Understand Telehealth Software Cost: Key Factors for Decision-Makers

Introduction
Understanding the financial landscape of telehealth software is essential as healthcare organizations navigate an increasingly digital environment. The rapid rise of remote medical services necessitates that decision-makers comprehend the various pricing models and hidden costs associated with these vital tools. Organizations must ensure they are making informed investments that align with their budget and the evolving needs of patient care.
Define Telehealth Software and Its Importance in Healthcare
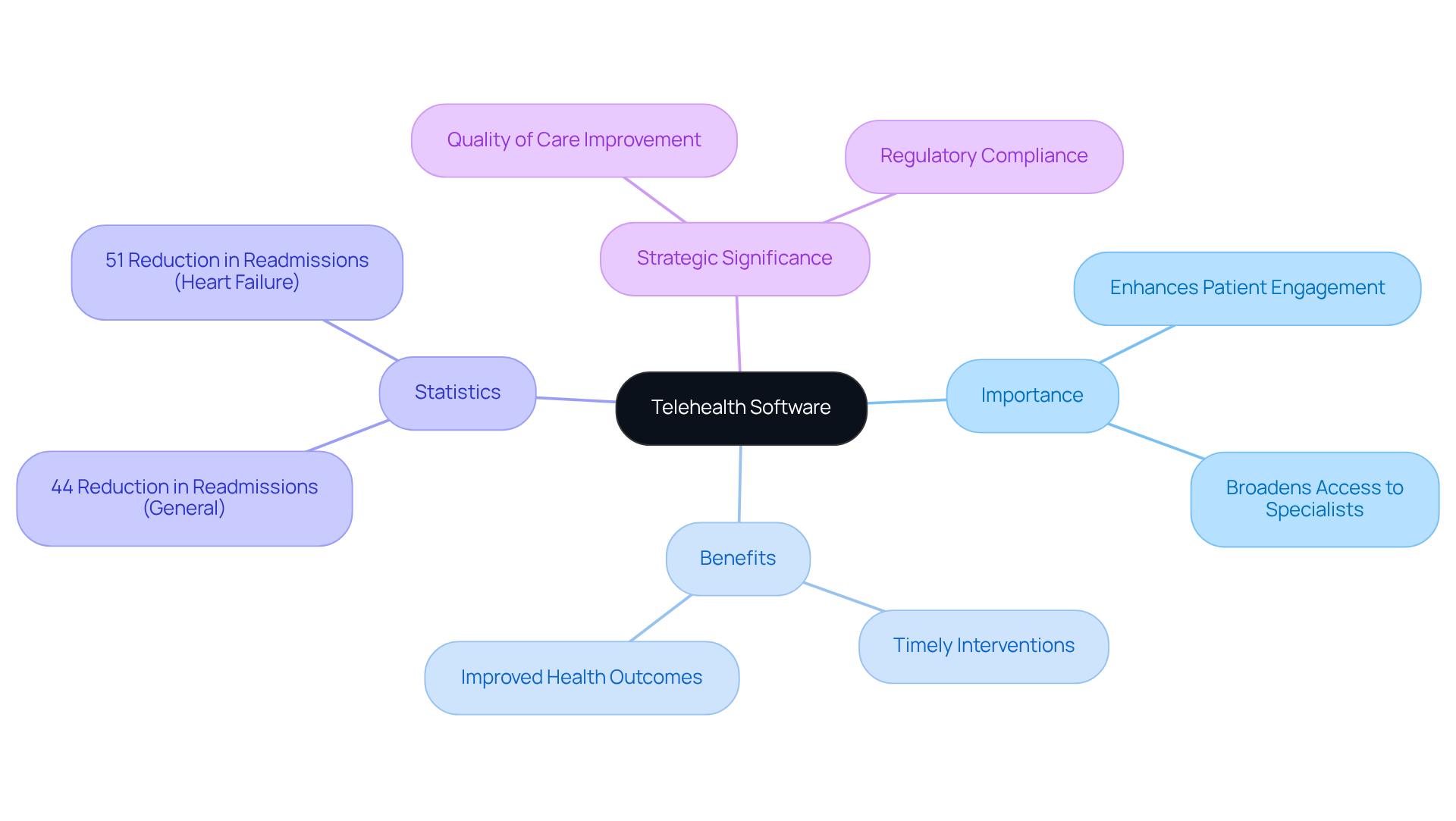
Telehealth software encompasses digital platforms that enable remote medical services via video conferencing, messaging, and other communication technologies. This software empowers medical providers to deliver care to patients irrespective of their physical location, effectively dismantling barriers to access. The importance of remote health software in medical care is profound; it enhances patient engagement, broadens access to specialists, and facilitates timely interventions, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes. For example, research indicates that patient readmissions decreased by 44% for individuals enrolled in telemedicine programs, while heart failure patients saw a 51% reduction in readmissions following the implementation of telemedicine services by the Veterans Health Administration.
