Introduction
In a rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, the demand for effective software solutions is more critical than ever. Stakeholders face the challenge of selecting the right tools – from Electronic Health Records to Telemedicine Platforms – to enhance patient care and operational efficiency. To navigate the complexities of healthcare software development, developers must adopt best practices that ensure compliance, security, and user engagement. This article explores essential strategies that streamline the development process while fostering innovation and trust in healthcare technology.
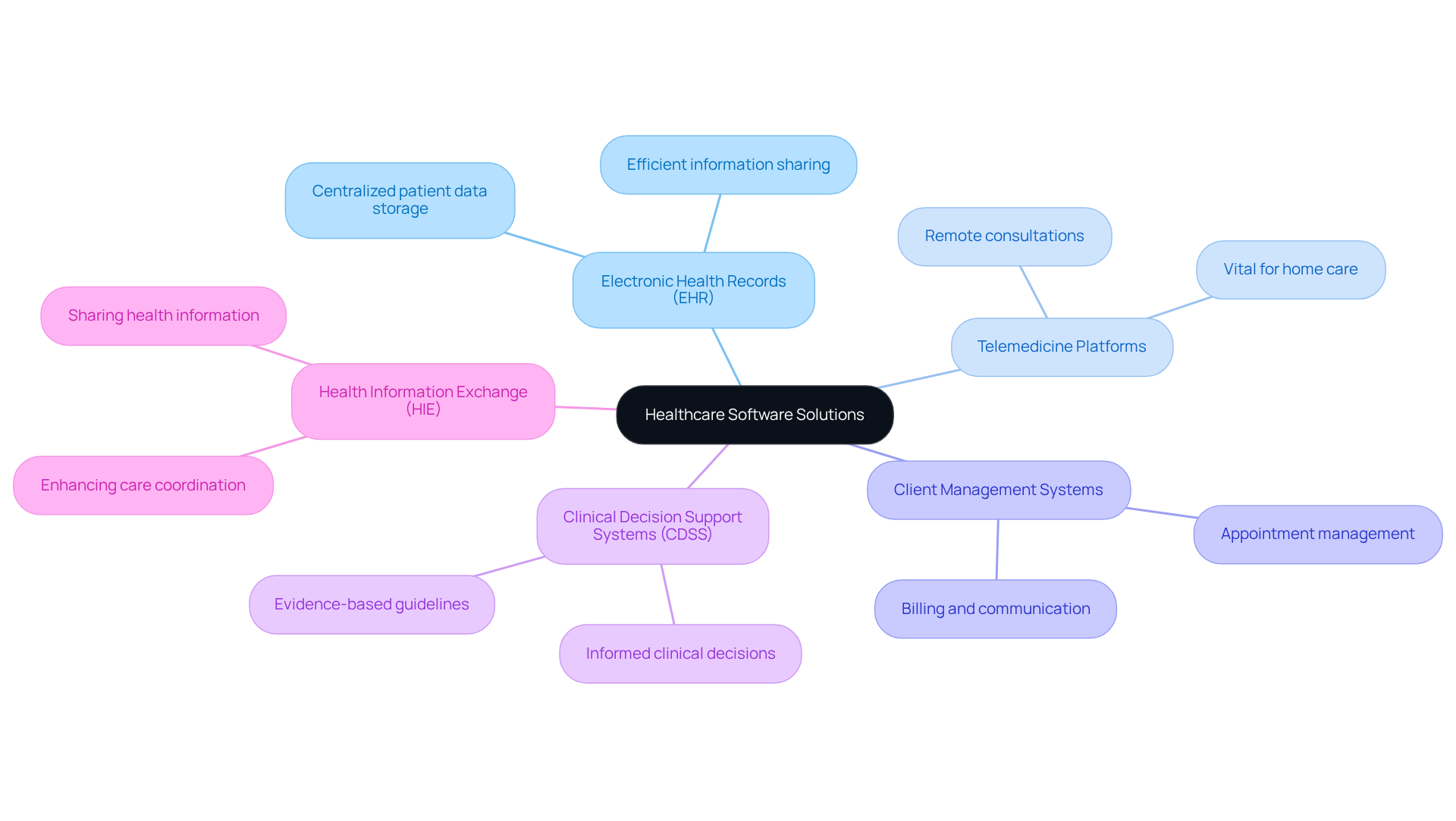
Identify Key Types of Healthcare Software Solutions
In the medical field, various software solutions cater to distinct operational needs. The key types include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): These are centralized systems that store patient data, enabling healthcare providers to access and share information efficiently.
