4 Key Comparisons of Software Design Models: Agile vs. Waterfall

Introduction
Understanding the nuances between Agile and Waterfall software design models is essential for organizations navigating the complexities of project management. Each methodology presents distinct advantages and drawbacks that significantly influence project outcomes, team dynamics, and customer satisfaction. As companies strive to optimize their development processes, a critical question emerges: how can one determine which model best aligns with their specific needs in a rapidly evolving technological landscape? This exploration examines the key comparisons between these two approaches, illuminating their suitability for various projects and the implications of their adoption.
Overview of Agile and Waterfall Software Design Models
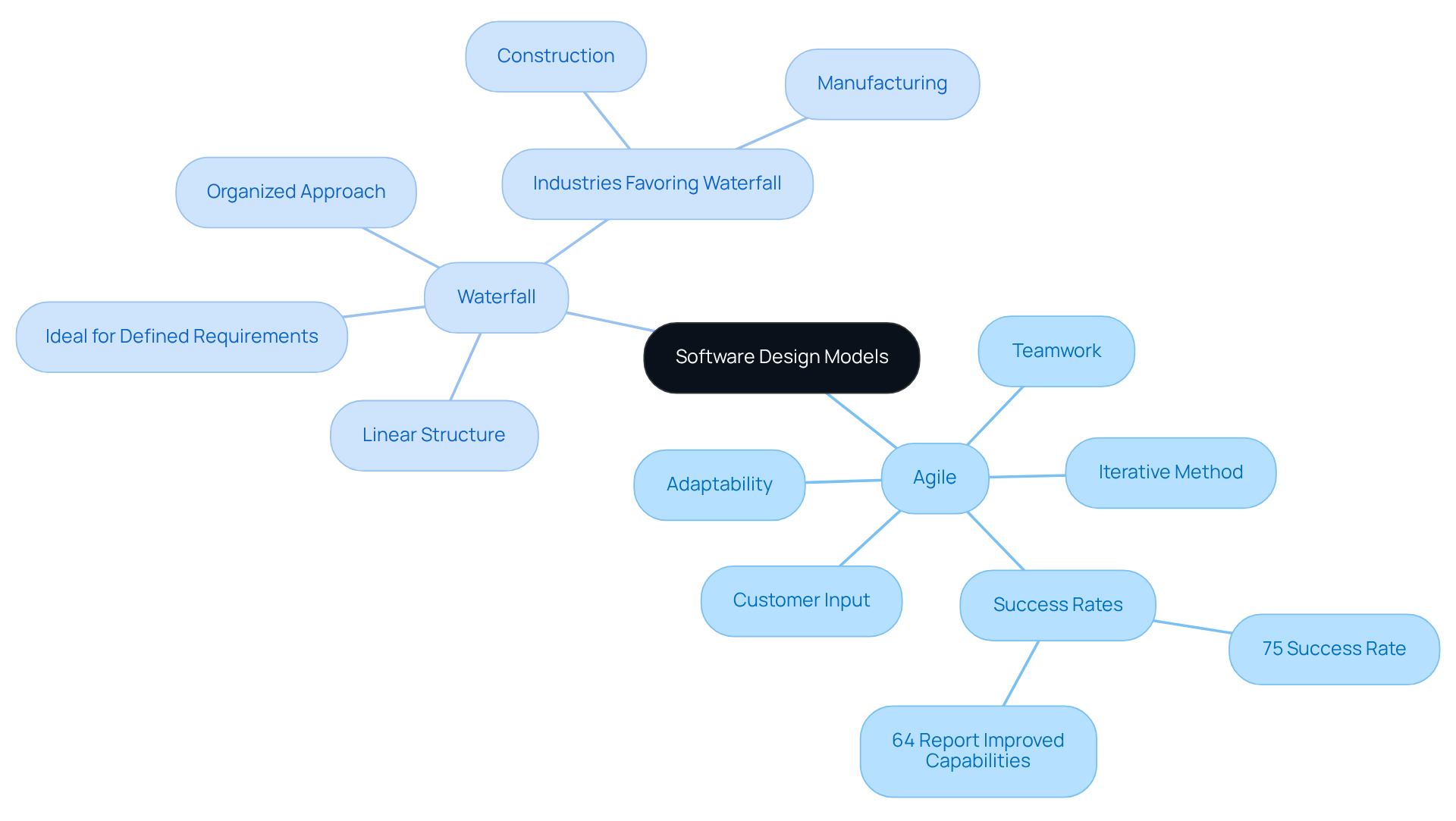
Waterfall and another foundational software design models represent two distinct philosophies and methodologies.
