Master the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) for Compliance Success

Introduction
In regulated industries such as finance and healthcare, the software development life cycle (SDLC) serves not just as a roadmap for application development; it is an essential tool for ensuring compliance with rigorous legal and regulatory standards. By diligently adhering to the phases of the SDLC, organizations can improve product quality while protecting themselves from the significant penalties that can arise from non-compliance. Given the dynamic nature of regulations and the growing complexity of software projects, the challenge remains: how can teams effectively incorporate compliance checks at every stage of development?
Understand the Importance of SDLC in Regulated Industries
In regulated sectors such as finance and healthcare, the software development life cycle (SDLC) serves not only as a framework for application development but is also essential for ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory standards. A robust development lifecycle enables organizations to systematically navigate the complexities of application development while adhering to industry regulations.
For instance, in financial services, compliance with regulations like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and GDPR is vital. A well-defined software development life cycle (SDLC) helps in documenting processes, tracking changes, and ensuring that all software components align from inception to deployment. By integrating compliance evaluations at each stage of the software development life cycle (SDLC), organizations can significantly reduce the risk of non-conformity, which may lead to costly penalties and reputational damage. In 2024, the average global cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million, highlighting the financial repercussions of non-compliance. Moreover, 74% of breaches involve human error, underscoring the importance of embedding compliance checks to mitigate associated risks.