- Telemedicine Platforms: These tools facilitate remote consultations, allowing individuals to receive care from home, a feature that has become increasingly vital.
- Client Management Systems: This software assists in managing appointments, billing, and communication, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): These systems support medical providers in making informed clinical decisions based on patient data and evidence-based guidelines.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE): These platforms enable the sharing of health information across various medical organizations, which enhances care coordination.
Understanding these categories of applications is crucial for stakeholders to select the appropriate solutions that align with their operational objectives and regulatory requirements.
Outline the Healthcare Software Development Process
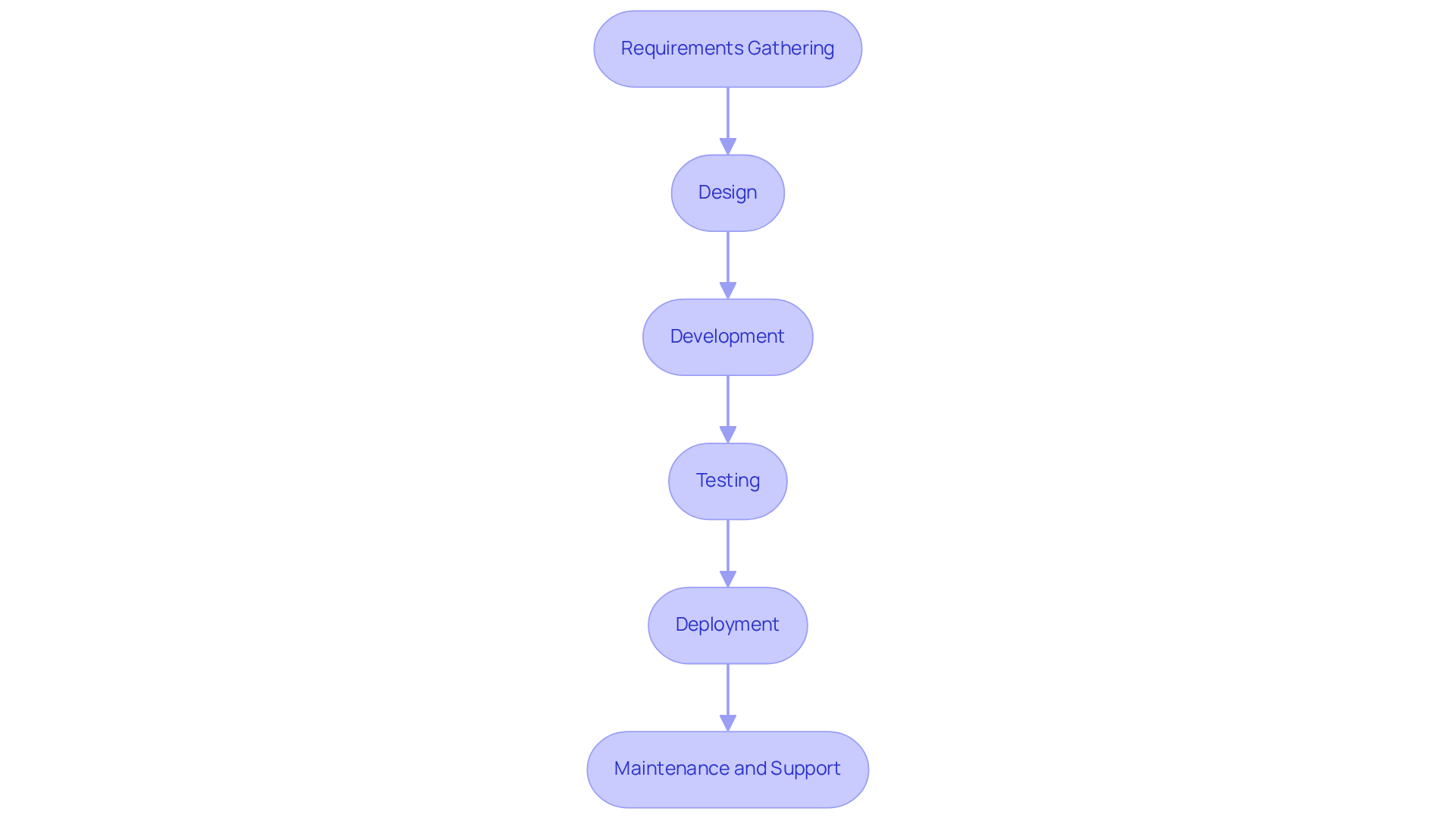
The healthcare software development process encompasses several critical stages that ensure the delivery of effective solutions tailored to meet regulatory standards and user needs:
-
Requirements Gathering: This initial phase involves engaging with stakeholders, including healthcare providers and patients, to thoroughly understand their needs. Efficient requirements collection is essential, as it establishes the basis for the system’s functionalities and experience for individuals. A well-executed requirements phase can significantly reduce development time and costs. As Weronika Michaluk, MedTech Practice Lead at HTD Health, observes, “There are numerous regulations, requirements, and detailed documentation to keep track of, making the development of medical device applications highly complex.”
-