The iterative method emphasizes adaptability, teamwork, and ongoing customer input. By dividing tasks into smaller, manageable segments known as sprints, this methodology enables teams to swiftly adjust to changes and deliver gradual enhancements. This model proves particularly advantageous in dynamic environments, such as technology and startups, where requirements frequently evolve. Recent trends indicate that 64% of organizations implementing flexible methodologies report improved capabilities in managing shifting priorities, with such initiatives achieving a success rate of 75%, significantly higher than the 56% success rate of conventional methods. Furthermore, organizations that align initiatives with business strategies experience a 57% increase in achieving their objectives, underscoring the strategic importance of Agile in today’s fast-paced market.
In contrast, the traditional model adheres to a linear and sequential structure, necessitating the completion of each phase before the next can commence. This model is characterized by its organized approach, making it ideal for projects with clearly defined requirements and minimal anticipated changes. Industries such as construction and manufacturing often favor a linear approach due to its emphasis on compliance and thorough documentation. For example, a construction firm exemplifies the sequential method by meticulously organizing each stage of a project, ensuring that all requirements are met before proceeding. As of 2026, this methodology remains relevant for endeavors similar to previous ones, where a strict timeline benefits stakeholders who prefer a hands-off approach.
Both software design models have distinct strengths and weaknesses. The flexible approach’s adaptability fosters innovation and responsiveness, while the sequential model’s structured nature guarantees clarity and predictability. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate model based on specific requirements and industry context.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile and Waterfall Models
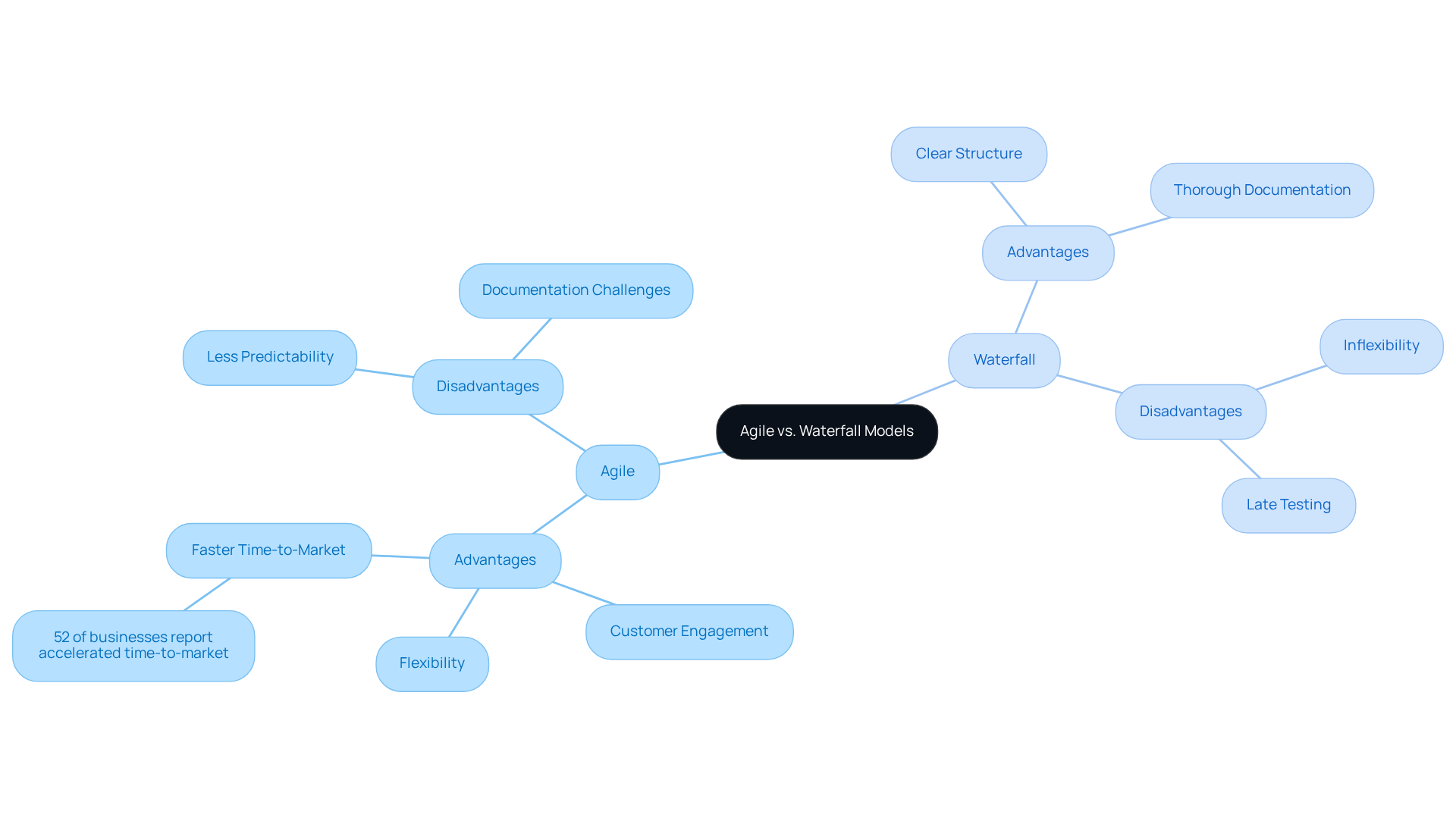
Advantages and Disadvantages of Agile and Waterfall Models
Agile Advantages:
- Flexibility: Agile’s iterative framework facilitates adjustments in project scope and requirements, effectively accommodating evolving client needs. This adaptability is crucial in fast-paced environments where market demands shift rapidly.
