Master Big Data Platform Architecture: Key Practices for Success

Introduction
Mastering big data platform architecture is essential in today’s data-driven landscape, where organizations face an overwhelming influx of information from various sources. This article explores the critical components and frameworks that form the foundation of effective big data architectures. It provides insights into how businesses can utilize these elements to improve data management and analytics.
However, organizations must navigate a range of architectural models, including:
- Lambda
- Kappa
- Lakehouse
Additionally, the integration of machine learning, along with the necessity for compliance and security, adds layers of complexity. How can organizations build robust systems that not only address their current requirements but also adapt to future challenges?
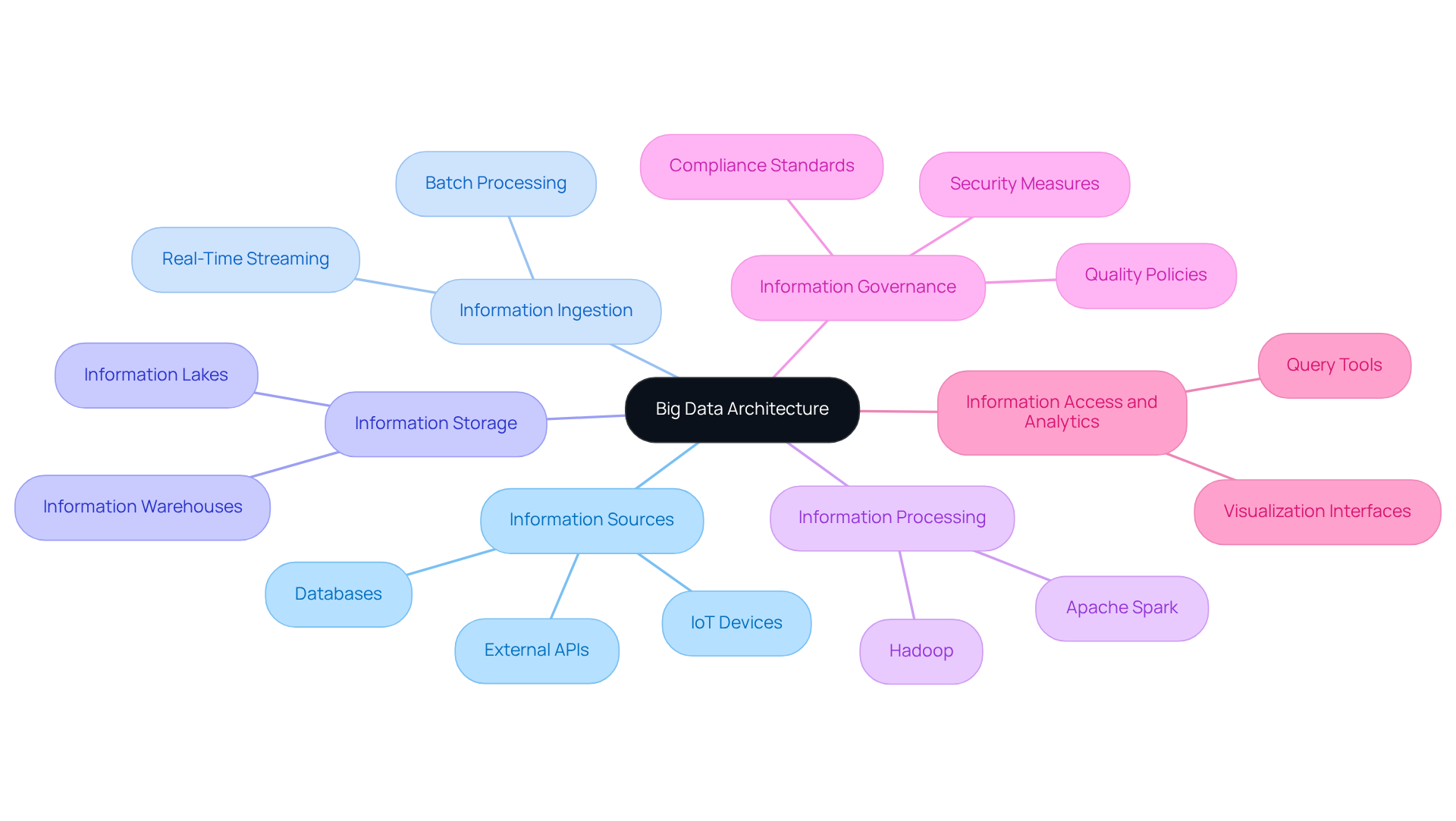
Identify Core Components of Big Data Architecture
To master big data platform architecture, identifying its core components is essential. These typically include:
- Information Sources: Understanding where information originates is crucial. This encompasses databases, IoT devices, and external APIs.