Design: In this stage, wireframes and prototypes are created to visualize the application’s interface and experience. This iterative design process allows for early feedback, ensuring that the final product aligns with user expectations and clinical objectives.
-
Development: During development, engineers write the code and construct the application according to the defined specifications. Utilizing compliant Agile methodologies enhances flexibility, allowing for iterative improvements based on ongoing feedback.
-
Testing: Rigorous evaluation is conducted to identify and rectify bugs, ensuring that the application meets quality standards and complies with healthcare regulations. This phase is crucial for confirming the system’s functionality and reliability, especially in a landscape where the Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) market is expected to reach USD 167.59 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.6%. The necessity for a sophisticated Quality Management System (QMS) as per ISO 13485 standards is critical during this phase to ensure compliance and enhance product quality.
-
Deployment: The software is launched in a live environment, ensuring that all systems are integrated and functioning correctly. This phase requires careful planning to minimize disruptions and ensure a seamless transition for individuals. Navigating the FDA submission process is also crucial at this stage, as it involves rigorous examination to ensure all regulatory standards are met.
-
Maintenance and Support: Ongoing support and updates are provided to address any issues and enhance functionality based on user feedback. Ongoing enhancement is essential, particularly as medical organizations encounter difficulties with documentation and administrative tasks, where doctors dedicate almost two hours to administrative responsibilities for each hour of care.