As healthcare systems increasingly adopt digital solutions, remote health software becomes vital for compliance with regulations and standards, ensuring that patient information is managed securely and efficiently. The American Medical Association emphasizes that sustainable remote health reform is crucial to preserving the enhanced access achieved during the pandemic, aligning with broader digital transformation goals in healthcare services. This highlights the imperative for decision-makers to invest in robust telehealth solutions that not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also significantly enhance patient outcomes. Notably, 50% of surveyed healthcare executives identified improving the quality of care as their primary motivation for implementing telemedicine, underscoring the strategic significance of these solutions.
Explore Pricing Models for Telehealth Software
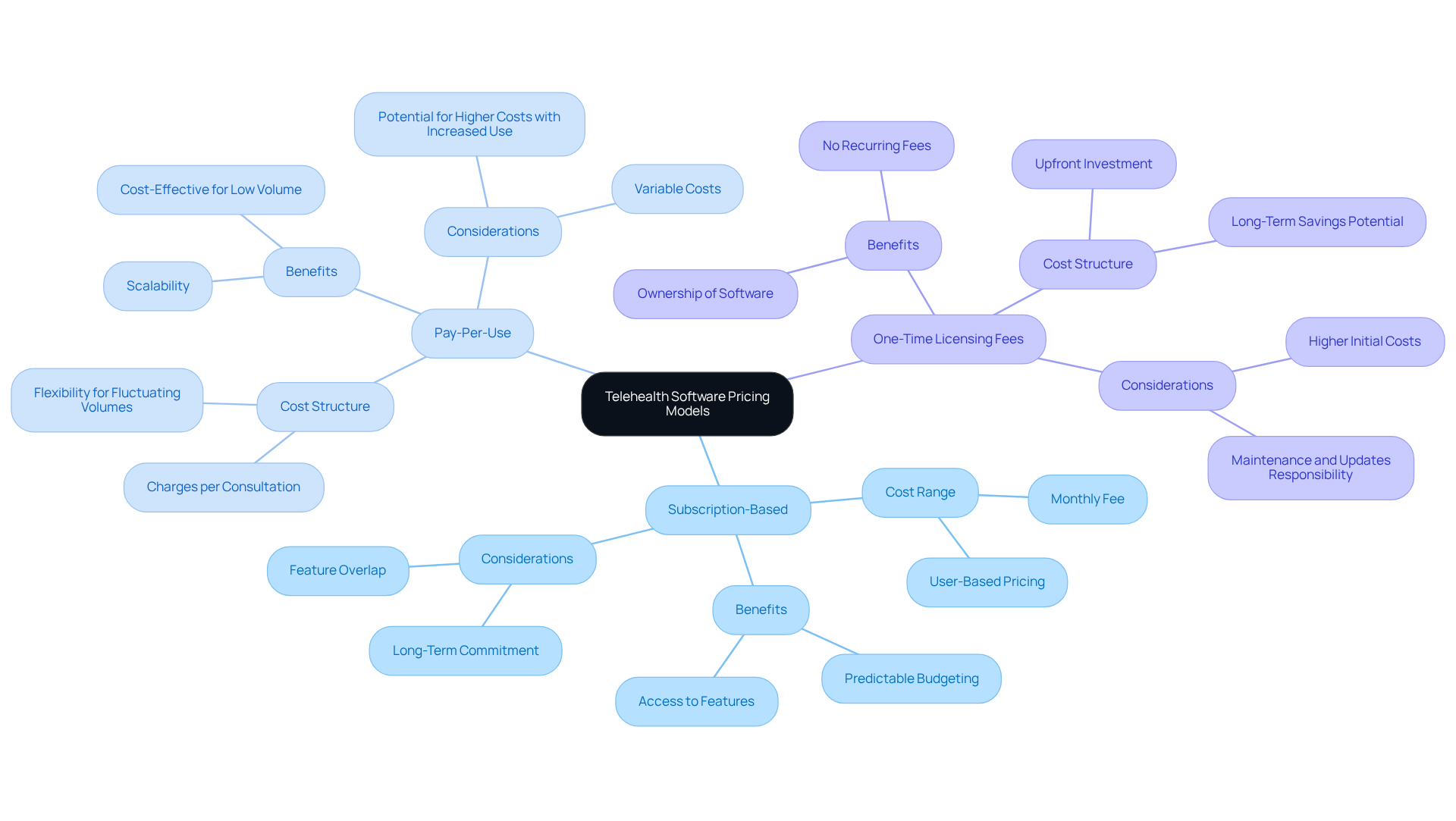
Telehealth software cost can vary as it operates under various pricing models, including subscription-based, pay-per-use, and one-time licensing fees. Subscription-based models typically charge a recurring fee, ranging from $30 to over $300 per user per month, depending on the features and services included. This model is particularly beneficial for entities seeking predictable budgeting aligned with their telehealth initiatives.