- Information Ingestion: This involves the techniques used to gather and import information into the system, such as batch processing or real-time streaming.
- Information Storage: Choosing the appropriate storage solution (e.g., information lakes, information warehouses) is vital for effectively managing substantial quantities of information.
- Information Processing: This includes the tools and frameworks employed to handle and analyze information, such as Apache Spark or Hadoop.
- Information Governance: Establishing policies for information quality, security, and compliance is critical, particularly in regulated industries.
- Information Access and Analytics: This encompasses the tools and interfaces that allow users to query and visualize information, ensuring that insights can be derived effectively.
By comprehending these elements, organizations can construct a robust big data platform architecture that effectively supports their large-scale information initiatives.
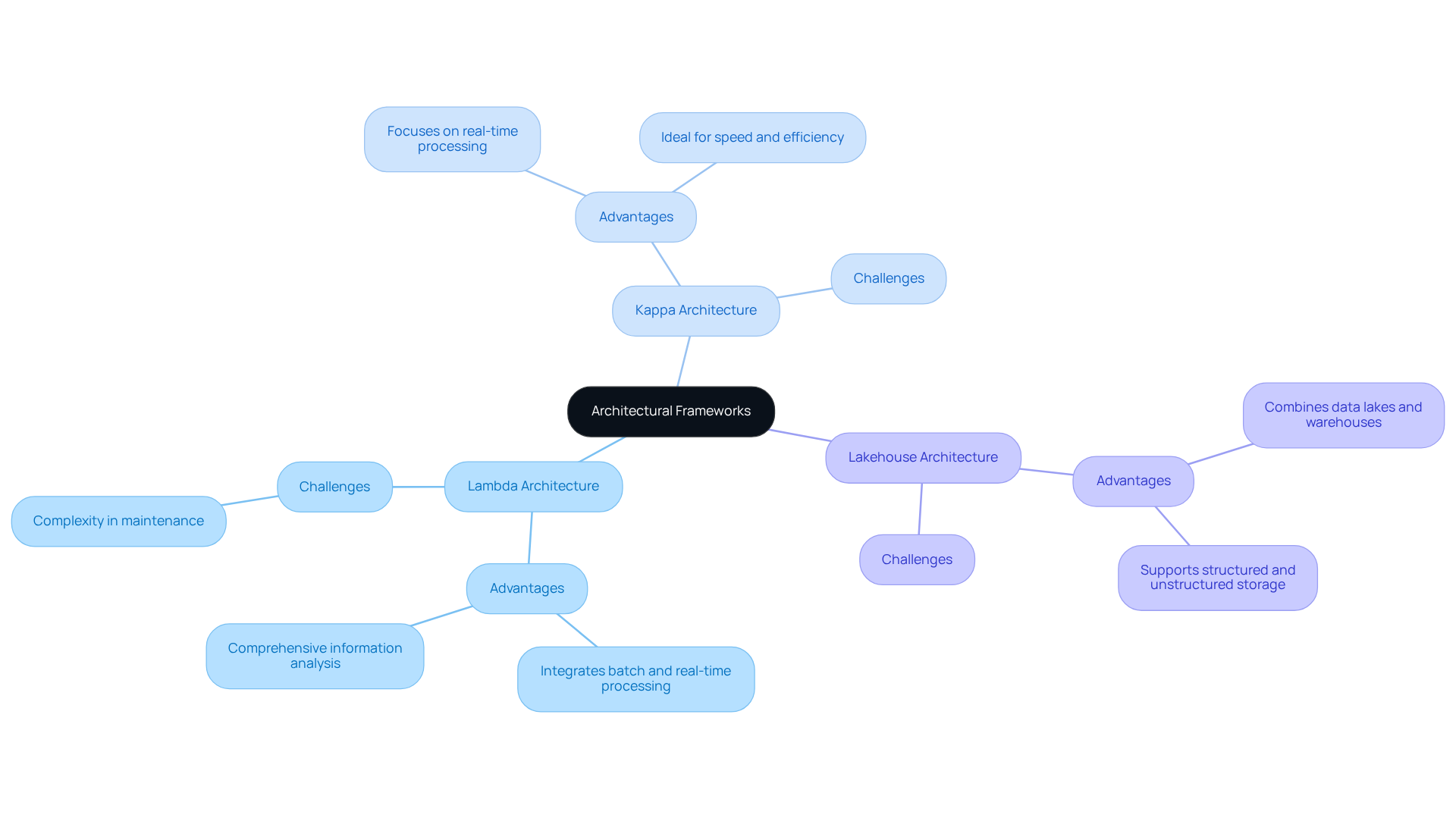
Evaluate Architectural Frameworks: Lambda, Kappa, and Lakehouse
When designing a big data platform architecture, it is essential to assess the appropriate framework. The following outlines three popular architectures:
-
Lambda Architecture: This framework integrates batch and real-time processing, facilitating comprehensive information analysis. It is particularly advantageous for applications that require both historical and real-time insights. However, the complexity of this architecture can pose maintenance challenges.
