Introduction
In the complex landscape of regulated industries, compliance is not merely a guideline; it is a necessity. Consequently, the design of software processes emerges as a critical endeavor. Developers encounter the dual challenge of adhering to stringent regulatory standards while simultaneously delivering functional and user-friendly applications. This article examines best practices that ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, while also enhancing quality assurance throughout the software development lifecycle.
How can organizations effectively navigate this intricate terrain and implement strategies that promote both compliance and innovation?
Understand the Unique Requirements of Regulated Industries
In regulated industries such as finance and healthcare, software development must adhere to strict guidelines and standards. Understanding these requirements involves recognizing the frameworks that govern operations, such as GDPR for data protection and HIPAA for healthcare privacy. As Steve Alder notes, “Healthcare regulatory adherence is the practice of meeting or exceeding the requirements of all applicable federal, state, local, and industry regulations.” Developers must ensure that their applications not only fulfill functional requirements but also comply with these regulations to avoid legal repercussions.
For instance, financial programs must incorporate features that facilitate audit trails and ensure data integrity, which are essential for compliance with financial regulations. Engaging with stakeholders early in the development process can clarify these requirements and ensure that the software aligns with both business objectives and compliance mandates.
Statistics indicate that failures in adherence within regulated industries can lead to costs exceeding $1 million per patient due to errors in data management, underscoring the importance of a robust adherence strategy. As Aditya Krishnaswamy emphasizes, “Transparency, validation, and human oversight are decisive” in navigating these complex regulatory landscapes. Furthermore, knowledge of GDPR and HIPAA adherence in engineering is vital for developers aiming to remain competitive in these evolving fields.
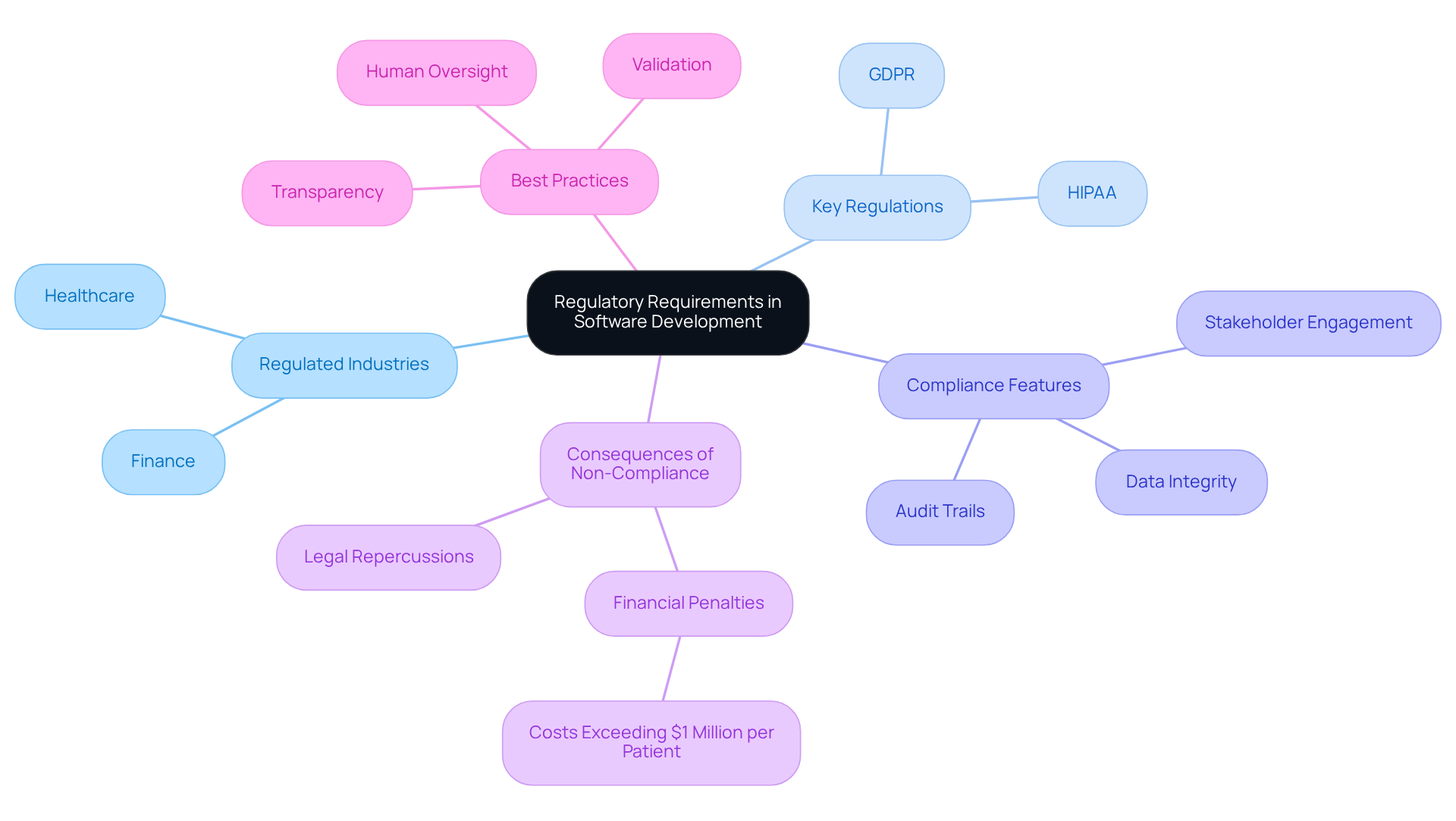
Incorporate Compliance and Quality Assurance in Design
To effectively integrate adherence and quality assurance into software design, Neutech teams adopt an ‘adherence-first’ approach, embedding checks at every stage of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). This strategy is underpinned by several key practices:
-
Utilization of Automated Testing Tools: Tools such as Automated Compliance Hardening (ACH) facilitate continuous monitoring and validation of compliance requirements. This significantly reduces the risk of non-compliance.
-
Regular Audits and Reviews: Conducting regular audits is crucial for identifying potential adherence gaps early. This proactive approach allows for prompt corrections before issues escalate.
-
Thorough Documentation Practices: Comprehensive documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance during official inspections. It must be seamlessly integrated into quality assurance processes.
-
Human Oversight in Automation: Acknowledging the challenges associated with automation, Neutech emphasizes the necessity of human oversight in exploratory testing and user experience validation.
By embedding these practices into the software process design phase and remaining vigilant against common pitfalls, Neutech enhances the reliability of its solutions while adeptly navigating the complexities of regulatory environments. Furthermore, Neutech’s focus on diverse development technologies, including React, Python, and GoLang, bolsters its capacity to deliver compliant solutions tailored to the specific requirements of regulated industries.
