Best Practices for Software Development for IoT Success

Introduction
The rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing industries. However, this growth also presents a complex landscape for software development. Understanding the core components – ranging from devices to connectivity and user interfaces – is essential for creating effective IoT solutions.
Developers often encounter significant challenges in this domain. Key issues include:
- Interoperability
- Security vulnerabilities
- Scalability concerns
These obstacles can hinder the development process and impact the overall effectiveness of IoT applications.
To navigate these challenges successfully, teams must adopt strategic approaches that ensure robust IoT software development. This is crucial for meeting the growing demands of a dynamic market, where adaptability and innovation are paramount.
Understand Core Components of IoT Software Development
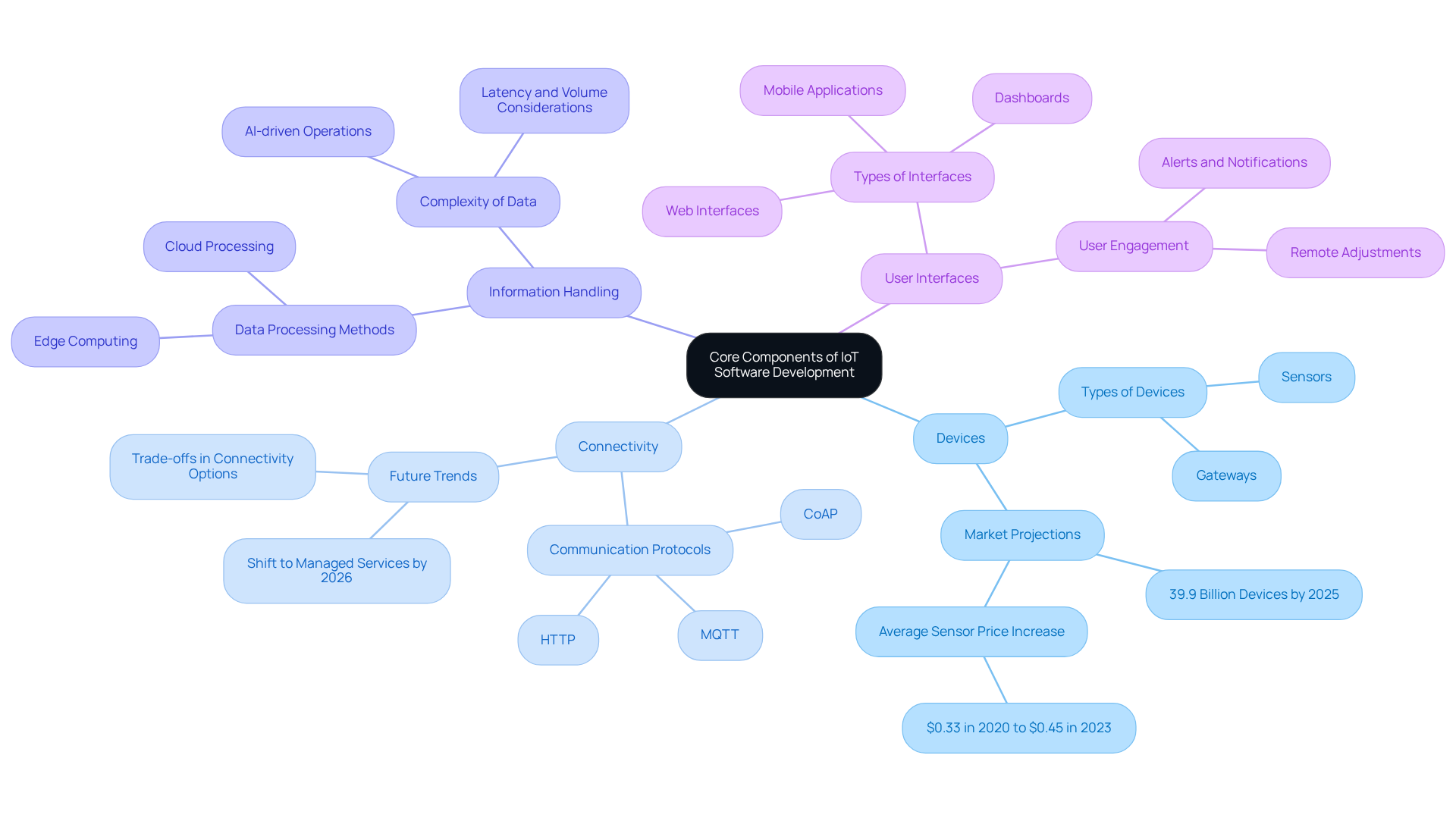
To effectively engage in software development for IoT, it is crucial to understand its fundamental elements, which include devices, connectivity, information processing, and user interfaces. Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality of an IoT solution.