- Customer Engagement: Continuous feedback loops are integral to the methodology, ensuring that the final product aligns closely with customer expectations. This engagement fosters a collaborative atmosphere, enhancing stakeholder satisfaction.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Incremental releases enable quicker delivery of functional software, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to market changes. In fact, 52% of businesses report that this methodology accelerates their time-to-market, a significant advantage in competitive sectors.
Agile Disadvantages:
- Less Predictability: The iterative nature of Agile can lead to scope creep if not managed properly, complicating the prediction of costs and resource needs upfront. This unpredictability can hinder budgeting and planning efforts.
- Documentation Challenges: Agile often prioritizes working software over comprehensive documentation, which can complicate future maintenance and onboarding processes. This lack of thorough documentation may pose risks in compliance-heavy industries.
Waterfall Advantages:
- Clear Structure: The linear approach of Waterfall provides a clear roadmap, simplifying the management of timelines and budgets. This organized approach is particularly advantageous for projects with clearly defined requirements.
- Thorough Documentation: Each phase of the development model is meticulously documented, which is beneficial for compliance-heavy initiatives. This thorough documentation ensures clarity and accountability throughout the initiative lifecycle.
Waterfall Disadvantages:
- Inflexibility: Once a phase is completed, making changes can be costly and time-consuming. This rigidity can hinder responsiveness to new information or shifting client needs.
- Late Testing: Testing occurs only after development is complete, which can lead to the discovery of critical issues late in the process. This delay can result in higher expenses and prolonged timelines, especially in complex endeavors.
Recent studies indicate that flexible methodologies have demonstrated a 75% success rate in management, compared to 56% for conventional sequential approaches. Nevertheless, the decision between flexible and Waterfall methodologies often relies on specific requirements and organizational culture, with numerous companies now embracing hybrid models to leverage the advantages of both methodologies.
