simplifies maintenance. Multi-tenancy, which illustrates what is a tenant in software, is particularly advantageous for SaaS providers, enabling them to deliver services to numerous customers without the need for separate instances for each.
Neutech’s extensive engineering services, including React, Python, and .NET development, are tailored to support such architectures, ensuring compliance with the strict standards of regulated sectors like finance and healthcare. Each technology contributes uniquely:
- React enhances user interfaces
- Python supports backend logic
- .NET provides robust frameworks for enterprise applications
However, this architecture necessitates robust security measures to ensure that data remains isolated and secure across different tenants, which raises the question of what is a tenant in software. It is widely adopted in industries where adherence to regulations is paramount, and the ability to scale efficiently is critical. By leveraging Neutech’s specialized application development capabilities, hedge fund managers can implement effective multi-tenant solutions, helping to clarify what is a tenant in software, that enhance operational efficiency and regulatory compliance, ultimately leading to significant cost savings.
Trace the Origin: Evolution of the Tenant Concept in Software
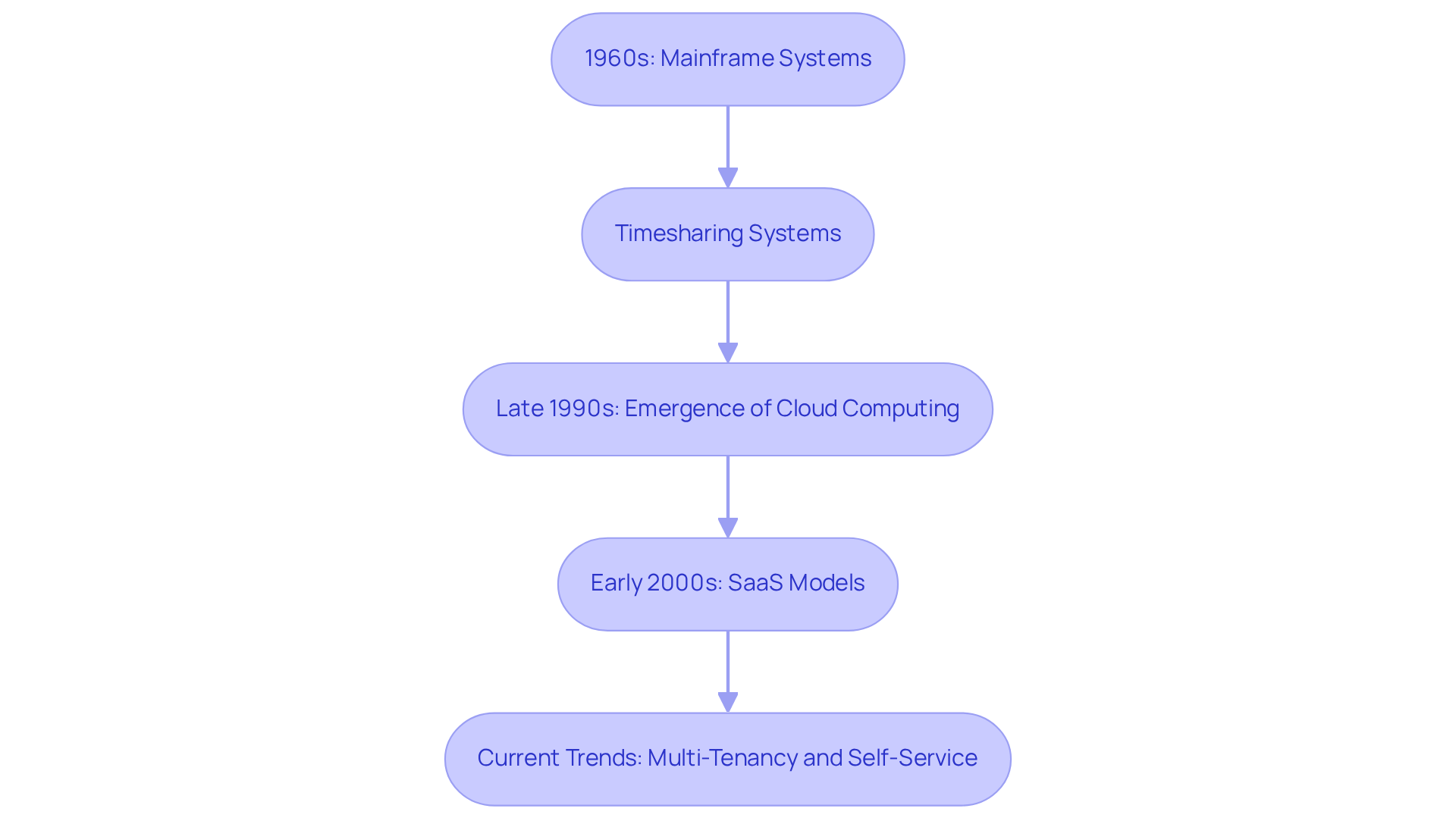
The concept of a user in technology has its roots in the early days of computing, particularly with the advent of mainframe systems in the 1960s. During this period, organizations employed timesharing systems that enabled multiple users to access a single mainframe computer, effectively sharing resources while maintaining distinct user environments. As technology progressed, the emergence of cloud computing and Software as a Service (SaaS) models in the late 1990s and early 2000s helped clarify what is a tenant in software, introducing a more structured approach to multi-tenancy. This evolution has led to the development of sophisticated architectures that prioritize scalability, security, and compliance, establishing the notion of occupants as a core element of modern design.
