Master How to Build a Data Warehouse for Financial Success

Introduction
Building a data warehouse has transitioned from being a luxury to an essential requirement for financial institutions aiming to improve decision-making and operational efficiency. Organizations are increasingly acknowledging the importance of centralized data storage, which enables them to integrate diverse information sources, perform historical analyses, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
However, the path to establishing an effective data warehouse is not without its challenges. Issues related to data quality and integration complexities often arise, posing significant obstacles. Financial entities must navigate these hurdles strategically to harness the full potential of a well-designed data repository.
Define the Data Warehouse and Its Importance in Financial Services
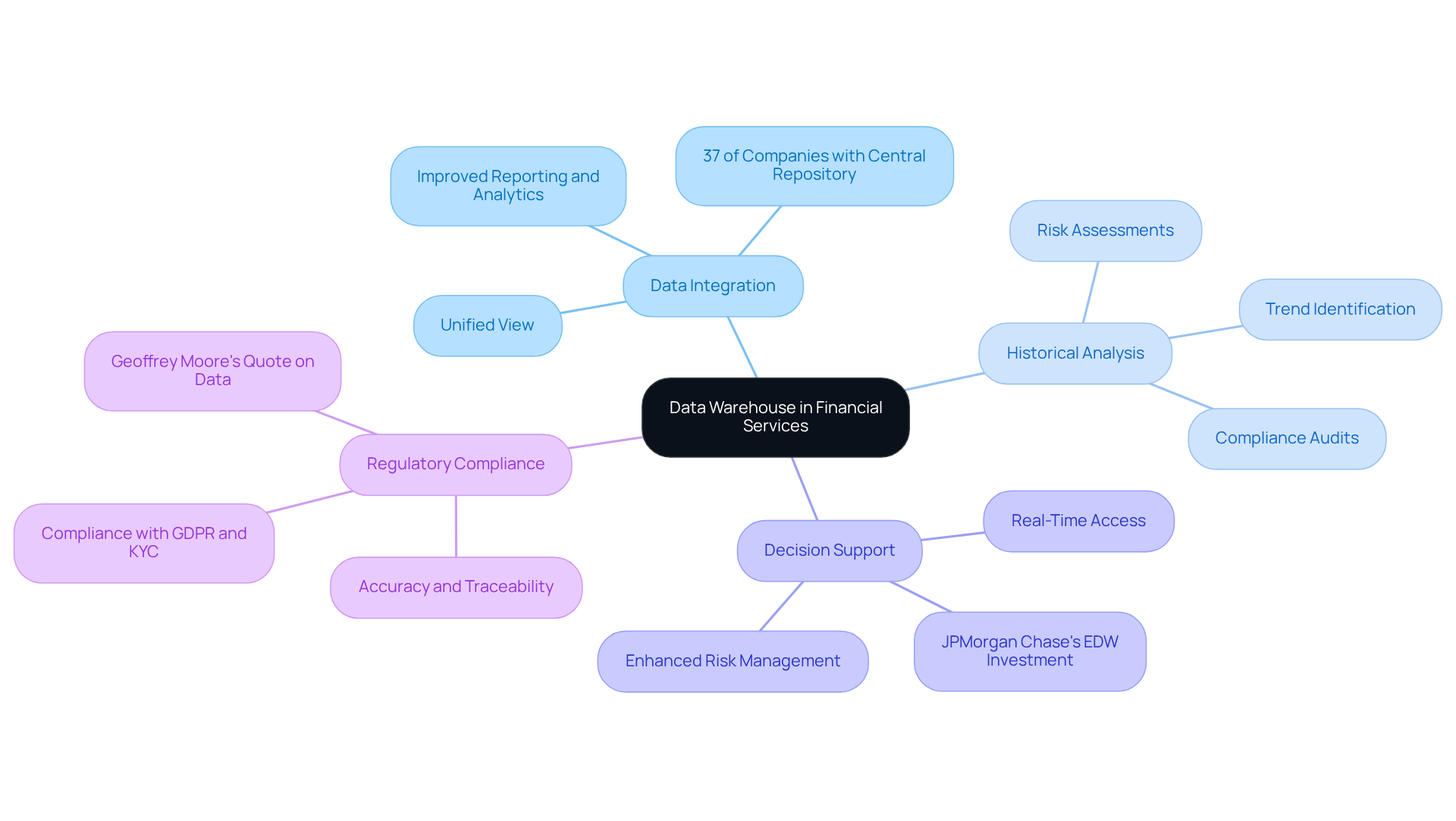
A centralized storage facility serves as a hub that aggregates information from various sources, enabling organizations to conduct complex inquiries and assessments essential for financial services. Its importance is highlighted by several key benefits:
-
Data Integration: By consolidating data from diverse sources, data warehouses offer a unified view that improves reporting and analytics. This integration is crucial, as 37% of companies have established a central information repository, indicating a growing recognition of its importance in financial decision-making. The increasing adoption of information storage underscores the necessity for financial institutions to leverage insights effectively.