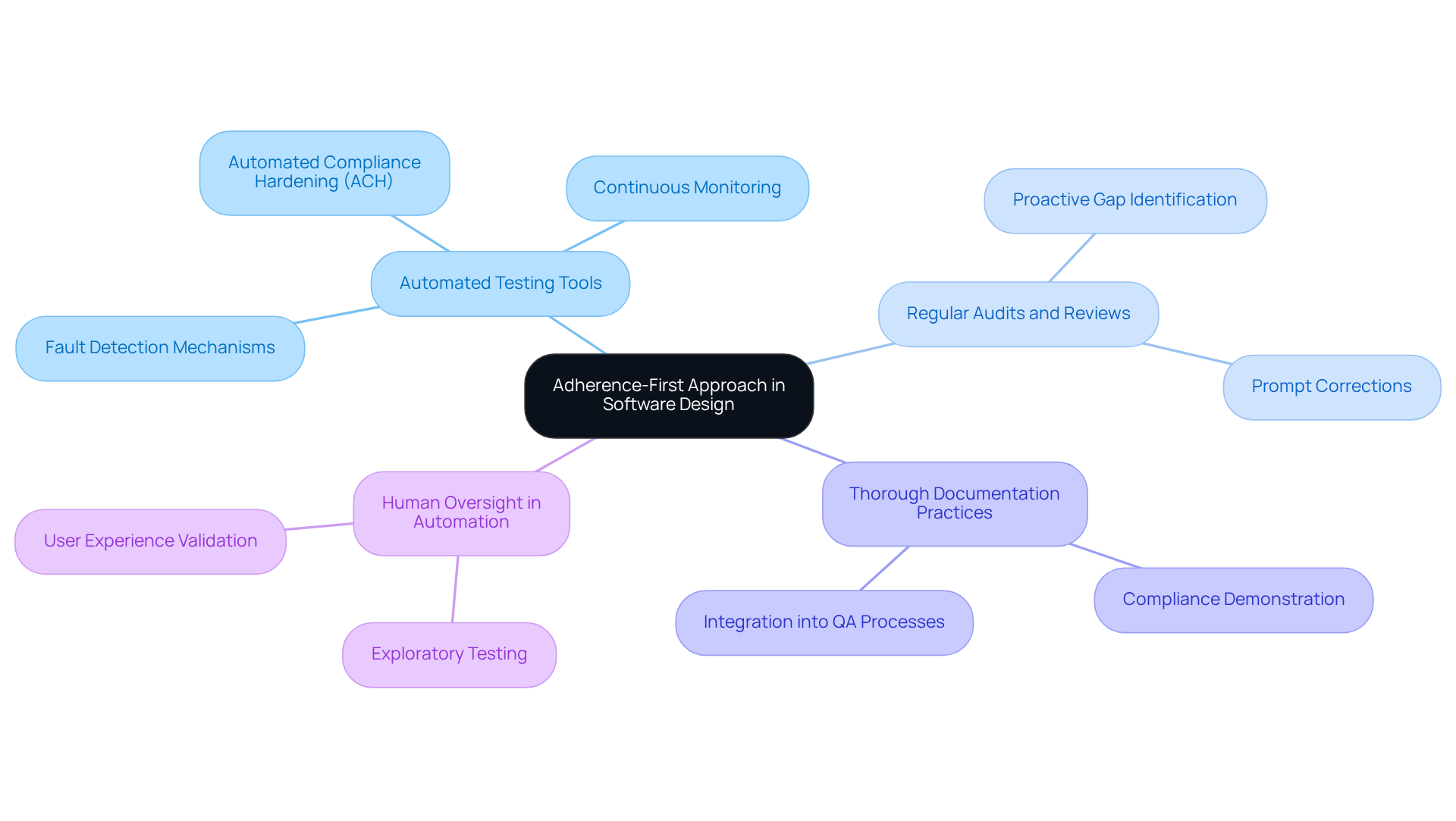
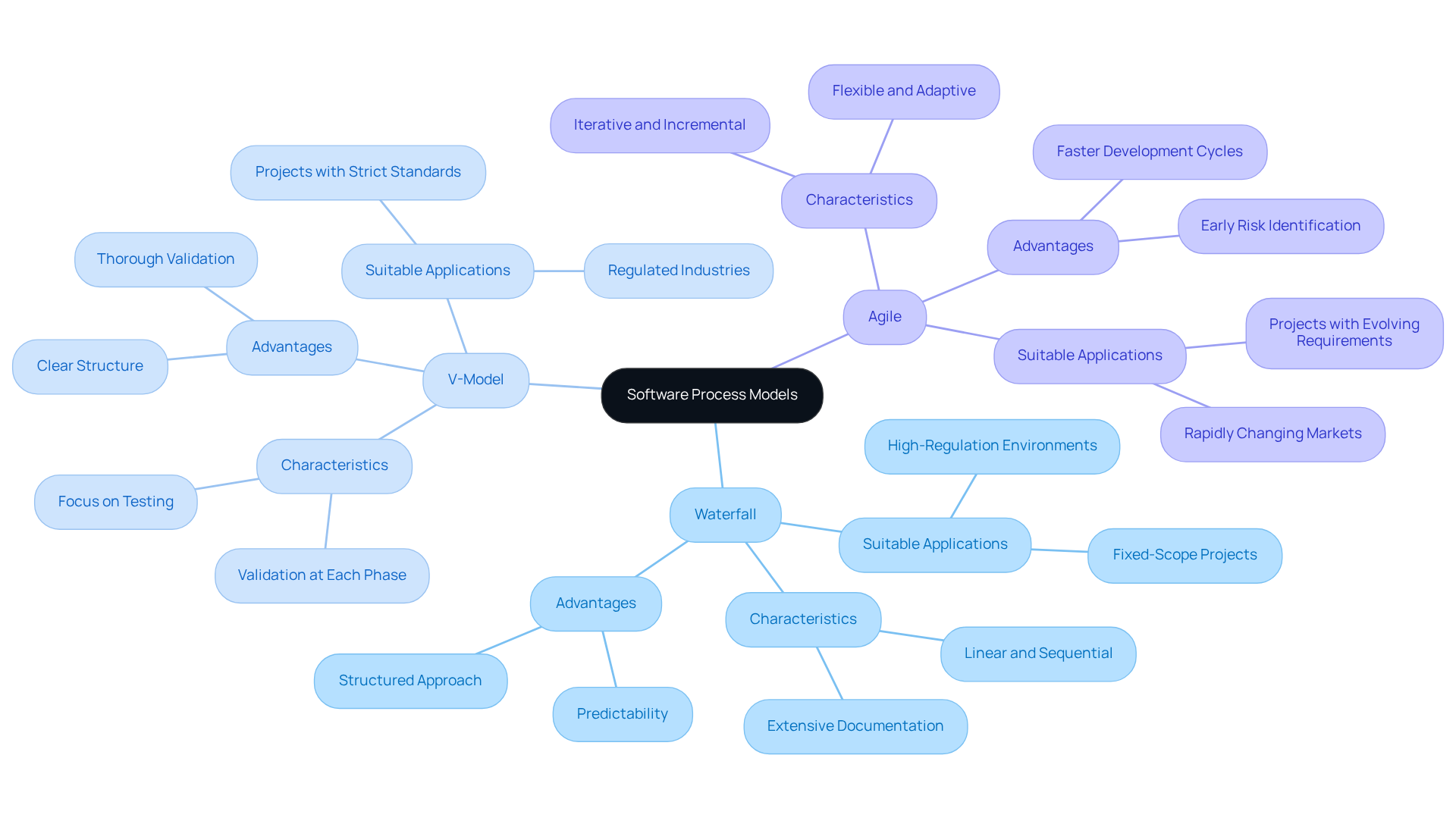
Select and Tailor Software Process Models for Industry Needs
Selecting the appropriate software process design model is essential for success in regulated industries. Conventional models, such as Waterfall and V-Model, are often favored due to their organized approaches, which facilitate thorough documentation and validation procedures necessary for meeting regulatory standards. Waterfall, with its linear and sequential methodology, proves particularly effective in environments characterized by well-defined requirements, ensuring predictability and comprehensive oversight. Conversely, the V-Model emphasizes validation at every development phase, making it suitable for projects where strict adherence to standards is paramount.
In recent years, Agile methodologies have increasingly been adapted to align with official standards by integrating rigorous documentation and compliance checks within iterative sprints. This adaptability enables teams to respond swiftly to evolving requirements while maintaining compliance with regulatory frameworks. For example, in financial technology projects, a V-Model approach can be beneficial due to its focus on validation; however, incorporating Agile practices can enhance responsiveness to stakeholder feedback and changing market conditions.
Statistics reveal that Agile methodologies can accelerate production cycles by delivering incremental progress, allowing teams to identify and address issues early. This is particularly advantageous in regulated environments, where late-stage risks can result in costly delays. Furthermore, oversight organizations, including the FDA, now recognize Agile as a viable method for application development and validation, provided that adherence measures are effectively integrated.