Currently, what is a tenant in software is essential in multi-tenancy, which plays a crucial role in delivering efficient B2B SaaS applications, allowing a single instance of an application to cater to multiple clients from a shared codebase and database. This architecture not only improves scalability but also optimizes resource utilization, enabling cloud providers to effectively address diverse customer needs. The ongoing evolution of multi-tenancy is propelled by advancements in container orchestration, edge computing, and artificial intelligence, ensuring that the concept of users remains pertinent in an increasingly intricate digital landscape.
Moreover, as cloud providers enhance their multitenancy strategies, the potential for confusion among consumers due to varying provider approaches underscores the necessity for clarity in this dynamic field. Additionally, the rising demand for self-service capabilities in SaaS applications signifies a shift towards empowering users to manage their own settings and configurations, further highlighting the operational aspects of multi-tenancy that are becoming progressively significant.
Identify Key Characteristics: Components of a Software Tenant
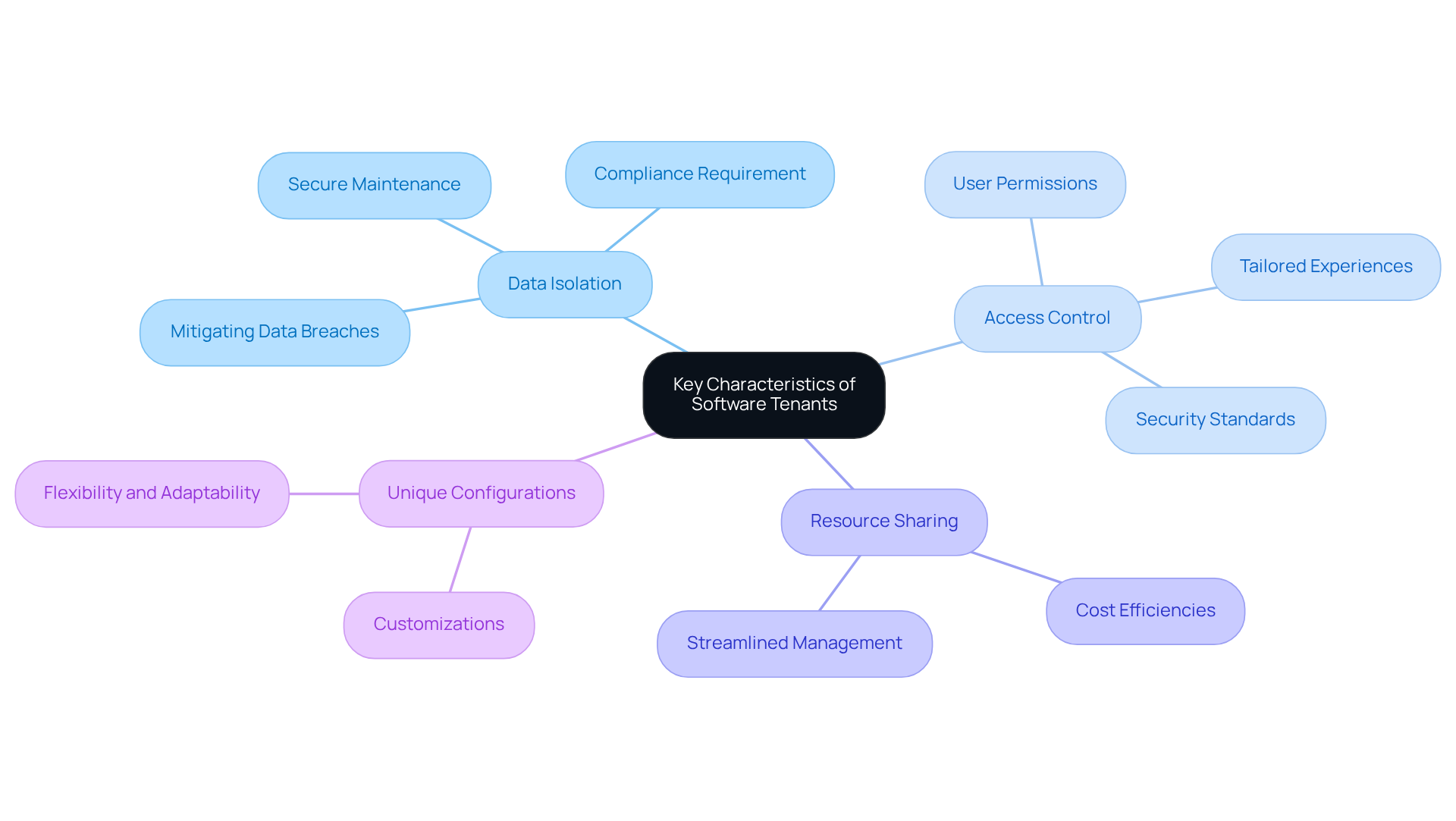
Key characteristics of software users encompass data isolation, access control, and resource sharing.
- Data isolation ensures that each client’s information is securely maintained separately from others, a critical requirement in regulated sectors where compliance is paramount.
- Access control mechanisms delineate the permissions and privileges assigned to each user within the application, facilitating tailored experiences while upholding security standards.
- Resource sharing allows users to leverage the same underlying infrastructure, which can result in cost efficiencies and streamlined management.
- Furthermore, what is a tenant in software may include unique configurations and customizations that meet their specific needs, thereby enhancing the flexibility and adaptability of multi-tenant systems.
Conclusion
In software architecture, the concept of a tenant is a fundamental building block, representing individual users or groups who share access to an application while maintaining distinct data and configurations. This multi-tenant approach enhances resource efficiency and ensures that each tenant’s data remains secure and compliant, particularly in sensitive industries such as finance and healthcare.
Key aspects of software tenancy include the critical importance of data isolation, access control, and resource sharing. The evolution of this concept from early mainframe systems to modern cloud-based solutions underscores the ongoing need for robust security measures and intelligent resource allocation. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as container orchestration and AI, have refined the multi-tenancy model, making it a vital component in delivering scalable and efficient software applications.