-
Historical Analysis: Financial institutions utilize information repositories to analyze past data, identify trends, and conduct risk assessments. This capability is vital for compliance audits, ensuring organizations can accurately track information and adhere to regulatory standards.
-
Decision Support: With real-time access to information, repositories empower hedge funds and banks to make informed decisions swiftly. For instance, JPMorgan Chase’s investment in an Enterprise Information Warehouse (EDW) has significantly enhanced its analytical capabilities, improving risk management and customer insights, which are critical for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Information repositories assist in meeting stringent regulatory requirements by ensuring accuracy and traceability. This is particularly significant in the financial sector, where compliance with regulations such as GDPR and KYC is essential. As Geoffrey Moore aptly states, “information is absolutely crucial to making smart business decisions,” highlighting the role of information repositories in facilitating informed decision-making.
Understanding how to build a data warehouse is essential for anyone aiming to develop a repository tailored for the financial industry, as it directly contributes to operational efficiency and strategic decision-making. However, it is also important to recognize the challenges faced in establishing information repositories, such as security concerns and the complexity of integrating legacy systems, which must be addressed to fully realize the benefits.
Explore Data Warehouse Design Approaches: Inmon, Kimball, and More
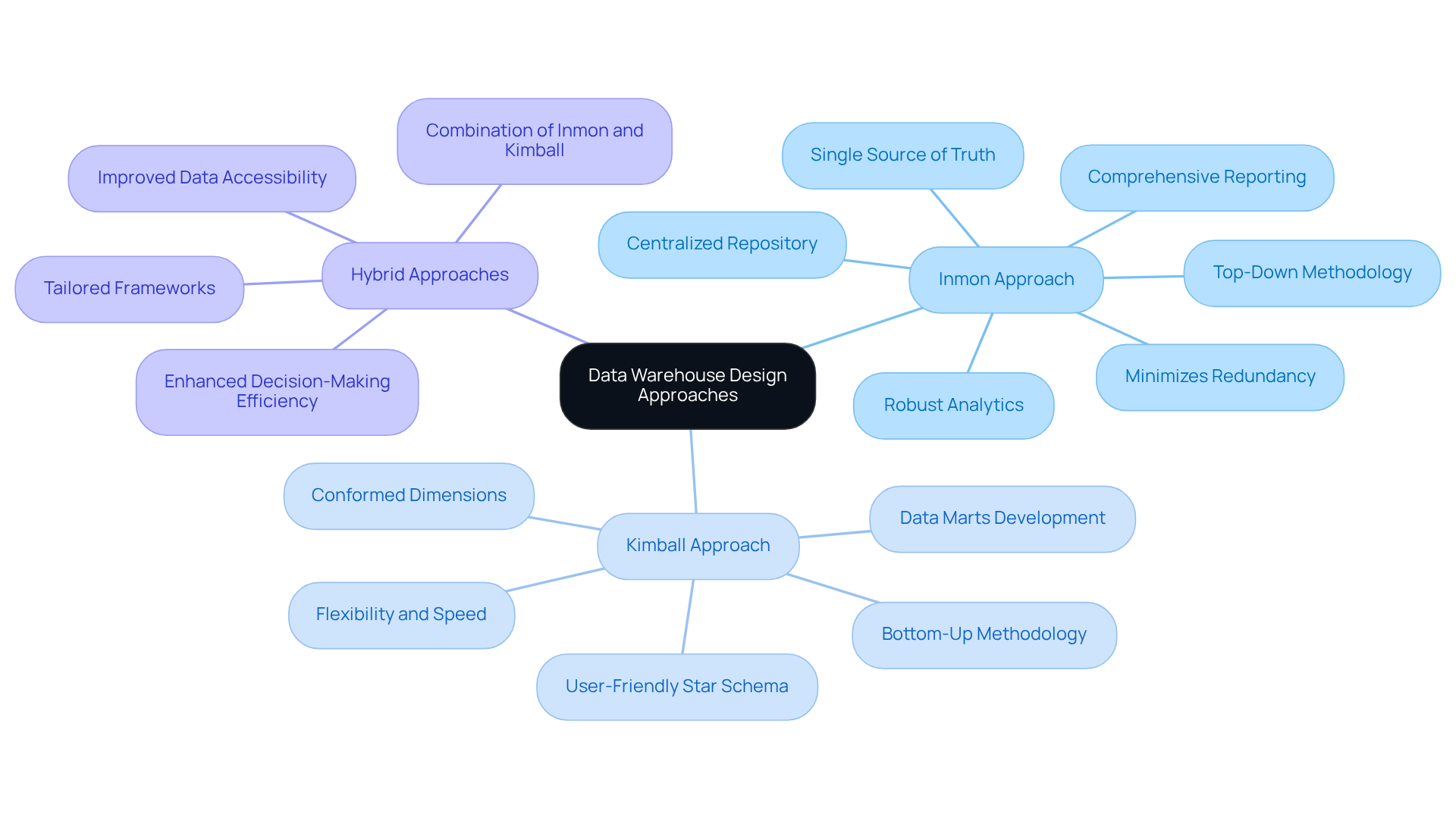
In the realm of information storage design, two primary methodologies emerge: the Inmon and Kimball approaches, each offering distinct advantages tailored to various organizational needs.
-