By following this organized approach, developers in the medical field can produce dependable, user-friendly healthcare software development solutions that not only meet regulatory standards but also enhance patient care and operational effectiveness. This organized method not only reduces risks but also encourages innovation, as emphasized by the significance of psychological safety in promoting creative solutions within medical technology.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance and Security Measures
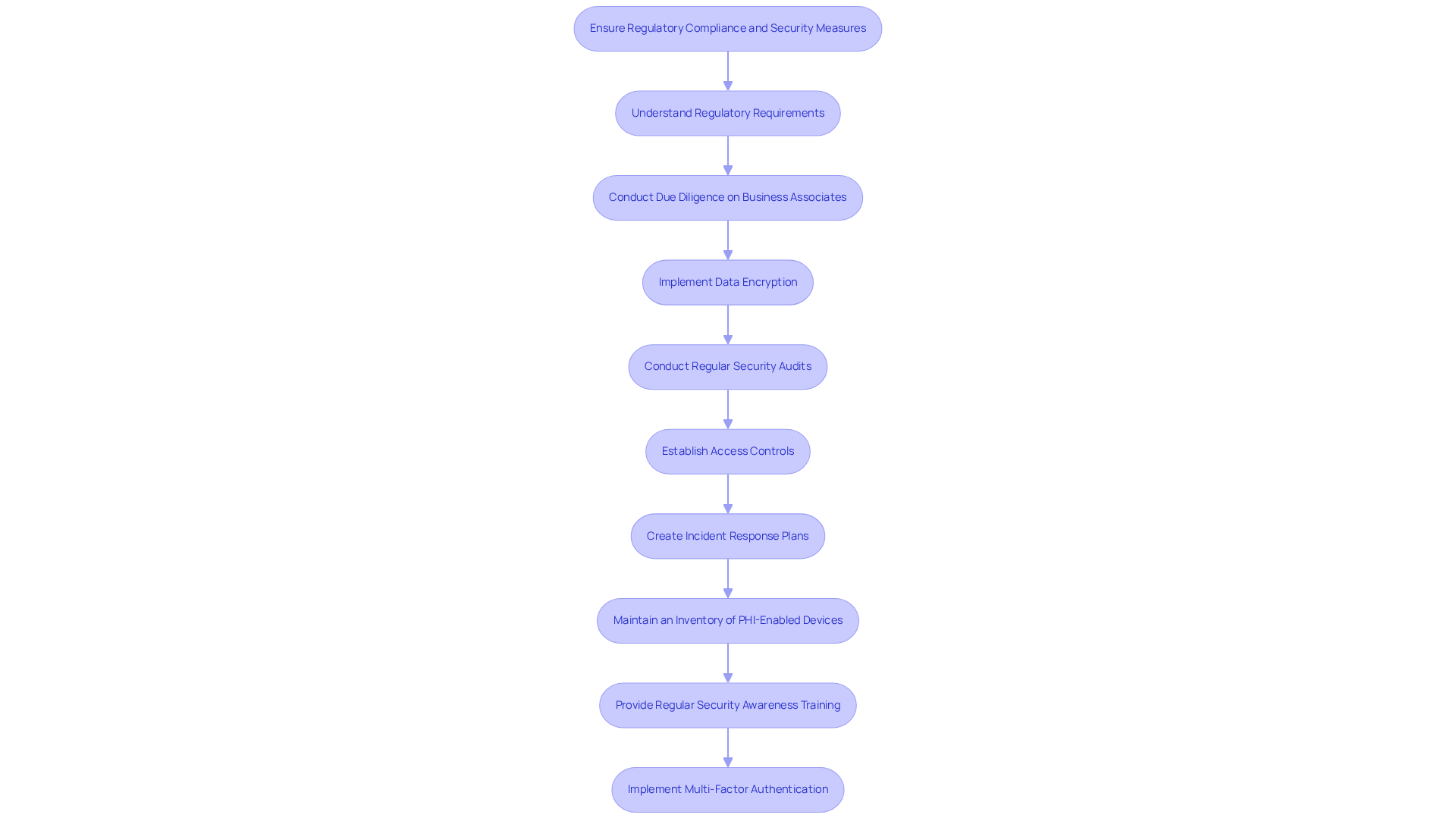
To ensure regulatory compliance and security in healthcare software development solutions, it is essential to adopt best practices that address both legal standards and cybersecurity threats.
-
Understand Regulatory Requirements: Familiarizing yourself with essential regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA guidelines is crucial. This knowledge ensures that your software adheres to legal standards, as compliance failures can result in significant penalties and operational disruptions.
-
Conduct Due Diligence on Business Associates: Implementing thorough due diligence processes for all business associates handling protected health information (PHI) is vital. This practice secures supply chains and ensures compliance in regulated sectors, particularly in medical services.
-
Implement Data Encryption: Employing robust encryption techniques for both data at rest and in transit is necessary to protect sensitive patient information from unauthorized access. Given the rising occurrence of cyberattacks targeting medical data, this measure is increasingly important.
-
Conduct Regular Security Audits: Scheduling routine audits and vulnerability assessments allows organizations to proactively identify and address potential security risks. Regular evaluations help maintain compliance with security standards and stay ahead of evolving threats.
