Master the Software Development Cycle: Best Practices for Compliance

Introduction
Navigating the complex landscape of software development necessitates not only technical expertise but also a thorough understanding of regulatory compliance. As industries encounter heightened scrutiny and evolving legal frameworks, mastering the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is essential for organizations that seek to protect their projects from costly missteps. This article explores best practices that can bolster compliance throughout the SDLC, providing actionable insights that enable teams to align their development processes with regulatory requirements.
How can organizations effectively integrate compliance into their software development strategies while preserving agility and fostering innovation?
Understand Regulatory Requirements in SDLC
To excel in adherence within the software creation cycle, it is crucial to possess a comprehensive grasp of the legal framework that oversees your sector. This includes familiarizing yourself with laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for data protection, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare, and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) for financial services. Each of these regulations has specific requirements that impact how software is developed, tested, and deployed.
Actionable Steps:
- Conduct a Regulatory Audit: Identify all applicable regulations and standards relevant to your project.
- Engage Regulatory Experts: Collaborate with legal and regulatory teams to interpret regulations accurately.
- Document Requirements: Create a checklist that conforms with legal stipulations to assist the creation process.
Real-World Example: A financial services company faced significant fines due to non-compliance with SOX. By implementing a regulatory audit and involving compliance experts early in the SDLC, they were able to align their software development practices with legal requirements, thus avoiding future penalties.
Implement Structured Phases of the SDLC
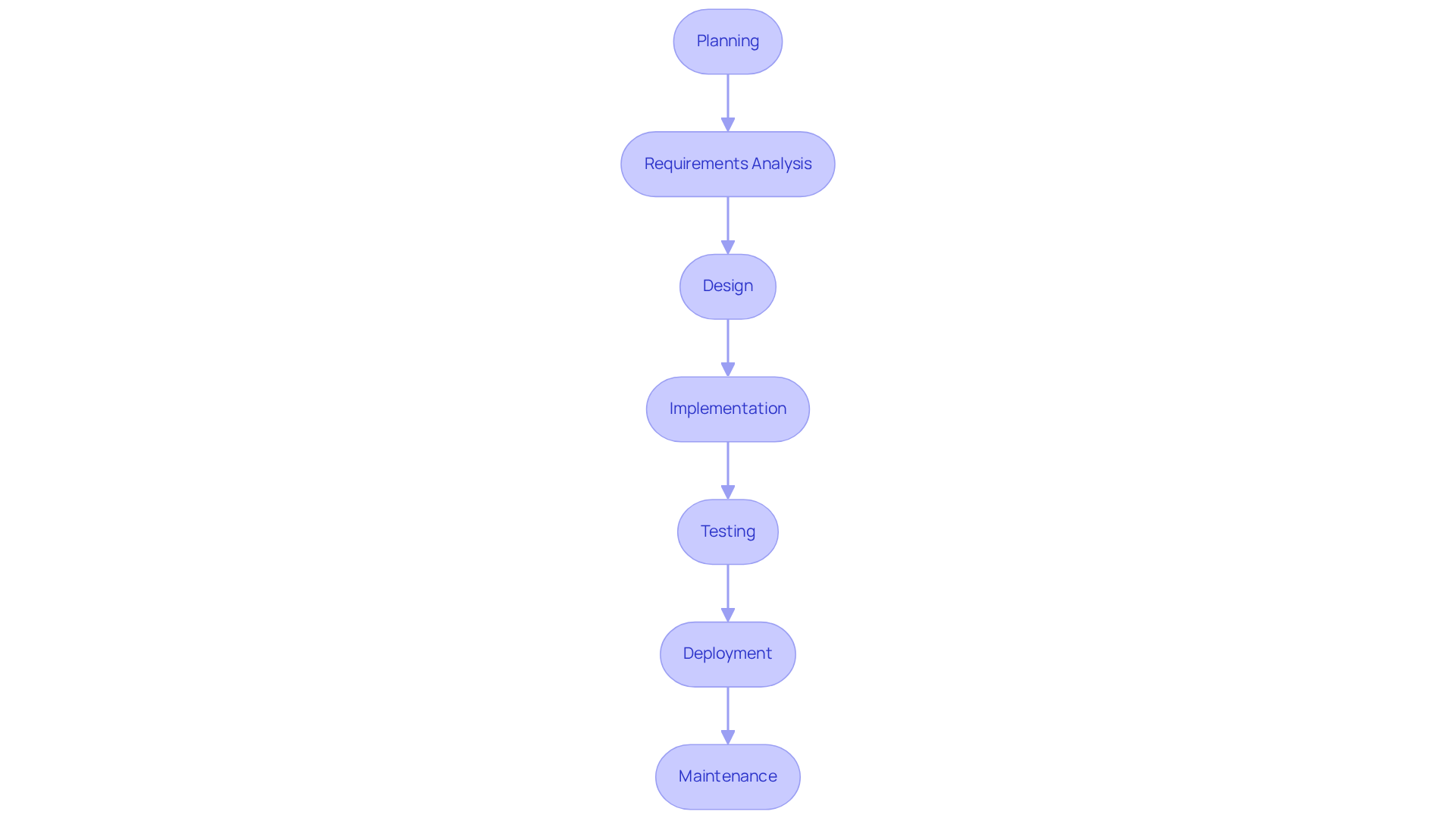
A well-defined Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) consists of several structured phases: Planning, Requirements Analysis, Design, Implementation, Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance and upholding high-quality standards throughout the development process.