Suitability of Agile vs. Waterfall for Various Projects
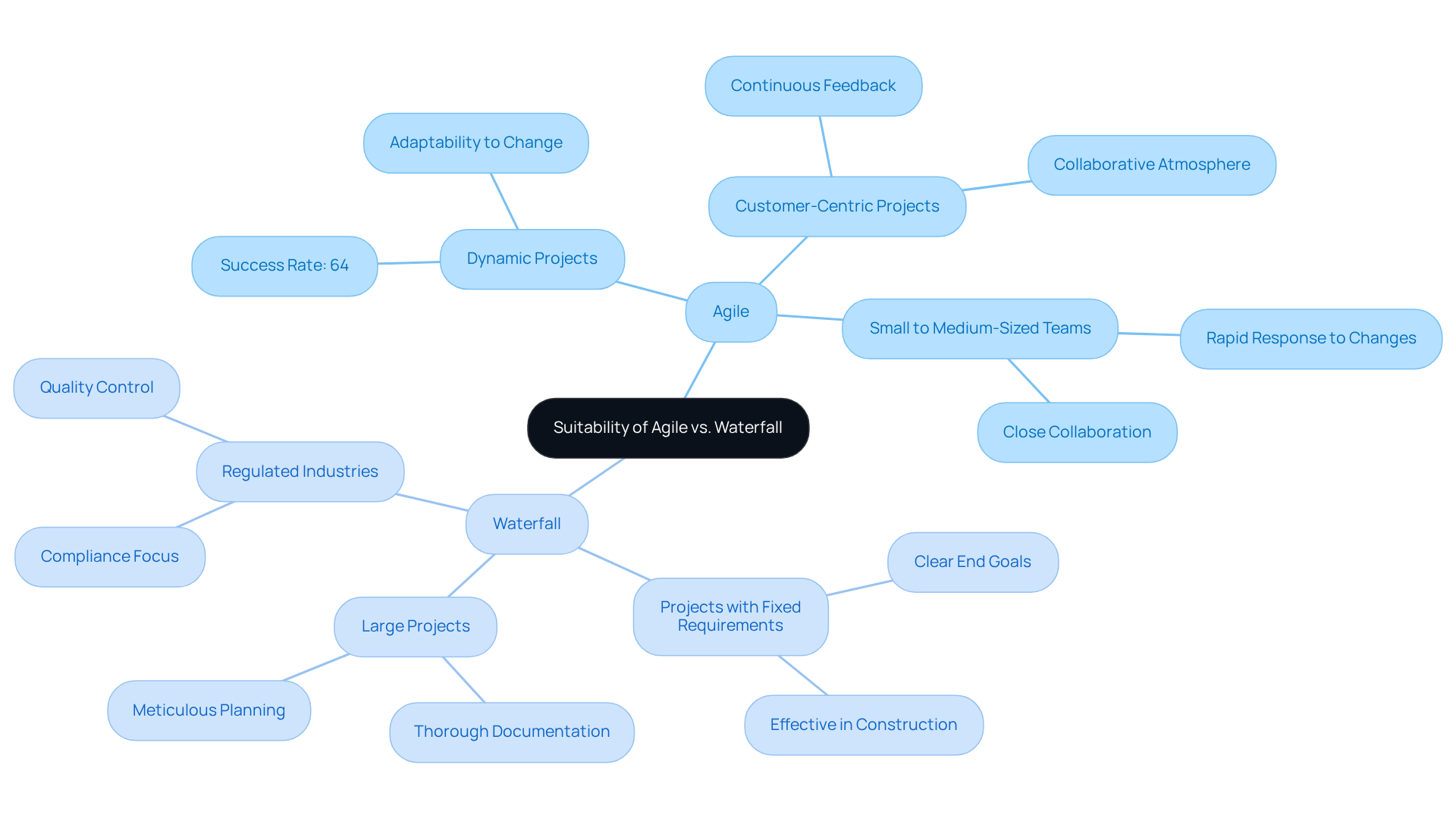
Agile is best suited for:
- Dynamic Projects: Agile methodologies excel in environments where requirements are likely to change, particularly in software development for startups or tech companies. Flexible initiatives achieve a success rate of 64%, highlighting their efficiency in adapting to evolving requirements.
- Customer-Centric Projects: In scenarios where continuous feedback from users is essential for success, Agile enables teams to adjust based on real-time insights. This fosters a collaborative atmosphere that enhances project outcomes.