-
Establish Access Controls: Implementing role-based access controls restricts data access to authorized personnel only. This significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, especially in environments where hybrid work is prevalent, as unauthorized access can lead to severe data exposure.
-
Create Incident Response Plans: Developing and maintaining a comprehensive incident response plan is essential for addressing data breaches or security incidents. A well-defined plan ensures swift action to mitigate damage and restore operations, reinforcing confidence with clients and stakeholders.
-
Maintain an Inventory of PHI-Enabled Devices: Regularly reviewing and managing an inventory of all devices that access PHI ensures that only authorized individuals have access, further enhancing security measures.
-
Provide Regular Security Awareness Training: Ongoing training for remote staff to recognize phishing threats and utilize company-approved cloud services is crucial, particularly as hybrid work increases the risk of data breaches.
-
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Requiring multi-factor authentication for all remote logins enhances security measures against unauthorized access.
By prioritizing these compliance and security measures, developers can establish trust with individuals and effectively safeguard sensitive medical information while leveraging healthcare software development solutions to address the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
Enhance User Adoption and Engagement Strategies
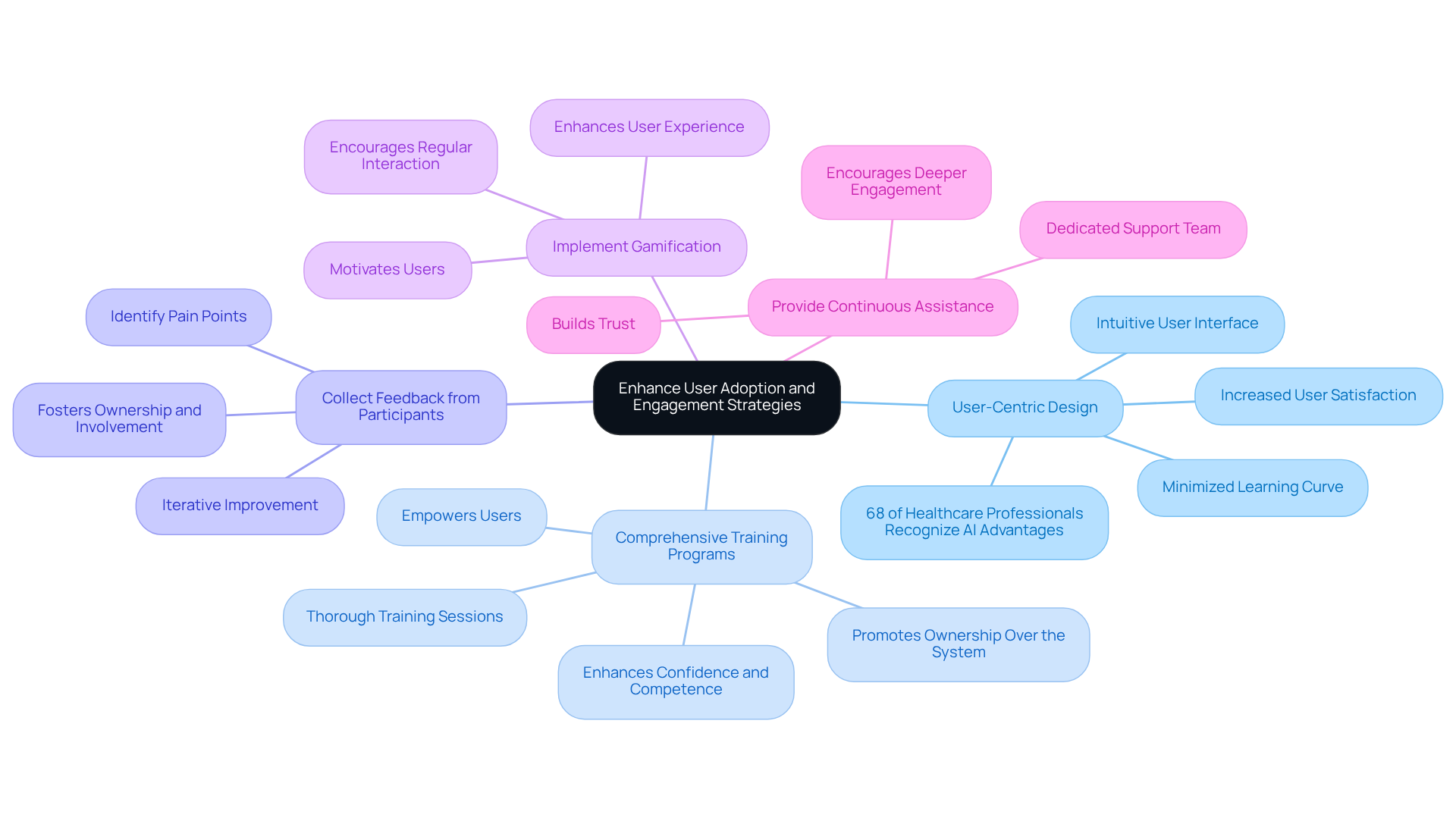
To enhance user adoption and engagement in healthcare software, several strategies should be considered:
-
User-Centric Design: Prioritizing an intuitive user interface is essential for simplifying navigation and minimizing the learning curve. A well-designed interface can significantly enhance user satisfaction and reduce training time, ultimately leading to higher adoption rates. Notably, 68% of healthcare professionals recognize the advantages of AI in patient care, underscoring the importance of user-centric design in improving engagement.
-
Comprehensive Training Programs: Implementing thorough training sessions and resources empowers users to fully comprehend the features and functionalities of the application. Effective training programs have been shown to enhance confidence and competence among users, which are critical for efficient application utilization. As a healthcare instructor stated, “Effective training programs not only improve participant skills but also promote a sense of ownership over the system, leading to better outcomes.”
-
Collect Feedback from Participants: Regularly seeking input from users is vital for identifying pain points and areas for enhancement. This iterative approach ensures that the application evolves in accordance with user needs, fostering a sense of ownership and involvement.
-
Implement Gamification: Incorporating gamification techniques can motivate users and encourage regular interaction with the software. Engaging elements such as rewards and challenges enhance the user experience and promote consistent usage.
-