-
Devices are the physical objects equipped with sensors and actuators that collect and transmit data. Understanding the categories of devices, such as sensors and gateways, along with their capabilities, is essential for effective software design. The global market is projected to have over 39.9 billion smart sensors and IoT devices in use by 2025, according to TechRepublic, underscoring their significance in the ecosystem.
-
Connectivity refers to the communication protocols and networks that enable devices to connect and exchange information. Familiarity with protocols like MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP is necessary to ensure reliable data transmission. As enterprises are expected to transition towards managed services by 2026, understanding the trade-offs of different connectivity options will be vital for optimizing performance and mitigating operational risks.
-
Information Handling involves processing and analyzing the data once it is gathered. This can occur on-device through edge computing or in the cloud. Developers should select the appropriate architecture based on latency requirements and data volume. The increasing complexity of global connectivity necessitates robust information processing capabilities to effectively support AI-driven operations.
-
User Interfaces must provide intuitive ways for users to engage with the IoT network. This includes dashboards, mobile applications, and web interfaces that display data and facilitate equipment management. User intervention may be necessary in specific scenarios, such as responding to alerts or adjusting settings, highlighting the importance of user engagement in IoT solutions.
By thoroughly understanding these components, developers can excel in software development for IoT, creating robust solutions that meet user needs and industry standards. Additionally, they should be cognizant of potential operational challenges, such as managing switching profiles, which can complicate the deployment and maintenance of IoT systems.
Identify and Overcome Challenges in IoT Software Development
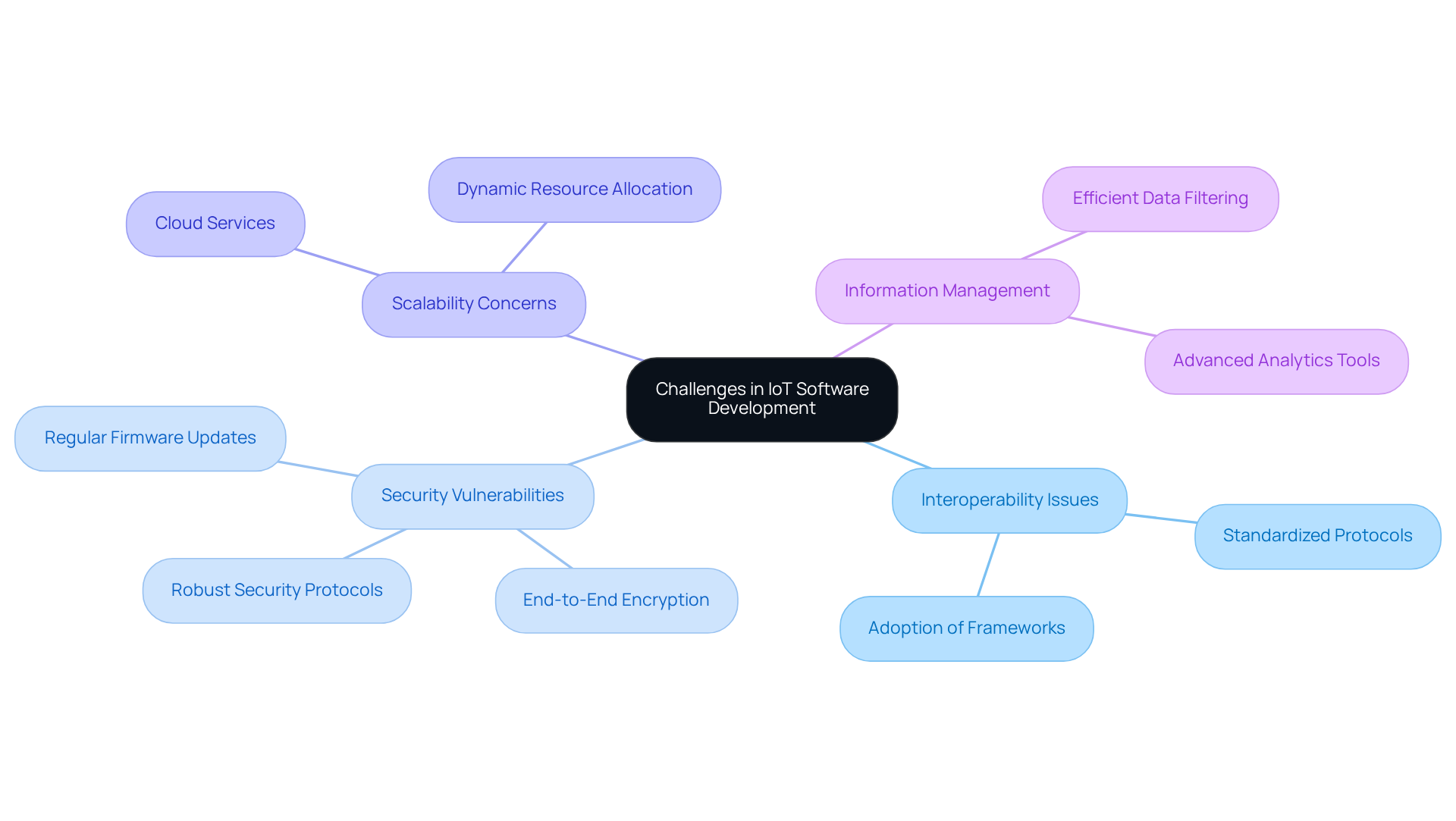