- Small to Medium-Sized Teams: Agile thrives in settings where teams can collaborate closely and adapt swiftly, making it particularly suitable for smaller teams that require flexibility and rapid responses to changes.
Waterfall is best suited for:
- Projects with Fixed Requirements: This model is especially effective in construction and manufacturing, where the scope is well-defined and changes are infrequent. As noted by Matt Bolton, the methodology is most effective when the end goal is clear from the outset.
- Large Projects: The structured approach is advantageous for extensive projects that require thorough documentation and compliance, ensuring meticulous planning of all aspects. This is crucial in sectors where adherence to guidelines is essential.
- Regulated Industries: In fields such as healthcare and finance, where strict compliance is vital, the traditional methodology offers a clear framework for managing processes. Real-world examples include the application of a sequential development model in healthcare systems to ensure regulatory compliance and quality control.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Agile and Waterfall
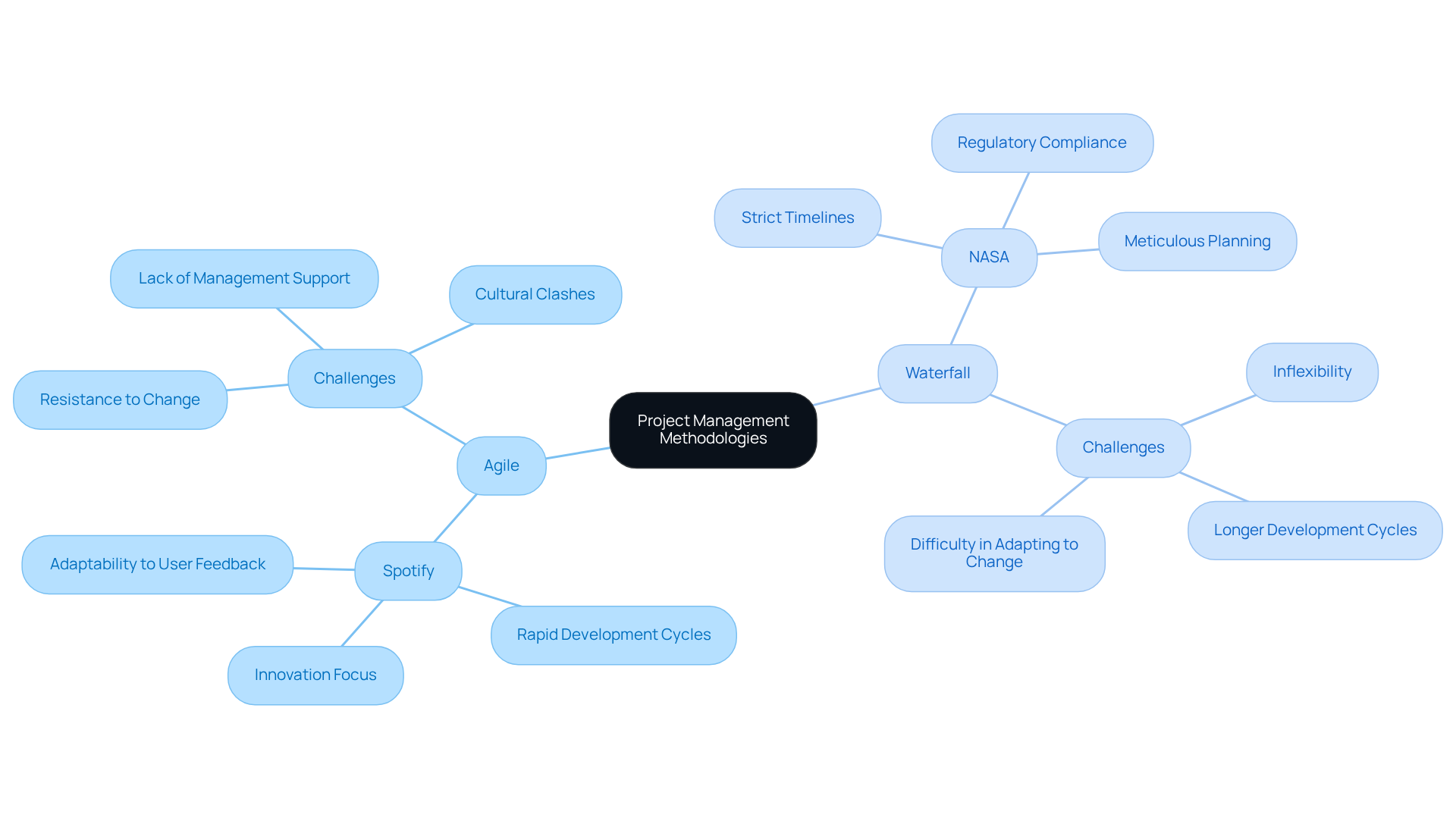
Agile Case Study:
Spotify: This company employs Agile methodologies to promote innovation and facilitate rapid development cycles. By doing so, teams can experiment and swiftly adapt to user feedback, enhancing their responsiveness to market demands.