Inmon Approach: This top-down methodology focuses on establishing a centralized repository that acts as a single source of truth. By normalizing data, it minimizes redundancy and ensures consistency throughout the organization. This approach is particularly beneficial for businesses requiring a comprehensive view of their information landscape, facilitating robust reporting and analytics. Bill Inmon, recognized as the Father of Information Storage, asserts, “An Inmon repository can function as a single source of truth,” underscoring its importance in effective information management.
-
Kimball Approach: In contrast, the Kimball methodology adopts a bottom-up strategy, emphasizing the development of data marts that cater to specific business functions. These marts are subsequently integrated into a broader information storage framework. This approach is favored for its flexibility and rapid implementation, making it suitable for organizations with rapidly changing reporting needs. Ralph Kimball notes that “the Kimball process starts with the identification of a business process that some subset of the warehouse must serve,” highlighting its practical relevance.
-
Hybrid Approaches: An increasing number of organizations are embracing hybrid models that combine elements from both methodologies. This strategy allows them to leverage the strengths of each approach, tailoring their framework to address unique operational demands. For instance, a financial institution might establish a centralized information repository using the Inmon approach while simultaneously developing agile data marts through the Kimball methodology to swiftly adapt to market fluctuations. Recent statistics indicate that organizations employing hybrid methods have experienced improved data accessibility and decision-making efficiency, which are critical in today’s fast-paced economic environment.
The choice of design methodology significantly influences data accessibility, performance, and scalability. As organizations navigate the complexities of information management, understanding these approaches is essential for developing effective information repositories that drive economic success. Tools such as the Astera Data Repository Builder can further enhance this process, enabling organizations to create and deploy information stores efficiently.