Pay-per-use models provide flexibility, charging according to the number of consultations or services provided. This makes them appropriate for entities with fluctuating patient volumes. Conversely, one-time licensing fees require a larger upfront investment but can lead to cost savings over time for organizations planning extensive use of the software.
Comprehending the telehealth software cost frameworks is crucial for aligning financial strategies with healthcare goals, especially as the industry evolves and the demand for innovative solutions rises. Significantly, the remote healthcare sector was anticipated to reach a market value of $194.1 billion in 2023, with earnings from virtual healthcare expected to rise to $559.52 billion by 2027.
As remote healthcare technologies are anticipated to save the U.S. healthcare system $305 billion each year, making informed choices about software investments becomes essential for optimizing both operational efficiency and patient care results. However, companies providing virtual health services will face reimbursement limbo for the sixth consecutive year heading into 2026, highlighting the challenges that may impact financial planning in this sector.
Identify Additional Costs Associated with Telehealth Implementation
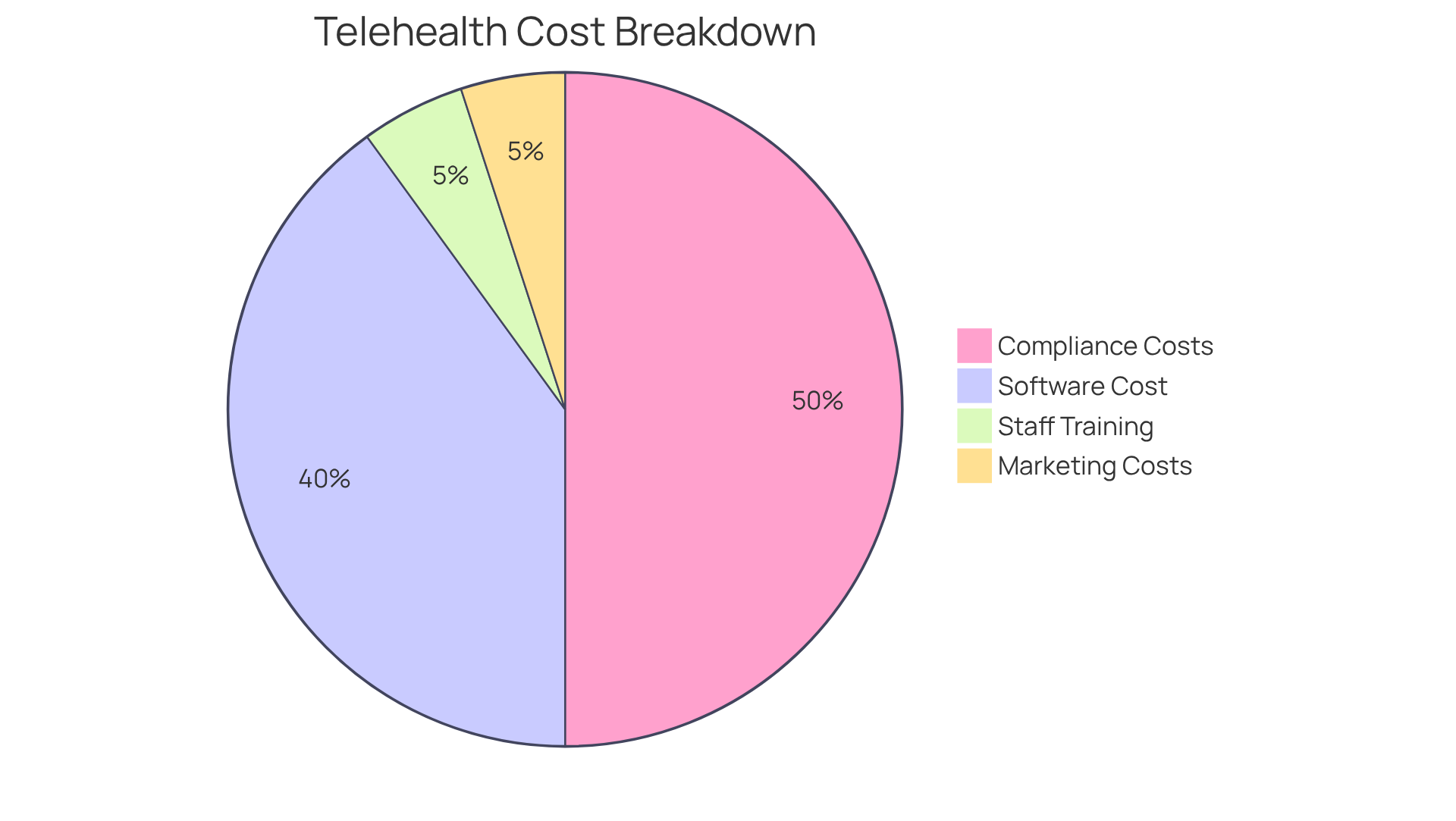
In addition to the primary telehealth software cost, organizations must consider various supplementary expenses that can significantly impact their budgets. One critical area is compliance with healthcare regulations, which can vary widely, ranging from $10,000 to $50,000. This variation depends on the complexity of the software and the specific regulatory environment in which the organization operates.