Waterfall Case Study:
NASA: In contrast, NASA utilizes the Waterfall model for its space missions, where strict adherence to timelines and regulatory compliance is essential. Each phase of the initiative is meticulously planned and executed, ensuring that mission success is achieved through careful coordination and oversight.
These case studies illustrate the significant impact that the choice of methodology can have on project outcomes, particularly in industries where compliance and adaptability are critical.
Conclusion
The comparison between Agile and Waterfall software design models reveals two fundamentally distinct approaches to project management. Agile excels in flexibility and adaptability, making it particularly suitable for dynamic environments where requirements frequently evolve. In contrast, the Waterfall model provides a structured and linear process, ideal for projects characterized by well-defined requirements and a necessity for comprehensive documentation.
Key arguments highlight Agile’s advantages, including faster time-to-market and improved customer engagement, while also acknowledging its challenges, such as unpredictability in scope management. Conversely, Waterfall’s strengths are rooted in its clarity and thorough documentation; however, its rigidity can present difficulties in responding to changing project needs. This article emphasizes that the decision between these methodologies should be guided by specific project requirements and industry contexts, with many organizations increasingly adopting hybrid approaches to leverage the benefits of both frameworks.
Ultimately, grasping the nuances of Agile and Waterfall methodologies is essential for organizations striving to optimize project outcomes. Whether one embraces the iterative nature of Agile or the structured approach of Waterfall, selecting the appropriate methodology can significantly impact success. As industries continue to evolve, harnessing the strengths of these models will be crucial for navigating the complexities of software development and addressing the demands of an ever-changing market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main characteristics of the Agile software design model?
The Agile software design model emphasizes adaptability, teamwork, and ongoing customer input. It divides tasks into smaller segments known as sprints, allowing teams to adjust to changes and deliver gradual enhancements.
In what types of environments is the Agile model particularly advantageous?
The Agile model is particularly advantageous in dynamic environments, such as technology and startups, where requirements frequently evolve.
What success rates are associated with organizations using Agile methodologies?
Organizations implementing Agile methodologies report a success rate of 75%, which is significantly higher than the 56% success rate of conventional methods.
How does aligning initiatives with business strategies impact Agile project success?
Organizations that align initiatives with business strategies experience a 57% increase in achieving their objectives, highlighting the strategic importance of Agile in today’s market.
What are the main characteristics of the Waterfall software design model?
The Waterfall model adheres to a linear and sequential structure, requiring the completion of each phase before the next can begin. It is organized and ideal for projects with clearly defined requirements and minimal anticipated changes.
Which industries commonly prefer the Waterfall model?
Industries such as construction and manufacturing often favor the Waterfall model due to its emphasis on compliance and thorough documentation.
Why is the Waterfall model still relevant as of 2026?
The Waterfall model remains relevant for endeavors similar to previous ones, where a strict timeline benefits stakeholders who prefer a hands-off approach.
What are the strengths and weaknesses of both software design models?
The Agile model’s strengths include adaptability and fostering innovation, while its weaknesses may involve less predictability. The Waterfall model’s strengths include clarity and predictability, with weaknesses related to inflexibility in changing requirements.
Why is it important to understand the differences between Agile and Waterfall models?
Understanding the differences between Agile and Waterfall models is crucial for selecting the appropriate model based on specific requirements and industry context.