Software development for IoT presents several challenges that can significantly impact project success. Identifying these challenges early enables teams to implement effective strategies to navigate them:
-
Interoperability Issues: The diverse range of equipment and platforms often leads to communication obstacles. To address this, adopting standardized protocols and frameworks is essential for facilitating seamless integration. As noted by Forrester, “Interoperability isn’t optional – it’s the gateway to true IoT value.” Industry experts emphasize that interoperability is crucial for realizing the full potential of IoT technologies, as it can enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
-
Security Vulnerabilities: IoT devices are prime targets for cyberattacks, with many lacking adequate security measures. To protect against these threats, it is vital to implement robust security protocols, including end-to-end encryption, secure boot processes, and regular firmware updates. Current trends indicate that many devices remain vulnerable due to outdated software and weak default security practices, highlighting the necessity for proactive security strategies.
-
Scalability Concerns: As the number of connected devices increases, maintaining performance can become increasingly challenging. It is crucial to create frameworks that prioritize scalability, employing cloud services capable of dynamically allocating resources based on real-time demand. This approach not only enhances performance but also ensures that systems can adapt to fluctuating workloads without compromising reliability.
-
Information Management: The vast volume of information generated by IoT devices can be overwhelming, complicating processing and storage. Utilizing advanced analytics tools is essential for efficiently filtering and examining information, ensuring that only relevant details are processed and stored. This not only streamlines operations but also enhances decision-making capabilities.
By proactively addressing these challenges, development teams can significantly enhance the reliability and effectiveness of their IoT solutions, which is essential for successful software development for IoT in regulated industries.