Understanding the role of tenants in software is essential for businesses aiming to leverage multi-tenant architectures effectively. As the demand for SaaS solutions continues to grow, embracing the principles of tenancy can lead to significant operational efficiencies and cost savings. Organizations are encouraged to explore and implement these strategies to enhance their software offerings, ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a tenant in software?
A tenant in software refers to an individual user or a group of users who share access to an application while maintaining distinct data and configurations, particularly in shared environments.
Why is the concept of a tenant important in shared environments?
The concept of a tenant is important in shared environments because it facilitates efficient resource sharing while ensuring robust data isolation, allowing multiple users to operate on a single software instance without compromising their data security.
How do tenants uphold their own policies and security measures?
Each tenant upholds its own policies, access guidelines, and audit configurations, which are essential for ensuring security and compliance, especially in regulated sectors like finance and healthcare.
Can you provide examples of industries that utilize multi-tenancy?
Banks and healthcare providers are examples of industries that utilize multi-tenancy, as they manage sensitive information securely while complying with regulations such as HIPAA.
What is the significance of data isolation in multi-tenant systems?
Data isolation is vital in multi-tenant systems as it protects sensitive information and ensures that one user’s activities do not adversely affect another’s.
How does multi-tenancy impact IT operational costs?
Multi-tenancy can significantly lower IT operational costs by allowing businesses to share infrastructure and maintenance expenses, with statistics indicating a potential 20% reduction in these costs.
What security measures are necessary in shared environments?
Strong encryption, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and compliance audits are necessary security measures in shared environments to ensure privacy across all user environments.
How can resource-intensive activities by one user affect others in a multi-tenant system?
Resource-intensive activities by one user can impact the performance of others, necessitating intelligent systems that dynamically allocate resources based on demand to maintain optimal performance.
Why is understanding users and their functions crucial in shared systems?
Understanding users and their functions is crucial as it supports the operational dynamics of shared systems, which are increasingly prevalent in cloud computing and SaaS applications.