-
Kappa Architecture: Streamlining the Lambda model, Kappa focuses exclusively on real-time information processing. This architecture is ideal for applications that prioritize speed and efficiency, making it well-suited for environments where immediate insights are critical.
-
Lakehouse Architecture: This hybrid approach combines the benefits of data lakes and warehouses, allowing for both structured and unstructured storage. It supports a variety of analytics workloads and is increasingly favored by organizations seeking to unify their data strategies.
The selection of the appropriate big data platform architecture depends on specific business needs, data volume, and processing requirements. Organizations should carefully evaluate their goals and resources before making a decision.
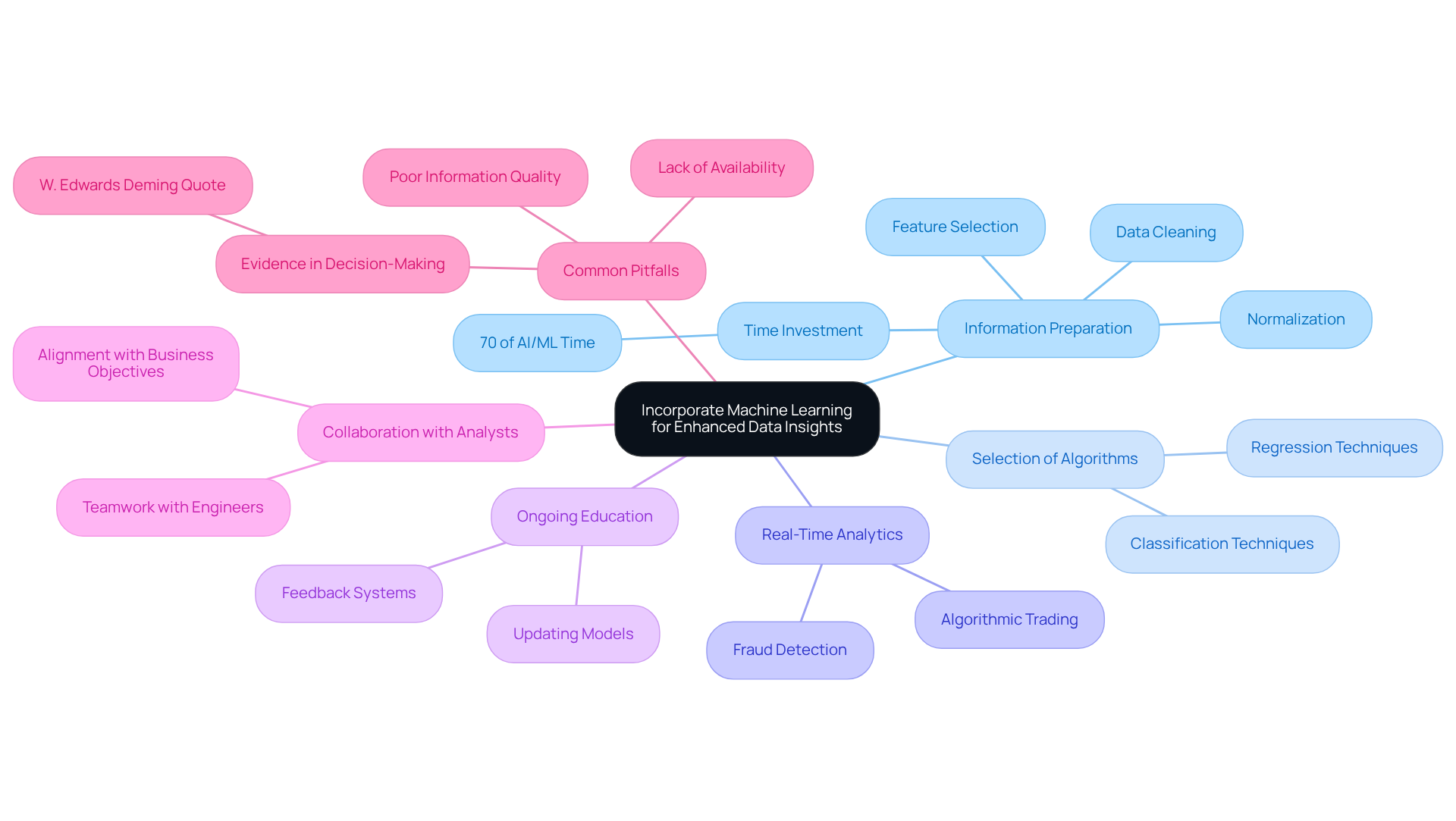
Incorporate Machine Learning for Enhanced Data Insights
Incorporating machine learning into large-scale information frameworks can significantly enhance insights. Here are key practices to consider:
-
Information Preparation: It is essential to ensure that the information is clean, well-organized, and relevant for machine learning systems. This includes critical steps such as normalization, transformation, and feature selection, which are vital for improving accuracy and fairness. Notably, 70% of AI/ML professionals’ time is dedicated to data preparation, underscoring its importance in the machine learning workflow.