Another important consideration is the cost of training staff to effectively utilize the telehealth platform. This training typically incurs expenses in the range of $2,000 to $5,000. Ensuring that staff are well-prepared to use the technology is essential for successful implementation.
Furthermore, companies may need to allocate funds for marketing efforts to promote their remote health offerings. This additional investment can further increase their budget by approximately $1,000 to $5,000.
Understanding the telehealth software cost along with these supplementary expenses is crucial for conducting a thorough financial evaluation of remote healthcare implementation.
Assess Organizational Readiness for Telehealth Services
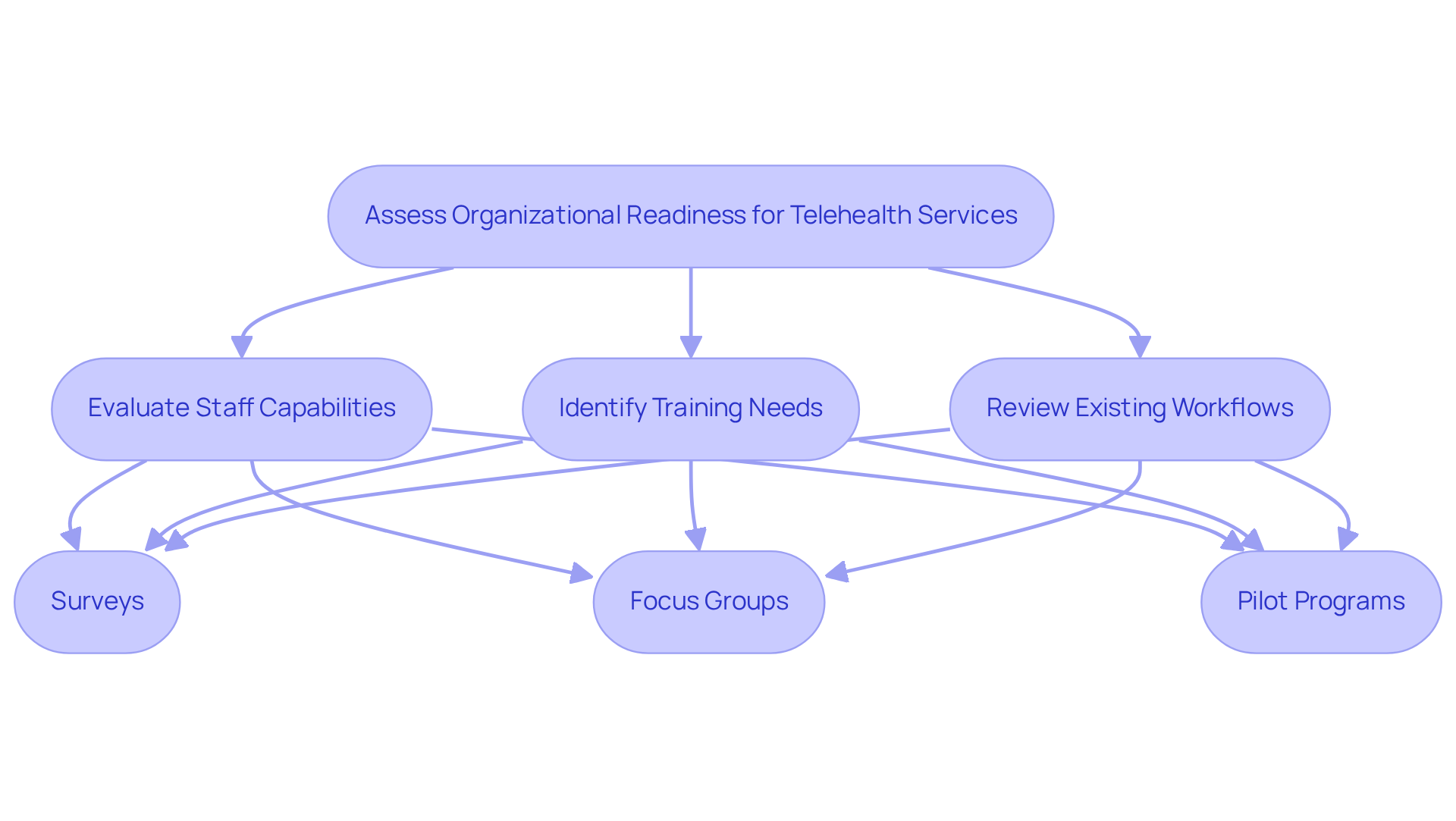
To implement telehealth services successfully, organizations must conduct a comprehensive readiness assessment that evaluates their existing technology infrastructure. This evaluation is crucial to ensure that current systems can effectively support remote healthcare applications. Key components of this assessment include:
- Evaluating staff capabilities
- Identifying training needs to facilitate a seamless transition to remote health services
- Reviewing existing workflows to determine how remote healthcare can be integrated smoothly
Conducting a readiness assessment may involve various methods, such as:
- Surveys
- Focus groups
- Pilot programs
These approaches help identify gaps in technology and processes, enabling organizations to address potential challenges proactively. For example, telemedicine usage surged from 0.12% in the prepandemic period to 3.43% during the pandemic, underscoring the urgent need for a robust infrastructure to accommodate increased demand. Moreover, remote healthcare claims skyrocketed by 2,938% from March 2020 to March 2021, highlighting the necessity for organizations to enhance their technological capabilities.
Incorporating insights from medical leaders can also provide valuable perspectives. According to the DLA Piper Handbook, the virtual healthcare market in the United States was valued at $5.6 billion in 2020, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25% from 2021 to 2026. By prioritizing these assessments, organizations can position themselves to launch telehealth services effectively, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of both patients and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost of telehealth software is crucial for healthcare decision-makers aiming to enhance service delivery and improve patient outcomes. Investing in appropriate telehealth solutions not only ensures compliance with regulations but also significantly enhances access to care. This makes it a strategic priority for organizations that seek to thrive in a digitally transforming healthcare landscape.