Implement the Step-by-Step Process for Building Your Data Warehouse
Building a data warehouse entails several critical steps specifically tailored to the financial services sector:
-
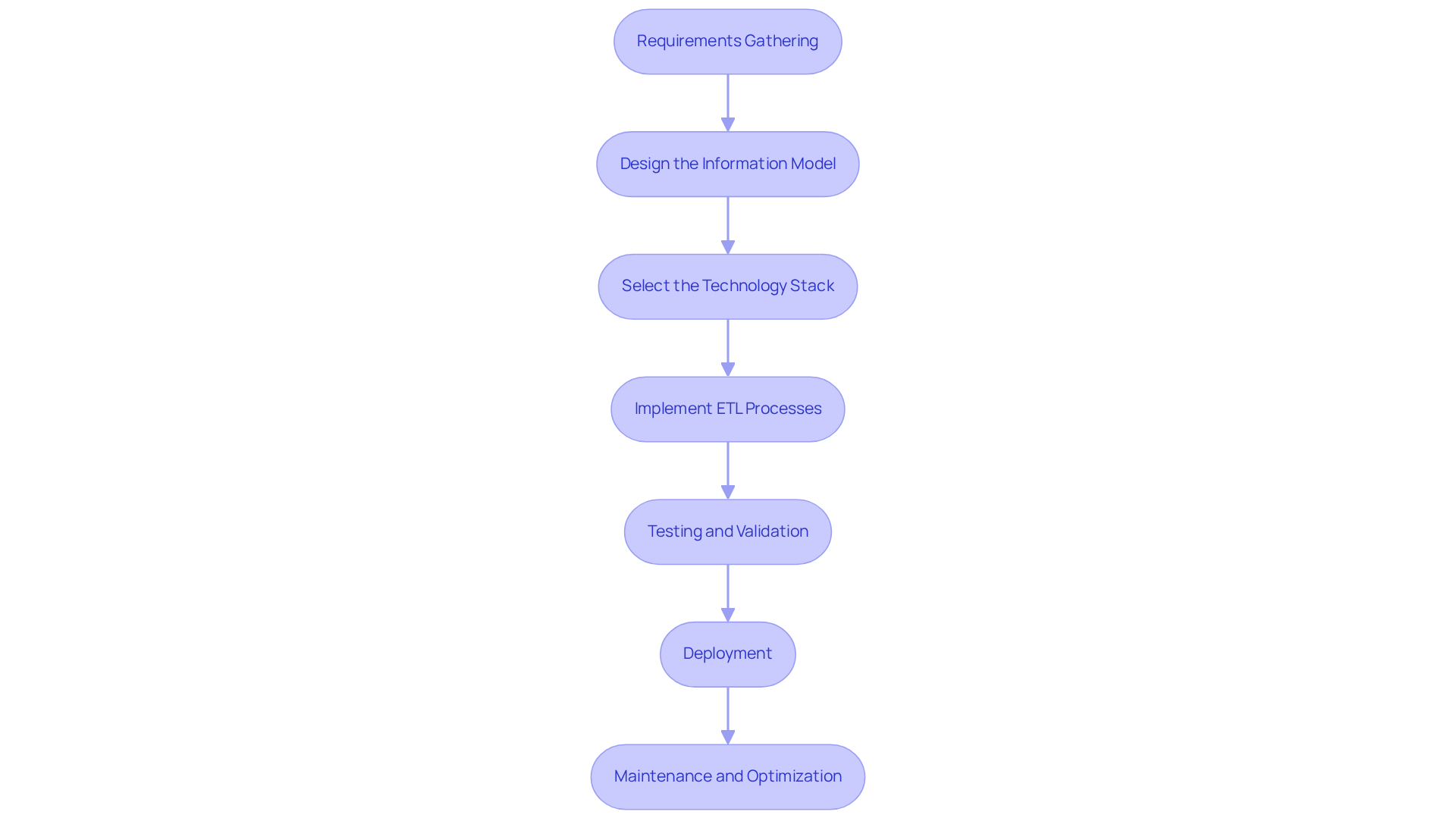
Requirements Gathering: Begin by identifying business needs and information sources. Engage stakeholders to ascertain the specific information necessary for informed decision-making, ensuring alignment with regulatory compliance and operational objectives. This step is vital, as financial institutions face significant challenges in becoming information-driven, despite substantial investments in technology.
-
Design the Information Model: Create both logical and physical information models. This involves defining the schema, types of information, and relationships between entities, which are crucial for maintaining integrity and enabling analytics.
-
Select the Technology Stack: Choose the appropriate tools and technologies for information storage, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and analytics. Consider cloud solutions for their scalability and flexibility, essential for accommodating varying information volumes and ensuring high availability. The cost of establishing an information storage facility can start at $70,000, making it imperative to select the right technology from the outset.
-
Implement ETL Processes: Develop robust ETL pipelines to extract information from multiple source systems, transform it into the required format, and load it into the information repository. This step is crucial for automating information management and ensuring timely access to accurate details. Real-world examples of ETL processes in financial repositories can illustrate the practical application of these steps.
-
Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing to verify information accuracy and integrity. Ensure that the storage facility meets the initial requirements and adheres to industry standards, such as those established by IFRS and Basel III, which is essential for regulatory compliance in financial institutions.
-
Deployment: Launch the information warehouse and make it accessible to users. Provide comprehensive training and documentation to facilitate effective utilization and foster a data-driven culture within the organization.