Implement Robust Security Measures for IoT Solutions
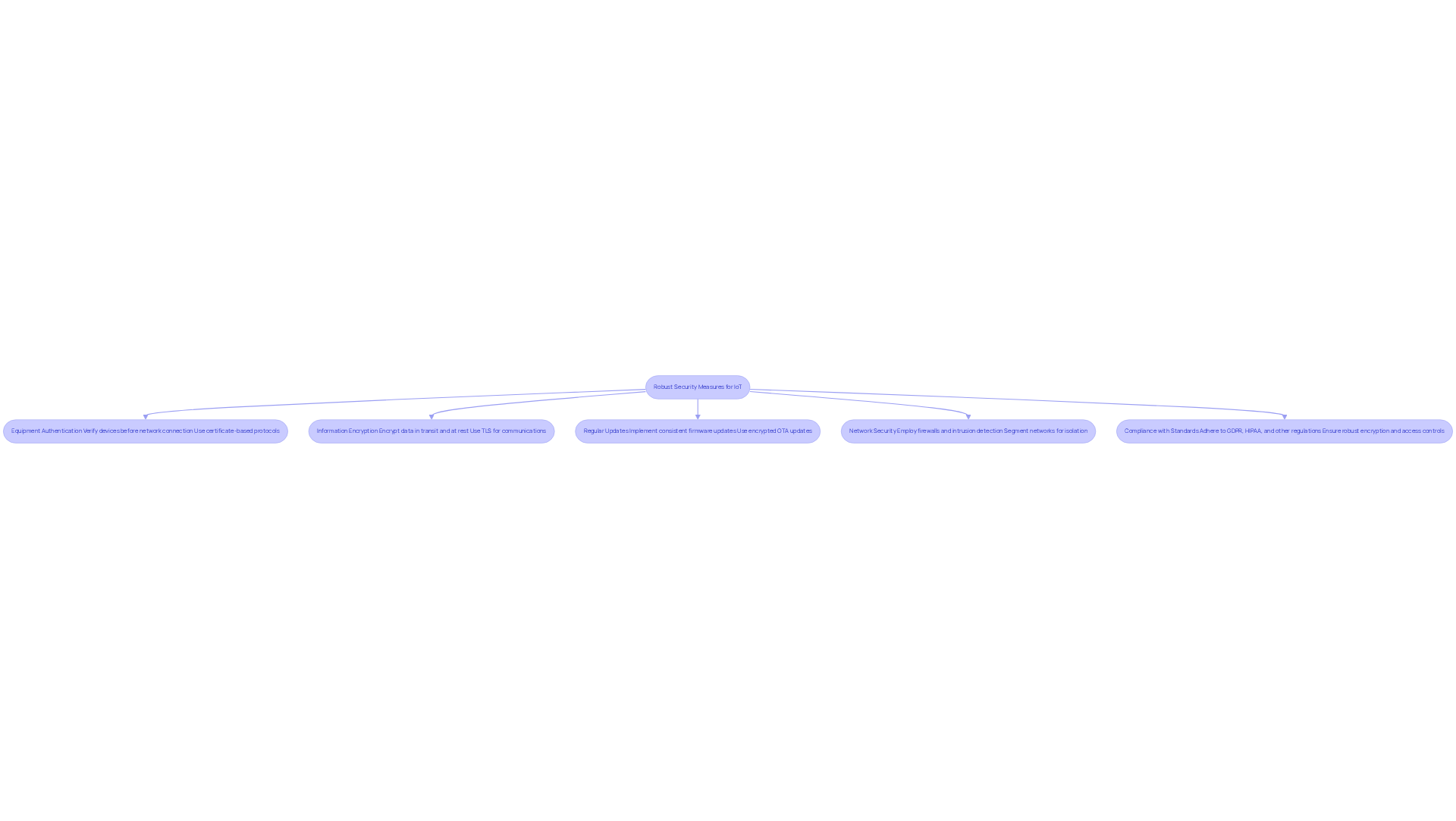
Security is a paramount concern in software development for IoT, especially when handling sensitive data. Implementing robust security measures is essential for safeguarding information and maintaining user trust. The following best practices are crucial:
-
Equipment Authentication: All devices must be verified before connecting to the network. Employ robust authentication protocols, such as certificate-based authentication, which significantly reduces risk, particularly when combined with hardware-backed storage. This approach prevents unauthorized access and ensures that each device possesses a distinct identity.
-
Information Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information from interception and unauthorized access. Utilize industry-standard encryption algorithms, such as TLS, for all device communications, and ensure that sensitive data stored locally is also encrypted.
-
Regular Updates: Establish a method for consistent firmware and software updates to address vulnerabilities as they arise. This includes implementing over-the-air (OTA) updates, which must be encrypted, verified prior to installation, fail-safe, and prevent rollbacks to vulnerable versions.
-
Network Security: Employ firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor network traffic and prevent unauthorized access. Segment networks to isolate IoT devices from core systems, thereby limiting the potential impact of breaches. Additionally, monitoring traffic patterns over time can help identify unusual behavior and potential compromises.