Define Clear Milestones: It is essential to establish specific goals and deliverables for each phase. This practice effectively tracks progress and ensures adherence to regulatory standards.
Integrate Regulatory Checks: Incorporating regulatory reviews at the conclusion of each phase is vital. This step verifies that all requirements are met before advancing to the next stage. Such a proactive approach minimizes risks and enhances accountability.
Utilize Agile Methodologies: Implementing Agile practices facilitates iterative evaluations and adjustments based on stakeholder feedback. This allows for greater flexibility and responsiveness to changing requirements.
Real-World Example: A healthcare software provider successfully implemented a structured SDLC that included verification checks at each phase. This approach not only improved product quality but also ensured compliance with HIPAA regulations, resulting in a successful audit and underscoring the importance of adhering to regulations in software development.
Choose the Right SDLC Model for Compliance
Choosing the appropriate Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) model-whether Waterfall, Agile, or Spiral-can significantly impact compliance outcomes. Each model presents distinct advantages and challenges regarding flexibility, documentation, and adherence to standards.
Assess Project Requirements: Start by evaluating the complexity, size, and specific regulatory demands of your project to determine the most suitable model.
Consider Stakeholder Involvement: Select a model that encourages sufficient stakeholder engagement, which is essential for ensuring compliance throughout the development process.
Review Past Projects: Examine previous projects to identify which SDLC models have successfully met regulatory requirements in similar contexts.
Real-World Example: A leading financial institution adopted the iterative model for developing a new trading platform. This approach enabled rapid iterations and regular assessments, allowing the organization to swiftly adapt to evolving regulations and maintain continuous compliance.
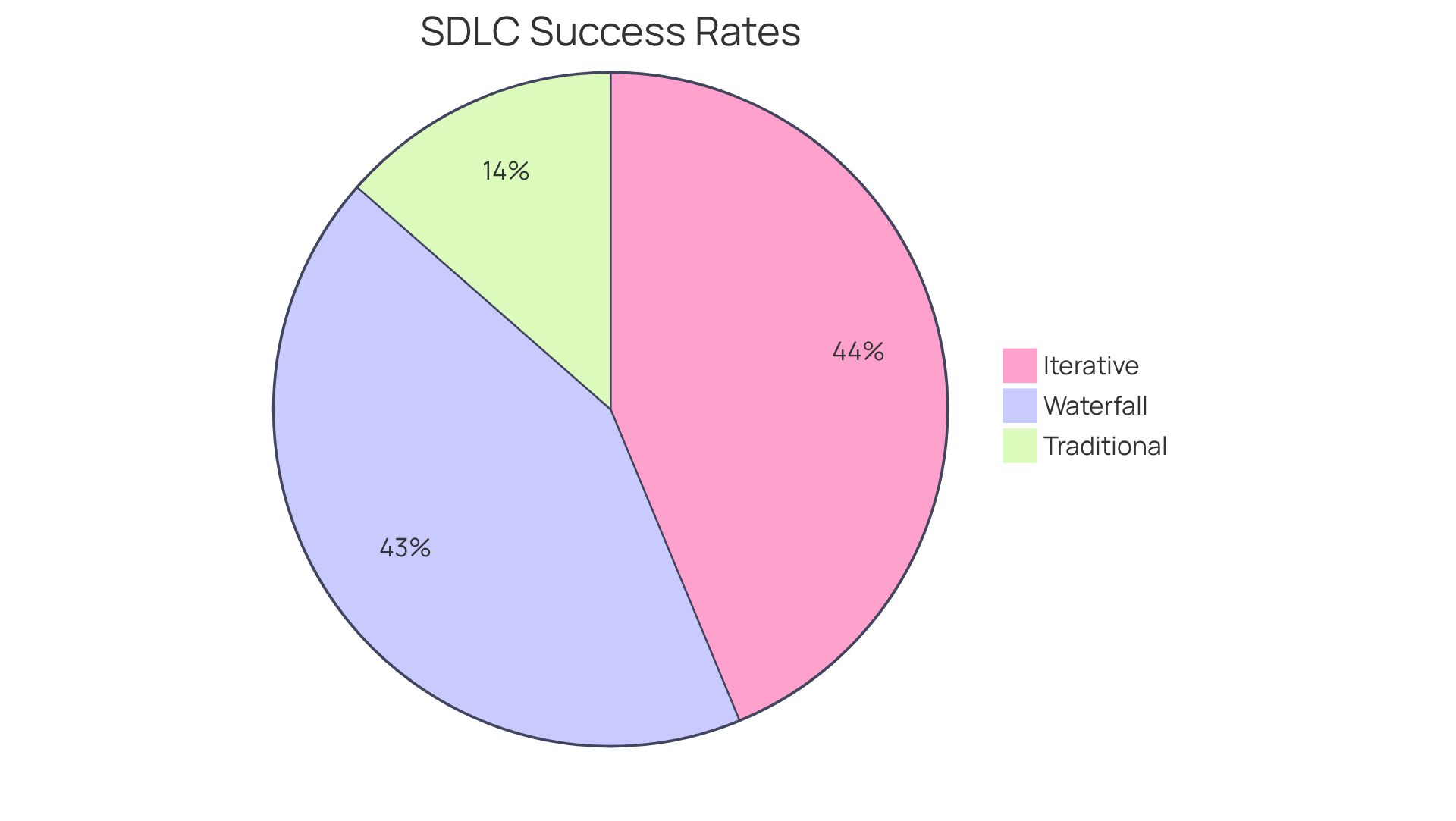
In terms of compliance success rates, iterative projects have demonstrated a higher success rate compared to traditional methods, achieving a 42% success rate versus the 13% of traditional methods. Notably, the Standish Group’s Chaos Report reveals that iterative projects have a significantly lower failure rate of 11%, in contrast to Waterfall’s staggering 59%. This disparity highlights the critical role of flexibility and ongoing stakeholder feedback in effectively navigating regulatory landscapes. Additionally, the Spiral model, which combines elements of both flexible methodologies and Waterfall, can enhance compliance by facilitating iterative progress while ensuring essential documentation and risk assessment. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that 32% of respondents currently employ the Agile methodology in software development, underscoring its relevance in today’s market.
Integrate Specialized Engineering Talent into the SDLC
To ensure adherence throughout the software development cycle, it is essential to incorporate specialized engineering talent from Neutech. Our engineers have a profound understanding of the regulatory landscape and can effectively implement best practices tailored to the specific needs of regulated industries, utilizing technologies such as React, Python, and AWS.
Actionable Steps:
- Hire Regulation-Focused Engineers: Seek engineers with proven experience in regulated sectors, ensuring they possess a robust grasp of regulatory requirements. Neutech can assist by providing candidate designers and developers who match your specific needs, including expertise in various technology fields.