-
Selection of Algorithms: Selecting appropriate machine learning techniques tailored to specific use cases is crucial. For instance, regression approaches are ideal for forecasting, while classification techniques excel in risk assessment scenarios.
-
Real-Time Analytics: Implementing real-time information processing capabilities enables machine learning systems to deliver insights as information is ingested. This is particularly beneficial in financial services, where timely fraud detection and algorithmic trading can significantly influence outcomes.
-
Ongoing Education: Establishing a feedback system that allows systems to be consistently updated with fresh information enhances their precision and relevance over time. This practice is essential for adapting to evolving market conditions and emerging threats.
-
Collaboration with Analysts: Fostering teamwork between software engineers and analysts ensures the efficient integration of machine learning models into the big data platform architecture. This alignment with business objectives is vital for maximizing the value derived from insights.
-
Common Pitfalls: It is important to be aware of challenges such as poor information quality and lack of availability, which can impede effective preparation. As W. Edwards Deming famously stated, ‘In God we trust; all others provide evidence,’ highlighting the critical role of information in decision-making.
By adhering to these practices, organizations can leverage machine learning to gain actionable insights and drive informed decision-making, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitive edge.
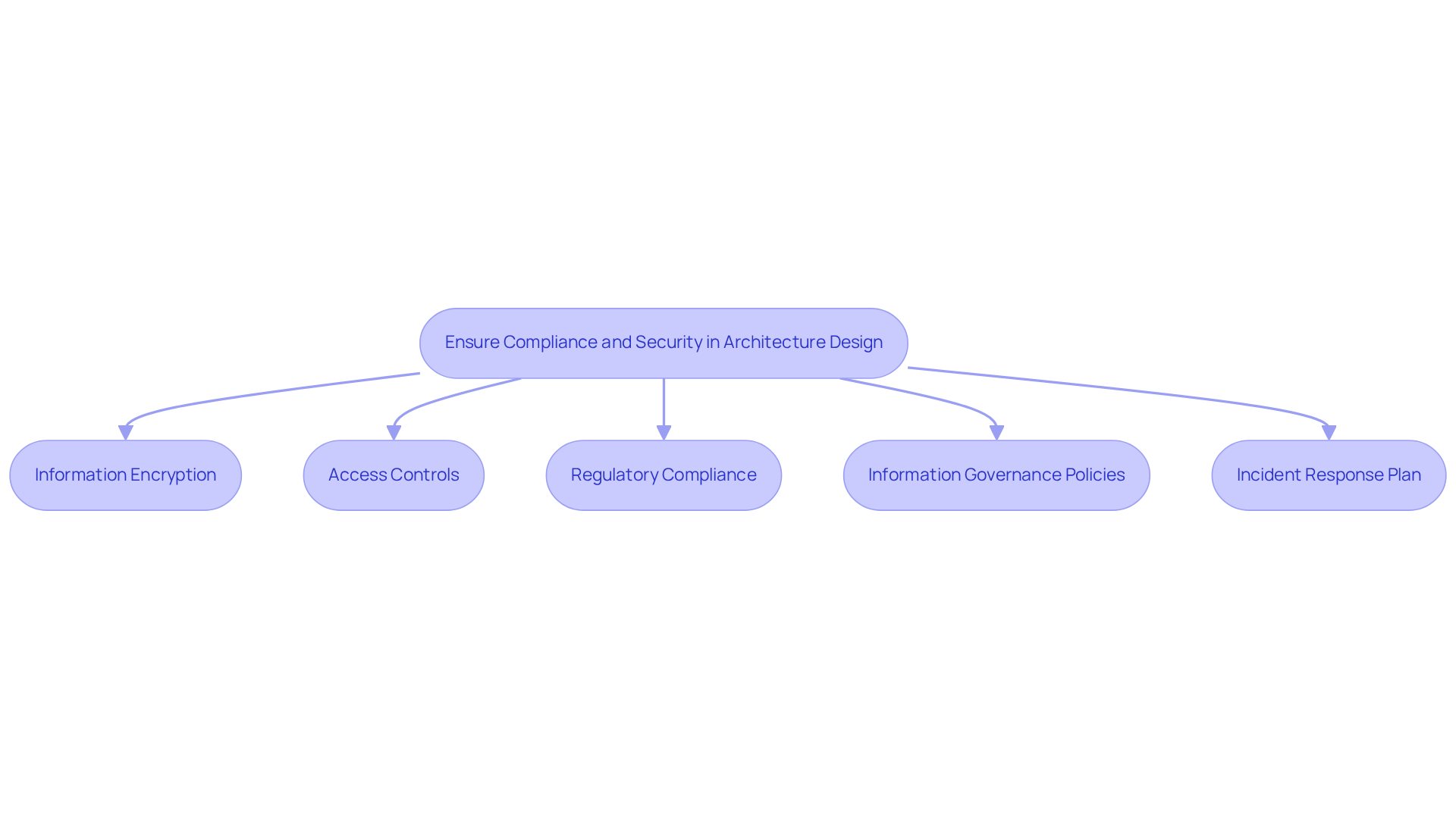
Ensure Compliance and Security in Architecture Design
In the realm of large-scale information architecture, compliance and security are non-negotiable. To ensure these aspects are adequately addressed, organizations should implement the following best practices:
-
Information Encryption: Implement encryption protocols for information at rest and in transit. This safeguards sensitive details from unauthorized access, ensuring that data remains protected throughout its lifecycle.
-
Access Controls: Establish strict access controls and authentication mechanisms. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information, thereby minimizing the risk of data breaches.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Stay informed about relevant regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. It is essential to design the architecture to comply with these standards, which may involve conducting regular audits and assessments to verify adherence.
-
Information Governance Policies: Create and implement comprehensive information governance policies. These policies should clearly outline how information is handled, stored, and shared within the organization, promoting accountability and transparency.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop a robust incident response plan. This plan should be designed to address potential breaches or security events promptly and efficiently, ensuring that the organization can respond effectively to any security threats.