-
Maintenance and Optimization: Regularly monitor performance, update information models as needed, and optimize ETL processes for efficiency. This ongoing maintenance is essential for adapting to evolving business requirements and ensuring the information repository continues to deliver value.
By adhering to these steps, organizations can learn how to build a data warehouse to establish a storage system that enhances decision-making, improves operational efficiency, and supports compliance with regulatory requirements. The information storage market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 24.5% by 2028, underscoring the increasing importance of these systems in the economic sector.
Identify and Overcome Common Challenges in Data Warehouse Projects
Organizations in the financial sector must understand how to build data warehouse effectively to navigate several significant challenges and ensure success.
-
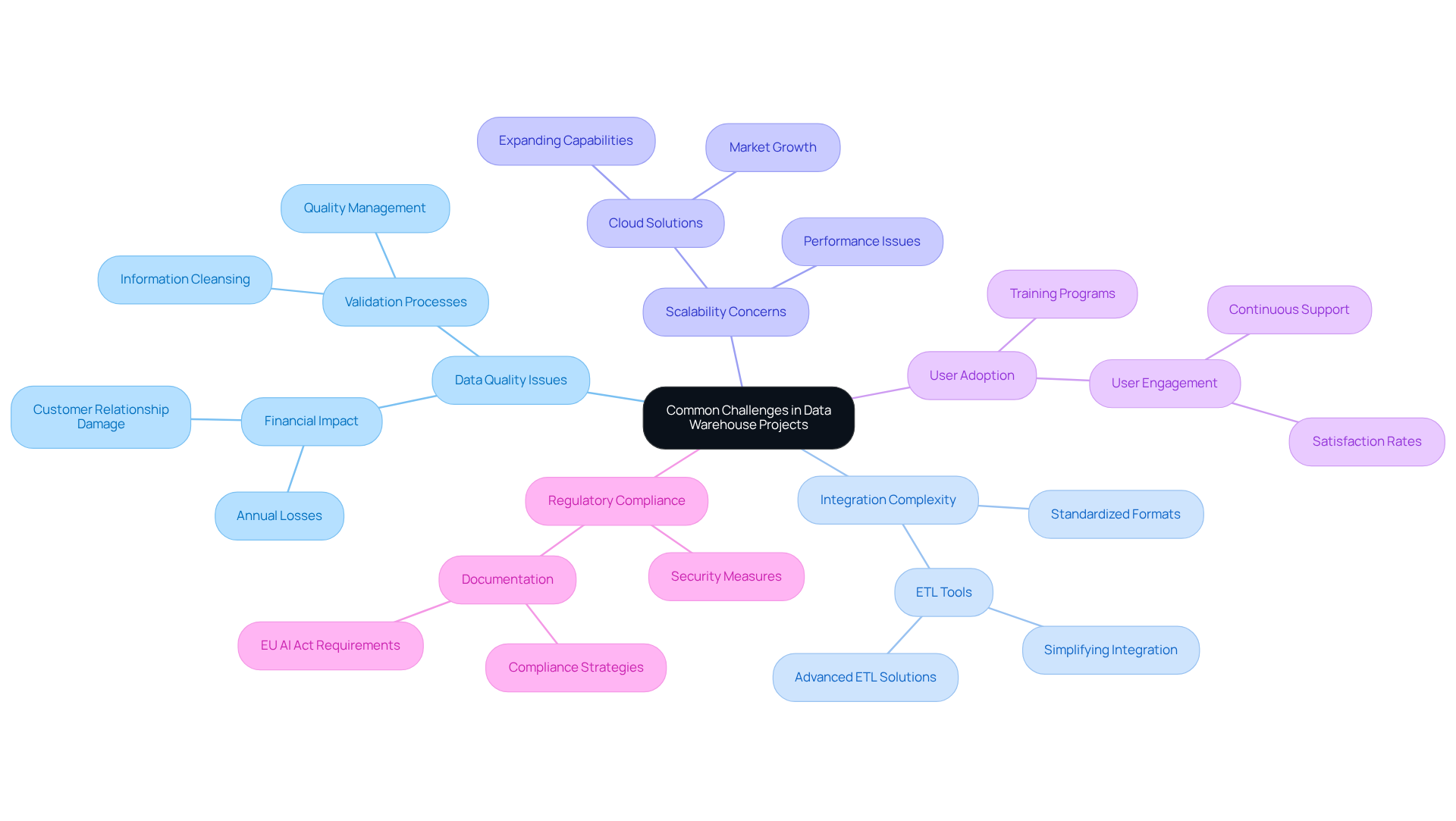
Data Quality Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can severely undermine the effectiveness of a data warehouse. Implementing robust information validation and cleansing processes is essential to maintain high-quality information. Subpar information quality can result in financial losses approximated at $15 million each year for organizations, highlighting the necessity for efficient information management.