In conclusion, a hybrid approach that combines the strengths of Waterfall, V-Model, and Agile within the framework of software process design can optimize project outcomes in regulated industries. By assessing the specific requirements of the project alongside the legal framework, teams can devise a tailored strategy that balances flexibility with the necessary compliance rigor.
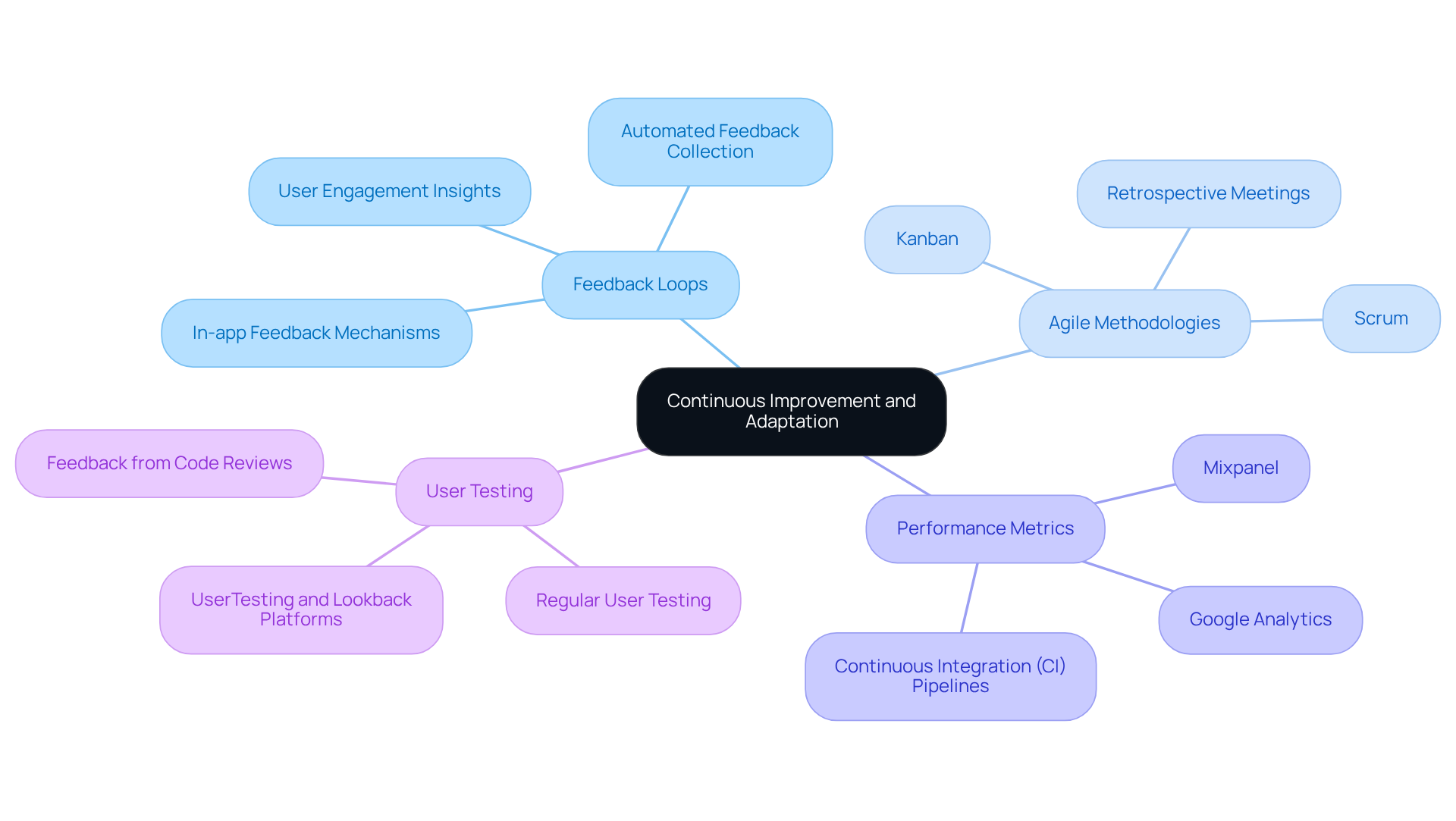
Emphasize Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Ongoing enhancement is a fundamental principle in the creation of technology for regulated sectors. Organizations should implement feedback loops that facilitate regular assessments of processes and outcomes, enabling teams to identify areas for improvement. Techniques such as Agile methodologies, including Scrum and Kanban, support the incorporation of iterative feedback. Additionally, in-app feedback mechanisms provide real-time insights into user experiences.