-
Compliance with Standards: Adhere to relevant security standards and regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, to ensure that your IoT solution meets legal requirements and industry best practices. This involves applying robust encryption and access controls for devices managing sensitive information.
By prioritizing security throughout the software development for IoT lifecycle, teams can foster trust with users and effectively protect their information. As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about current trends in data encryption and equipment authentication will be crucial for maintaining robust security measures.
Design for Scalability in IoT Software Development
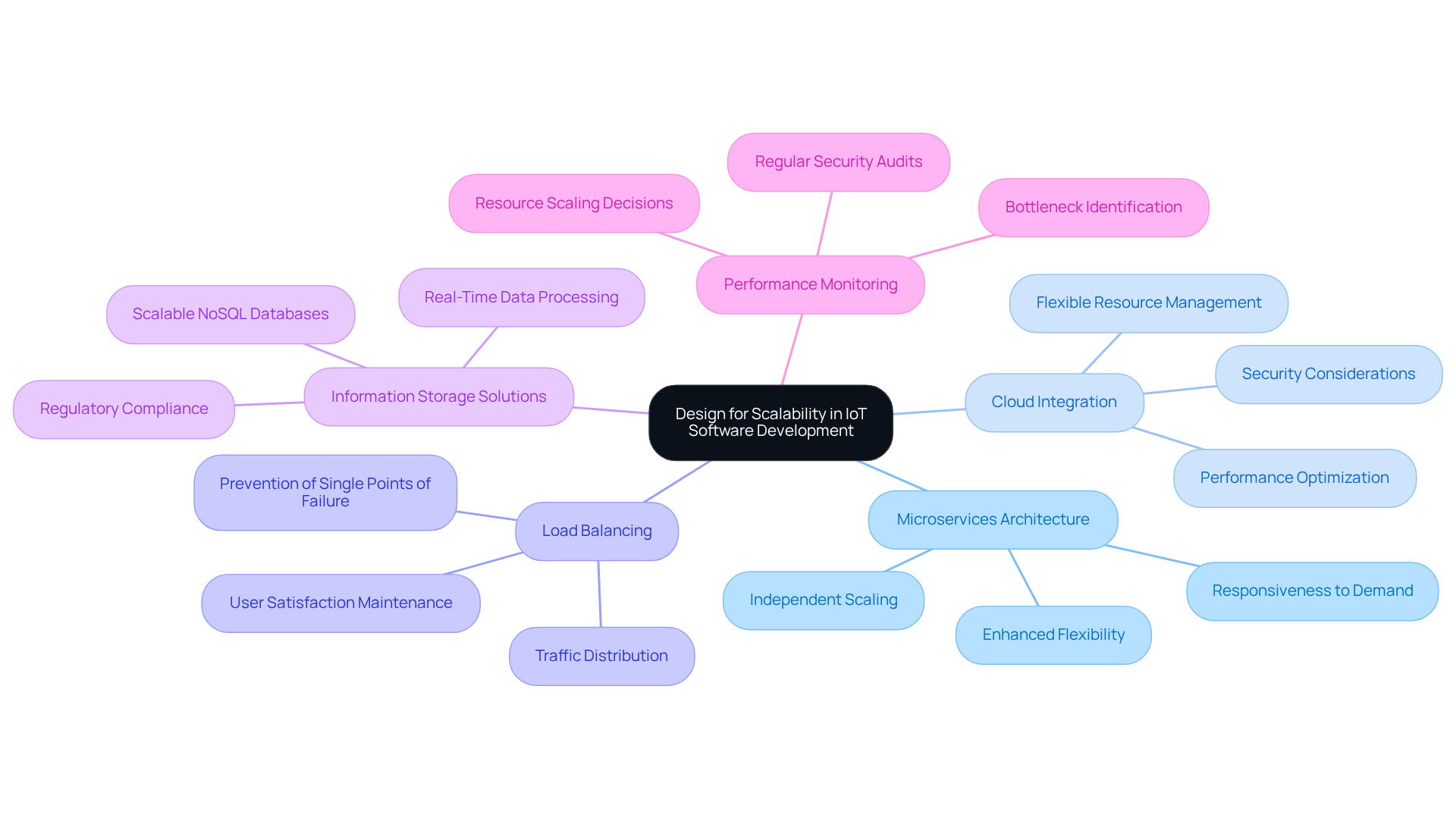
Scalability is a crucial element in the software development for IoT, since systems must effectively manage growing demands and integrate new components over time. Here are key strategies to design for scalability:
-
Microservices Architecture: Adopting a microservices architecture allows applications to be broken down into smaller, manageable services. These services can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness. This approach is essential, especially considering that the number of connected IoT devices is projected to reach 39 billion by 2030.