Provide Continuous Assistance: Establishing a dedicated support team to assist users with any challenges they encounter is crucial. Reliable support builds trust and encourages users to engage more deeply with the application.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare organizations can significantly improve user satisfaction and ensure that their software solutions are effectively utilized, ultimately enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Effective healthcare software development is essential for enhancing patient care and operational efficiency. Understanding the various types of healthcare software solutions enables stakeholders to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs. The development process, which includes stages from requirements gathering to maintenance, ensures that software products not only meet regulatory standards but also provide a seamless user experience.
Key arguments presented in this article emphasize the necessity of adhering to regulatory compliance and security measures. This includes a thorough understanding of essential regulations and the implementation of robust data protection strategies. Furthermore, fostering user adoption through user-centric design, comprehensive training, and continuous support is crucial for ensuring that healthcare software solutions are effectively utilized. Collectively, these practices contribute to the development of reliable and innovative healthcare technologies.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, prioritizing best practices in software development becomes increasingly significant. Organizations are encouraged to adopt these strategies not only to comply with regulations but also to enhance user engagement and satisfaction. By doing so, they can pave the way for improved patient outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system, ultimately transforming the delivery of care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Electronic Health Records (EHR)?
Electronic Health Records (EHR) are centralized systems that store patient data, allowing healthcare providers to access and share information efficiently.
What is the purpose of Telemedicine Platforms?
Telemedicine Platforms facilitate remote consultations, enabling individuals to receive care from home, which has become increasingly important.
What functions do Client Management Systems serve?
Client Management Systems assist in managing appointments, billing, and communication, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
How do Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) help medical providers?
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) support medical providers in making informed clinical decisions based on patient data and evidence-based guidelines.
What is the role of Health Information Exchange (HIE)?
Health Information Exchange (HIE) platforms enable the sharing of health information across various medical organizations, enhancing care coordination.
Why is it important for stakeholders to understand these healthcare software solutions?
Understanding these categories of applications is crucial for stakeholders to select appropriate solutions that align with their operational objectives and regulatory requirements.