Additionally, the record GDPR fine against Meta serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of failing to comply. A structured software development life cycle (SDLC) promotes transparency and accountability, which are essential for fostering trust with stakeholders and regulatory bodies.
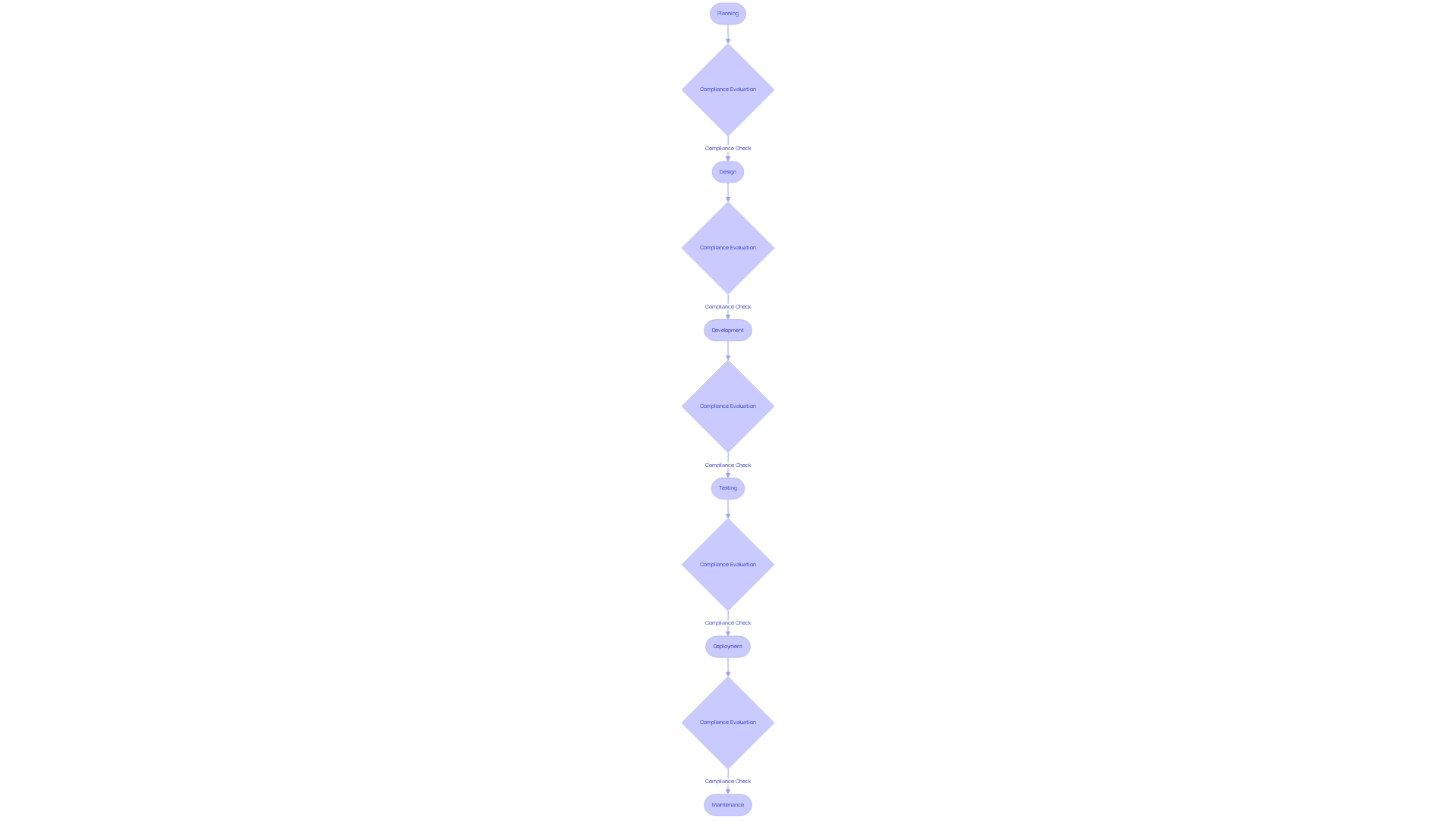
Explore the Phases of the Software Development Life Cycle
The software development life cycle (SDLC) includes several critical phases: Planning, Requirements Analysis, Design, Implementation, Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance. Each phase is essential for ensuring that the final product aligns with user needs and adheres to regulatory requirements.
- Planning: This initial phase is crucial for defining the project scope, objectives, and feasibility. It allows for the early identification of regulatory requirements, setting a solid foundation for the project.
- Requirements Analysis: This phase involves gathering and analyzing requirements to ensure that all stakeholder needs are addressed, including compliance with regulatory standards.
- Design: During this phase, the application’s structure is established, integrating security measures and regulatory considerations into the design framework.
- Implementation: This is where the actual coding takes place. Adherence to coding standards and best practices is vital to ensure conformity and quality.
- Testing: A rigorous evaluation is performed to identify and resolve any issues prior to deployment, ensuring that the application meets all regulatory requirements.
- Deployment: The application is launched for user access, accompanied by verification checks to confirm that all standards have been met.
- Maintenance: Ongoing support and updates are necessary to address any regulatory changes or system vulnerabilities that may arise post-deployment.
By diligently following the phases of the software development life cycle (SDLC), organizations can significantly enhance product quality and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
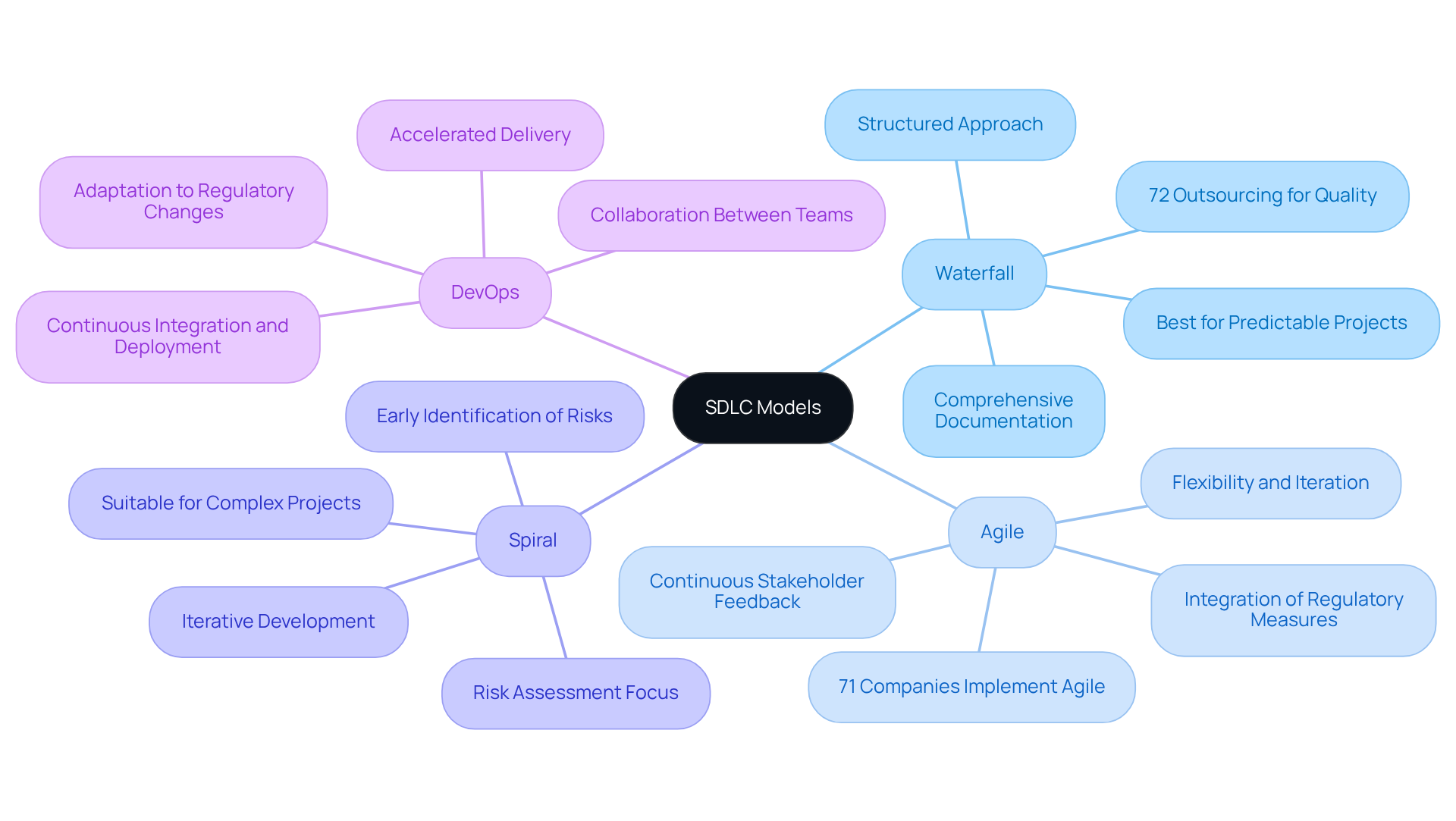
Select the Right SDLC Model for Your Project