Performance metrics and regular user testing yield valuable insights into the effectiveness of current practices, allowing teams to adapt swiftly. Staying informed about regulatory changes and industry trends is crucial for adjusting processes accordingly. For instance, integrating user feedback into the development cycle can lead to more user-friendly and compliant solutions. Analytics tools like Google Analytics and Mixpanel further assist in identifying user engagement and areas for enhancement.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can enhance product quality while ensuring ongoing compliance with evolving regulations. As Dr. Noushin Ashrafi states, ‘To remain competitive, software companies must establish practices that enhance quality and advance their software process design.’ By integrating these practices, organizations can develop a robust framework for continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Effective software process design in regulated industries relies heavily on a comprehensive understanding of specific compliance requirements and the integration of robust quality assurance practices. The primary message underscores the necessity for developers to navigate complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring that software not only fulfills functional needs but also adheres to stringent guidelines such as GDPR and HIPAA. By adopting an ‘adherence-first’ approach and selecting appropriate software process models, organizations can significantly enhance their capability to deliver compliant solutions tailored to the unique demands of their sectors.
Key practices are emphasized throughout the article, including:
- The importance of utilizing automated testing tools
- Conducting regular audits
- Maintaining comprehensive documentation
The discussion also highlights the value of selecting suitable software process models, such as Waterfall, V-Model, or Agile, to effectively balance compliance with the need for flexibility. Continuous improvement emerges as a critical theme, with feedback loops and performance metrics serving as essential tools for organizations to adapt and enhance their processes in response to evolving regulations and user needs.
Ultimately, the significance of implementing these best practices cannot be overstated. Organizations in regulated industries must prioritize compliance and quality assurance not only to avoid costly penalties but also to foster innovation and competitiveness in their software solutions. By committing to a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation, developers can ensure that their software processes remain effective, compliant, and responsive to the ever-changing landscape of regulatory demands.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the unique requirements for software development in regulated industries?
Software development in regulated industries such as finance and healthcare must adhere to strict guidelines and standards, including frameworks like GDPR for data protection and HIPAA for healthcare privacy.
Why is regulatory adherence important in healthcare?
Regulatory adherence in healthcare is crucial to meet or exceed the requirements of all applicable federal, state, local, and industry regulations, helping to avoid legal repercussions and ensuring patient privacy.
What features must financial programs incorporate to comply with regulations?
Financial programs must include features that facilitate audit trails and ensure data integrity, which are essential for compliance with financial regulations.
How can engaging with stakeholders benefit the software development process?
Engaging with stakeholders early in the development process can clarify regulatory requirements and ensure that the software aligns with both business objectives and compliance mandates.
What are the potential costs of failures in adherence within regulated industries?
Failures in adherence within regulated industries can lead to costs exceeding $1 million per patient due to errors in data management.
What key factors are essential for navigating regulatory landscapes according to experts?
Transparency, validation, and human oversight are decisive factors in navigating complex regulatory landscapes.
Why is knowledge of GDPR and HIPAA important for developers?
Knowledge of GDPR and HIPAA adherence is vital for developers to remain competitive in the evolving fields of finance and healthcare.