By prioritizing compliance and security in architecture design, organizations can mitigate risks and build a resilient big data platform architecture that meets industry standards.
Conclusion
Mastering big data platform architecture necessitates a thorough understanding of its fundamental components and frameworks. By pinpointing core elements such as:
- Information sources
- Ingestion methods
- Storage solutions
- Processing tools
- Governance policies
- Analytics capabilities
organizations can construct a robust architecture that effectively supports their data-driven initiatives.
The examination of architectural frameworks like Lambda, Kappa, and Lakehouse underscores the significance of selecting the appropriate model based on specific business needs and data processing requirements. Each framework presents distinct advantages:
- Lambda offers comprehensive analysis capabilities
- Kappa provides streamlined processing
- Lakehouse architecture combines hybrid benefits
Furthermore, the integration of machine learning practices enhances data insights, empowering organizations to adapt and thrive in an ever-evolving landscape.
Prioritizing compliance and security within big data architecture is essential for mitigating risks and safeguarding sensitive information. By adopting best practices such as:
- Encryption
- Access controls
- Comprehensive governance policies
organizations can cultivate a secure environment that not only meets regulatory standards but also boosts operational efficiency. Embracing these critical practices will enable organizations to leverage the full potential of big data, facilitating informed decision-making and sustaining a competitive advantage in their respective industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core components of big data architecture?
The core components of big data architecture include information sources, information ingestion, information storage, information processing, information governance, and information access and analytics.
What are information sources in big data architecture?
Information sources refer to where information originates, including databases, IoT devices, and external APIs.
What does information ingestion involve?
Information ingestion involves the techniques used to gather and import information into the system, such as batch processing or real-time streaming.
Why is information storage important in big data architecture?
Information storage is vital for effectively managing substantial quantities of information, and it includes choosing appropriate solutions like information lakes and information warehouses.
What tools are used for information processing in big data?
Tools and frameworks used for information processing include Apache Spark and Hadoop.
What is the role of information governance in big data architecture?
Information governance involves establishing policies for information quality, security, and compliance, which is particularly critical in regulated industries.
How do information access and analytics function in big data architecture?
Information access and analytics encompass the tools and interfaces that allow users to query and visualize information, ensuring that insights can be derived effectively.