Choosing the appropriate software development life cycle (SDLC) model is crucial for the success of software initiatives, particularly in regulated sectors. The primary models – Waterfall, Agile, Spiral, and DevOps – each offer distinct advantages and challenges that must be carefully assessed based on project requirements, team dynamics, and regulatory obligations.
-
Waterfall: This traditional linear model is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal anticipated changes. Its structured approach is particularly beneficial in highly regulated environments, where comprehensive documentation and compliance tracking are vital. The clarity and simplicity of the Waterfall model make it ideal for predictable projects, as evidenced by the fact that 72% of organizations outsource software development to gain better access to talent and enhance quality.
-
Agile: Agile methodologies emphasize flexibility and iterative development, making them ideal for projects that necessitate rapid adaptation and ongoing stakeholder feedback. In fact, 71% of companies implement Agile practices in their software development life cycle (SDLC), which highlights its effectiveness in dynamic environments. However, it is imperative for teams to integrate regulatory measures into each iteration to ensure compliance throughout the development process.
-
Spiral: The Spiral model merges iterative development with a strong emphasis on risk assessment, rendering it particularly effective for complex projects where risk management is critical. This model facilitates the early identification and mitigation of potential regulatory issues, thereby enhancing the stability of the initiative. The iterative nature of the Spiral model is advantageous, especially in projects where requirements are subject to change.
-
DevOps: By promoting collaboration between development and operations teams, DevOps accelerates delivery while ensuring compliance through practices such as continuous integration and deployment. This model supports a dynamic approach to application development, enabling swift adjustments in response to regulatory changes. As organizations increasingly incorporate AI tools into their software development processes, the integration of DevOps practices becomes even more essential.