The article explored key factors influencing telehealth software costs, including various pricing models such as:
- Subscription-based
- Pay-per-use
- One-time licensing fees
It also emphasized the importance of considering supplementary costs – ranging from compliance expenses to staff training and marketing – as essential for effective financial planning. Furthermore, assessing organizational readiness for telehealth services, including evaluating existing technology and staff capabilities, emerged as a vital step in ensuring successful implementation.
As the telehealth market continues to expand, with projections indicating substantial growth in the coming years, it is imperative for healthcare organizations to adopt a comprehensive approach to budgeting and investment. By understanding the multifaceted nature of telehealth software costs and preparing adequately, decision-makers can optimize operational efficiency and enhance the quality of care provided to patients. Embracing telehealth solutions today is not merely a response to current demands; it is a proactive strategy for creating a more accessible and effective healthcare system in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is telehealth software?
Telehealth software refers to digital platforms that enable remote medical services through video conferencing, messaging, and other communication technologies, allowing healthcare providers to deliver care to patients regardless of their physical location.
Why is telehealth software important in healthcare?
Telehealth software is important because it enhances patient engagement, broadens access to specialists, facilitates timely interventions, and ultimately leads to improved health outcomes by dismantling barriers to access.
What impact has telemedicine had on patient readmissions?
Research indicates that telemedicine programs have significantly reduced patient readmissions, with a 44% decrease for enrolled individuals and a 51% reduction for heart failure patients following the implementation of telemedicine services by the Veterans Health Administration.
How does telehealth software contribute to regulatory compliance?
Telehealth software is vital for compliance with regulations and standards, ensuring that patient information is managed securely and efficiently as healthcare systems adopt digital solutions.
What is the American Medical Association’s stance on telehealth?
The American Medical Association emphasizes the need for sustainable remote health reform to maintain the enhanced access achieved during the pandemic, aligning with broader digital transformation goals in healthcare services.
What motivates healthcare executives to implement telemedicine?
According to a survey, 50% of healthcare executives identified improving the quality of care as their primary motivation for implementing telemedicine, highlighting its strategic significance in healthcare.