- Provide Ongoing Training: Commit to continuous education for your team, keeping them updated on the latest regulations and best practices for adherence.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourage teamwork between regulatory specialists and development groups, making adherence a collective responsibility throughout the organization.
Common Pitfalls: Be aware of the challenges regulatory teams face, such as the complexity of regulations and the necessity for thorough documentation. Failing to address these issues can lead to regulatory failures.
Real-World Example: A healthcare software company successfully integrated compliance specialists into their development teams, resulting in a significant decrease in compliance-related issues during audits. This proactive strategy not only strengthened their regulatory position but also markedly improved the overall quality of their software.
Expert Insight: According to John McCarthy, SVP, BSA/OFAC Officer at Bank of Hope, “Hiring engineers with a strong compliance background is essential for navigating the complexities of regulatory requirements in today’s environment.
Conclusion
Mastering the software development cycle with a strong emphasis on compliance is crucial for organizations seeking to effectively navigate the complexities of regulatory landscapes. A thorough understanding of the legal requirements governing each industry, the implementation of structured phases within the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), and the selection of an appropriate development model are essential steps that ensure adherence to compliance standards.
Key insights highlighted in this article include:
- The necessity of conducting regulatory audits
- Integrating compliance checks at each phase of development
- Selecting a model that aligns with project requirements and stakeholder engagement
Additionally, incorporating specialized engineering talent into the SDLC can significantly bolster compliance efforts, as these professionals provide valuable expertise that mitigates risks associated with regulatory failures.
Ultimately, prioritizing compliance in the software development lifecycle transcends mere legal obligation; it represents a strategic advantage that can enhance product quality and bolster organizational reputation. By adopting these best practices, companies can cultivate a culture of compliance that not only meets regulatory standards but also positions them for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Embracing these principles is essential for any organization aiming to thrive in the modern software development environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to understand regulatory requirements in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
Understanding regulatory requirements is crucial for ensuring compliance with laws that govern your sector, which impacts how software is developed, tested, and deployed.
What are some key regulations to be aware of in software development?
Important regulations include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for data protection, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare, and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) for financial services.
What actionable steps can be taken to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements?
Key steps include conducting a regulatory audit to identify applicable regulations, engaging regulatory experts to interpret these regulations, and documenting requirements through a checklist that aligns with legal stipulations.
Can you provide an example of the consequences of non-compliance with regulations?
A financial services company faced significant fines due to non-compliance with SOX. By implementing a regulatory audit and involving compliance experts early in the SDLC, they were able to align their software development practices with legal requirements and avoid future penalties.