Ultimately, the choice of a software development life cycle (SDLC) model should align with the project’s objectives, the regulatory landscape, and the competencies of the development team, ensuring adherence to the SDLC is maintained without sacrificing efficiency.
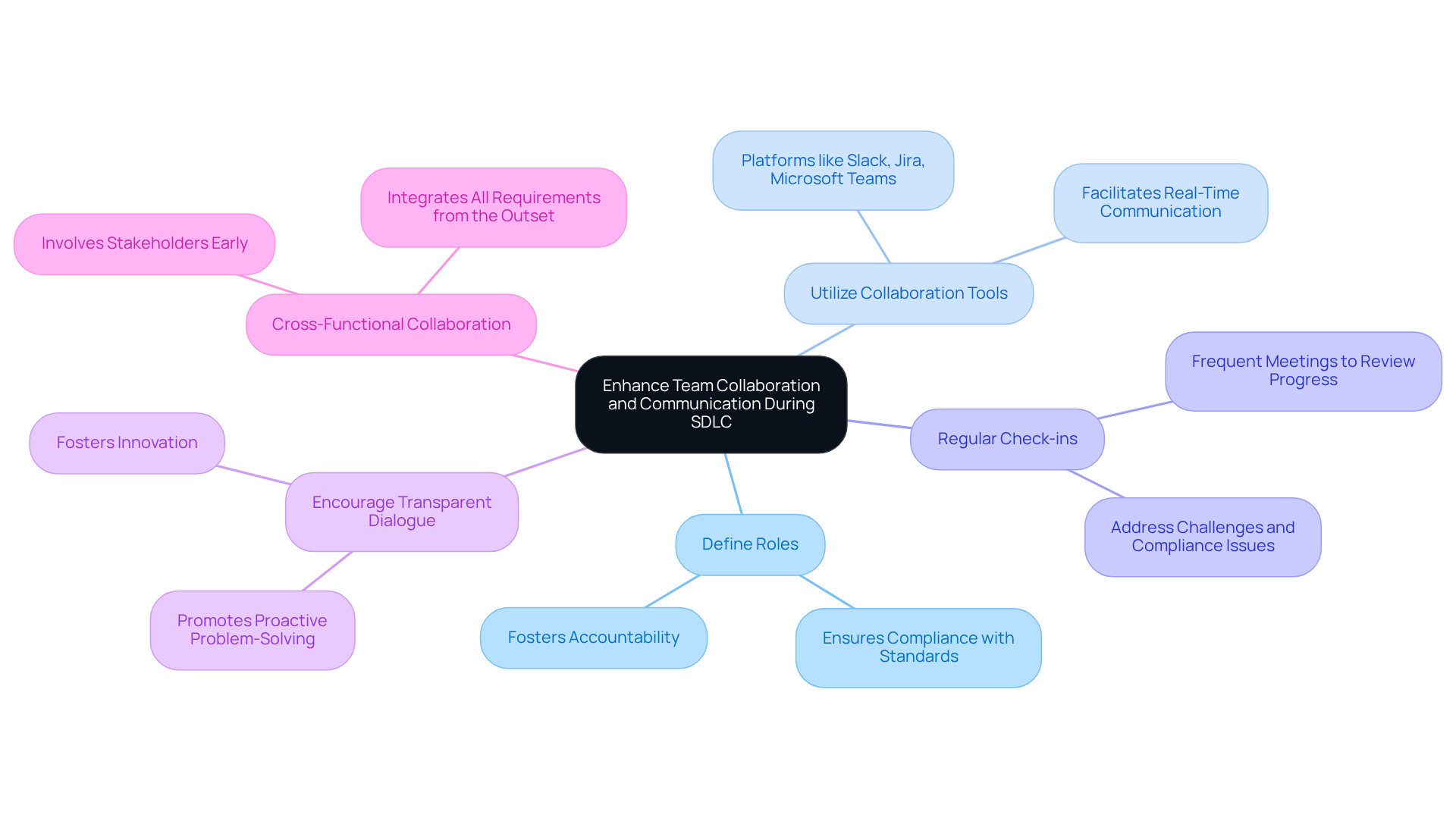
Enhance Team Collaboration and Communication During SDLC
Effective teamwork and communication are essential throughout the software development life cycle (SDLC), particularly in regulated sectors where compliance with standards is critical. To enhance team dynamics, consider the following key practices:
-
Clearly defining each team member’s role within the software development life cycle (SDLC) fosters accountability and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
-
Utilize Collaboration Tools: Leveraging platforms such as Slack, Jira, or Microsoft Teams facilitates real-time communication and document sharing, keeping all team members aligned and informed.