-
Integration Complexity: The merging of information from various sources can be intricate and fraught with challenges. Employing standardized information formats and advanced ETL tools can simplify this process, decreasing integration challenges that 95% of IT leaders mention as obstacles to AI implementation. A well-organized integration strategy is essential for achieving a unified information environment.
-
Scalability Concerns: As information volumes continue to expand, performance can become a critical issue. Designing the architecture with scalability in mind is vital; leveraging cloud solutions allows organizations to expand their capabilities as needed. The global cloud storage market is projected to reach $10.42 billion by 2026, reflecting the increasing reliance on scalable cloud infrastructures, with a growth rate of 22.56% expected by that year.
-
User Adoption: Ensuring that end-users are comfortable with the new system is critical for success. Delivering thorough training and continuous assistance can promote user acceptance, aiding teams in utilizing the full potential of the information warehouse. Organizations that prioritize user engagement often see improved outcomes and higher satisfaction rates.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Financial institutions must adhere to stringent regulations regarding information handling and privacy. Implementing robust security measures and maintaining thorough documentation is essential to ensure compliance. With the EU AI Act enforcing tougher standards on information governance starting August 2, 2026, entities must be proactive in their compliance strategies.
By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can significantly enhance the likelihood of a successful data warehouse implementation, which is crucial for understanding how to build data warehouse effectively, ultimately driving better decision-making and financial performance.
Conclusion
Building a data warehouse represents a strategic initiative that can significantly enhance financial success for organizations within the sector. By centralizing data storage, financial institutions can integrate information from various sources, conduct comprehensive historical analyses, and support critical decision-making processes. The significance of a well-structured data warehouse is paramount, as it directly contributes to operational efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards.
This article has provided key insights into the design methodologies – Inmon and Kimball – as well as a step-by-step process for constructing a data warehouse tailored to the financial industry. Addressing common challenges such as data quality, integration complexity, and user adoption is essential for ensuring successful implementation. By understanding these factors, organizations can develop a robust data repository that not only meets current needs but also adapts to future demands.
Ultimately, the capability to effectively build and manage a data warehouse will empower financial institutions to make informed decisions, enhance their competitive edge, and drive sustainable growth. As the landscape of financial services continues to evolve, embracing best practices in data warehousing will be crucial for navigating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities in an increasingly data-driven environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a data warehouse?
A data warehouse is a centralized storage facility that aggregates information from various sources, enabling organizations to conduct complex inquiries and assessments essential for financial services.
Why is a data warehouse important in financial services?
A data warehouse is important in financial services because it facilitates data integration, historical analysis, decision support, and regulatory compliance, all of which are crucial for informed financial decision-making.
How does data integration benefit financial institutions?
Data integration benefits financial institutions by providing a unified view of data from diverse sources, which improves reporting and analytics, thereby enhancing financial decision-making.
What role does historical analysis play in financial institutions?
Historical analysis allows financial institutions to analyze past data, identify trends, and conduct risk assessments, which are vital for compliance audits and regulatory adherence.
How does a data warehouse support decision-making in financial services?
A data warehouse supports decision-making by providing real-time access to information, enabling organizations like hedge funds and banks to make informed decisions swiftly.
Can you provide an example of a company that has benefited from a data warehouse?
JPMorgan Chase has enhanced its analytical capabilities and improved risk management and customer insights through its investment in an Enterprise Information Warehouse (EDW), which is critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
How does a data warehouse assist with regulatory compliance?
A data warehouse helps ensure accuracy and traceability, which are essential for meeting stringent regulatory requirements such as GDPR and KYC in the financial sector.
What challenges are associated with building a data warehouse?
Challenges in building a data warehouse include security concerns and the complexity of integrating legacy systems, which must be addressed to fully realize the benefits of the repository.