-
Cloud Integration: Leveraging cloud services provides flexible resources that can scale up or down based on demand. This capability allows for the efficient handling of varying workloads without compromising performance. Industry experts emphasize that “Security is no longer optional,” highlighting the necessity for robust cloud solutions that prioritize security alongside scalability.
-
Load Balancing: Implementing load balancing techniques is vital for distributing traffic evenly across servers. This prevents any single point of failure and ensures consistent performance, which is crucial for maintaining user satisfaction in high-demand environments.
-
Information Storage Solutions: Selecting scalable information storage solutions, such as NoSQL databases, is essential for managing large volumes of data and providing quick access to information. This is particularly important for applications that rely on real-time data processing, especially in light of regulatory pressures like the upcoming EU Cyber Resilience Act, which is expected to influence global cybersecurity standards.
-
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitoring performance and user behavior helps identify bottlenecks and areas for enhancement. Utilizing analytics informs decisions about scaling resources effectively. Regular security audits and adherence to industry standards are crucial for maintaining a secure IoT environment, as customers increasingly demand trust in IoT devices.
By engaging in software development for IoT with scalability in mind, developers can ensure that their applications remain effective and responsive as user demands grow. Incorporating these strategies not only prepares systems for future growth but also aligns with the projected $565 billion revenue growth in the IoT industry by 2026.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of software development for IoT is essential for creating successful and effective solutions. By grasping the core components – devices, connectivity, information processing, and user interfaces – developers can build robust systems that cater to user needs and industry standards. This foundational knowledge, combined with strategic approaches to overcome challenges, is vital for navigating the complexities of the IoT landscape.
Key insights shared throughout the article highlight the importance of addressing:
- Interoperability issues
- Enhancing security measures
- Designing for scalability
By employing standardized protocols, robust encryption, and cloud integration, developers can mitigate risks and ensure their solutions are prepared for future demands. Furthermore, embracing a microservices architecture and utilizing advanced analytics tools can streamline operations and improve decision-making capabilities.
In conclusion, the significance of adopting best practices in IoT software development cannot be overstated. As the industry evolves and the number of connected devices continues to grow, staying informed about emerging trends and implementing effective strategies is crucial. By prioritizing security, scalability, and a deep understanding of core components, developers can contribute to the successful advancement of IoT technologies, ultimately shaping a more connected and efficient future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core components of IoT software development?
The core components of IoT software development include devices, connectivity, information processing, and user interfaces.
What role do devices play in IoT?
Devices are physical objects equipped with sensors and actuators that collect and transmit data. Understanding the categories of devices, such as sensors and gateways, is essential for effective software design.
How many smart sensors and IoT devices are projected to be in use by 2025?
The global market is projected to have over 39.9 billion smart sensors and IoT devices in use by 2025.
What is meant by connectivity in IoT?
Connectivity refers to the communication protocols and networks that enable devices to connect and exchange information. Familiarity with protocols like MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP is necessary for reliable data transmission.
Why is understanding connectivity options important for enterprises?
As enterprises are expected to transition towards managed services by 2026, understanding the trade-offs of different connectivity options will be vital for optimizing performance and mitigating operational risks.
What does information handling involve in IoT?
Information handling involves processing and analyzing the data gathered by devices, which can occur on-device through edge computing or in the cloud. Developers must select the appropriate architecture based on latency requirements and data volume.
How does user interface design impact IoT solutions?
User interfaces must provide intuitive ways for users to engage with the IoT network, including dashboards, mobile applications, and web interfaces. User engagement is important for responding to alerts or adjusting settings.
What operational challenges might developers face in IoT?
Developers should be aware of potential operational challenges, such as managing switching profiles, which can complicate the deployment and maintenance of IoT systems.