-
Regular Check-ins and Updates: Frequent meetings to review progress, address challenges, and discuss compliance issues help keep the team synchronized and allow for timely adjustments to the project.
-
Encourage a Climate of Transparent Dialogue: Creating an environment where team members feel comfortable expressing concerns and ideas related to compliance and task execution promotes proactive problem-solving and innovation.
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involving stakeholders from various departments, including regulatory and legal, early in the software development life cycle (SDLC) ensures that all requirements are integrated from the outset.
Incorporating these practices can significantly improve team dynamics and project outcomes. For example, studies indicate that high-performing regulatory programs enable earlier risk detection and quicker remediation, which is vital in regulated environments. Additionally, as Maya Chen emphasizes, centralizing incident intake and establishing a standard triage workflow can enhance communication and improve adherence to regulations. By prioritizing these collaborative practices, teams can effectively navigate the complexities of the software development life cycle (SDLC), ensuring that regulations are upheld throughout the software development life cycle (SDLC) process. This approach not only enhances project results but also strengthens the overall integrity of the system being developed. At Neutech, we specialize in providing comprehensive engineering services tailored for regulated industries and startups, including expertise in React Development, Python Development, and more, ensuring that our development processes align with compliance requirements while delivering high-quality software solutions.
Conclusion
Mastering the software development life cycle (SDLC) is essential for organizations in regulated industries. This structured approach to application development not only ensures compliance with legal and regulatory standards but also mitigates risks and fosters stakeholder trust. By embedding compliance checks throughout the SDLC, businesses can avoid costly penalties and enhance their operational integrity.
The critical phases of the SDLC are:
- Planning
- Requirements Analysis
- Design
- Implementation
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance
Each phase plays a vital role in aligning the final product with user needs and regulatory requirements. Selecting the appropriate SDLC model, whether it be Waterfall, Agile, Spiral, or DevOps, is crucial to meet project objectives and compliance needs. Furthermore, effective team collaboration and communication are essential practices for navigating the complexities of the SDLC, ensuring that regulatory standards are consistently upheld.
In conclusion, organizations must acknowledge the importance of a well-structured SDLC in achieving compliance success. By prioritizing adherence to each phase of the SDLC and fostering a collaborative environment, businesses can enhance product quality, mitigate risks, and adeptly navigate the evolving regulatory landscape. Embracing these best practices will lead to successful software development and safeguard against the repercussions of non-compliance in today’s competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in regulated industries?
The SDLC serves as a framework for application development and is essential for ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory standards in regulated sectors such as finance and healthcare.
How does SDLC help organizations in regulated sectors?
A robust SDLC enables organizations to systematically navigate the complexities of application development while adhering to industry regulations, helping to document processes, track changes, and ensure alignment from inception to deployment.
Why is compliance important in the financial services sector?
Compliance with regulations like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and GDPR is vital in the financial services sector to avoid costly penalties and reputational damage associated with non-compliance.
What are the financial repercussions of non-compliance?
In 2024, the average global cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million, highlighting the significant financial consequences of non-compliance.
What role do human errors play in data breaches?
Human error is involved in 74% of data breaches, emphasizing the importance of embedding compliance checks within the SDLC to mitigate associated risks.
What consequences can organizations face for failing to comply with regulations?
Organizations may face severe penalties, as illustrated by the record GDPR fine against Meta, which serves as a reminder of the potential consequences of non-compliance.
How does a structured SDLC promote trust with stakeholders?
A structured SDLC promotes transparency and accountability, which are essential for fostering trust with stakeholders and regulatory bodies.